Difference between revisions of "OpenBTS: Pola Multi OpenBTS"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) (→PBX) |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
===Asterisk=== | ===Asterisk=== | ||
| + | Beruntung, kita tidak perlu mengubah konfigurasi Asterisk | ||
Fortunately, Asterisk does not need to be reconfigured unless it is accessing the subscriber registry over the network. | Fortunately, Asterisk does not need to be reconfigured unless it is accessing the subscriber registry over the network. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 41: | ||
<X-PRE-PROCESS cmd="set" data="smqueue_port=5063"/> | <X-PRE-PROCESS cmd="set" data="smqueue_port=5063"/> | ||
<X-PRE-PROCESS cmd="set" data="smqueue_host=192.168.1.0"/> | <X-PRE-PROCESS cmd="set" data="smqueue_host=192.168.1.0"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Yate=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Semoga tidak perlu di ubah apa-apa. | ||
==smqueue== | ==smqueue== | ||
Revision as of 10:36, 10 August 2012
Sumber: http://wush.net/trac/rangepublic/wiki/multiBTS
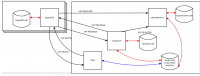
Di rangenetworks.com, multi-BTS biasa di jalankan. Sebuah network dengan 2-BTS adalah konfigurasi yang paling sederhana bagi kita yang ingin mengembangkan kemampuan mobilitas & handover.
Jaringan MultiBTS
Dengan semakin berkembangnya jaringan, kita biasanya menginginkan untuk dapat tersambung ke lebih dari satu OpenBTS system yang berjalan bersamaan. Hal ini relatif mudah untuk dilakukan. Pada dasarnya, setiap node OpenBTS berjalan di mesin yang berbeda, semua tersambung ke sipauthserve, PBX dan smqueue yang terpusat (tidak harus berjalan di satu mesin). Berikut adalah dokumentasi caranya.
Kebutuhan Awal
Pertama-tama, instalasi dasar tidak mendukung komunikasi VoIP yang aman. Di samping itu, kita perlu menginstalasi Asterisk Real-Time atau FreeSWITCH atau Yate.
Kedua, kita perlu memindahkan file konfigurasi (seperti, OpenBTS.db) ke mesin yang menjalankan proses OpenBTS. Ingat kita sekarang akan mempunyai banyak OpenBTS, file OpenBTS.db harus berbeda untuk setiap lokasi BTS. Jika harus kita angat bahwa semua proses (kecuali PBX) akan menginginkan file konfigurasinya di /etc/OpenBTS.
System Diagram
Configuration
Kita perlu mengubah konfigurasi default database untuk menunjuk ke mesin yang menjalankan server. Contoh:
PBX (Asterisk)- 192.168.0.3:5060 smqueue - 192.168.0.3:5063 sipauthserve - 192.168.0.3: 5064 OpenBTS (1st BTS) - 192.168.0.3:5062 OpenBTS (2nd BTS) -192.168.0.122:5062
PBX
Asterisk
Beruntung, kita tidak perlu mengubah konfigurasi Asterisk Fortunately, Asterisk does not need to be reconfigured unless it is accessing the subscriber registry over the network.
FreeSWITCH
The FreeSWITCH install needs to know the location of smqueue in order to forward SIP MESSAGEs. To do this, change (FS ROOT)/conf/vars.xml to the network location of smqueue:
<X-PRE-PROCESS cmd="set" data="smqueue_port=5063"/> <X-PRE-PROCESS cmd="set" data="smqueue_host=192.168.1.0"/>
Yate
Semoga tidak perlu di ubah apa-apa.
smqueue
/etc/OpenBTS/smqueue.db has numerous variables that need to be set to the new network locations of each service
Asterisk.address -> 192.168.1.0 The network location of the PBX SIP.myIP2 -> 192.168.1.0 The external-facing IP address of smqueue SIP.Proxy.Registration -> 192.168.1.0:5064 The location of sipauthserve
sipauthserve
Fortunately, sipauthserve is a passive engine that does not need to know where any other services are located.
OpenBTS
Running multiple BTS's concurrently is a difficult task. Each BTS must not only be configured to know the location of the network services, but also configured to not interfere with their nearby BTS neighbors.
Network Configuration
Every OpenBTS install must be configured (at /etc/OpenBTS/OpenBTS.db) to the smqueue, sipauthserve, and PBX services. This can be done either with the sqlite3 client or via the OpenBTS [command-line interface].
SIP.Local.IP -> 192.168.1.1 (or .2) The external IP of the OpenBTS install. SIP.Proxy.Registration -> 192.168.1.0:5064 The IP/Port of sipauthserve SIP.Proxy.SMS -> 192.168.1.0:5063 The IP/Port of smqueue (or FreeSWITCH) SIP.Proxy.Speech -> 192.168.1.0:5060 The IP/Port of the PBX
BTS Configuration
There are two types of BTS configurations needed to put together a network. First, a number of variables must be THE SAME for all BTSs on a network:
GSM.Identity.MCC The mobile country code GSM.Identity.MNC The mobile network code GSM.Identity.BSIC.NCC The network color code, must be unique from all other networks around you. GSM.CellSelection.NCCsPermitted The NCCs permitted by your BTS. Should include the above.
The following have to be DIFFERENT for each BTS.
GSM.CellSelection.BSIC.BCC The BTS color code. Each BTS should have a different color code. GSM.Identity.LAC The Location area code. Have to be unique for each BTS GSM.Identity.CID Cell ID, again unique per BTS.
Debugging
It's pretty easy to get these wrong. For network configuration, use a tool like [ wireshark] to trace the traffic.
Referensi
Pranala Menarik
Persiapan
- USRP: High Precision Clock
- USRP: Menyambungkan ClockTamer ke USRP1
- USRP: Kalibrasi ClockTamer
- USRP: ClockTamer Control Protocol
- USRP: Instalasi Board
- OpenBTS: GIT Source Code
- USRP: Rangkaian Board USRP
- OpenBTS: Tethr untuk Bencana Alam
OpenBTS 2.6
- GNURadio
- GNURadio: Ubuntu Install
- GNURadio: Menggunakan UHD
- GNURadio: Ubuntu Install GNURadio 3.4.2 RECOMMENDED
- GNURadio: Ubuntu Install GNURadio 3.4.2 Clock 52MHz RECOMMENDED
- GNURadio: Contoh Aplikasi
- GNURadio: Spectrum Analizer GSM
- GNURadio: Mengubah board RFX1800 menjadi RFX900
- GNURadio: Programming Untuk Pemula
- OpenBTS: Ubuntu Install RECOMMENDED
- OpenBTS: Ubuntu Install OpenBTS 2.6 Clock 52MHz RECOMMENDED
- OpenBTS: Konfigurasi RECOMMENDED
- OpenBTS: Kalibrasi
- OpenBTS: Konfigurasi Asterisk untuk OpenBTS RECOMMENDED
- OpenBTS: Menjalankan smqueue
- OpenBTS: Mengoperasikan BTS RECOMMENDED
- OpenBTS: Tampilan di Nokia saat pakai OpenBTS
- OpenBTS: Operasi 1800 MHz
- OpenBTS: Beberapa Tips
- OpenBTS: USRP2
- OpenBTS: Amplifier
- OpenBTS: SMS
- AirProbe
OpenBTS 2.8
- GNURadio: Ubuntu 11.10 Install NOT RECOMMENED
- GNURadio: Ubuntu 11.10 instalasi menggunakan Repo NOT RECOMMENDED
- GNURadio: Download GNURadio
- GNURadio: Install UHD
- GNURadio: Ubuntu 11.10 Instal GNURadio 3.3.0
- GNURadio: Ubuntu 11.10 Instal GNURadio 3.4.2 RECOMMENDED
- GNURadio: Ubuntu 12.04 Instal GNURadio 3.4.2 RECOMMENDED
- GNURadio: Ubuntu 11.10 Instal GNURadio 3.5.0 NOT RECOMMENDED
- GNURadio: Ubuntu 11.10 Instal GNURadio 3.5.3.2 NOT RECOMMENDED
- GNURadio: Ubuntu 11.10 Instal GNURadio 3.6.0 NOT RECOMMENDED
- GNURadio: Ubuntu 11.10 Install dari GIT GNURadio NOT RECOMMENDED
- GNURadio: Ubuntu 11.10 cek USRP Daughter Board
- GNURadio: UHD
- GNURadio: UHD Image
- GNURadio: UHD Identifikasi Device
- OpenBTS: Ubuntu 11.10 Install
- OpenBTS: dari GIT ttsou
- OpenBTS: 2.8 dari SVN Install
- OpenBTS: 2.8 dari SVN Install Clock 52MHz RECOMMENDED
- OpenBTS: 2.8 Edit User di sqlite3.db RECOMMEND
- OpenBTS: Yate Softswitch
- OpenBTS: Yate Config Test
- OpenBTS: 2.8 Instalasi Real Time Asterisk RECOMMENDED
- OpenBTS: 2.8 Menjalankan RECOMMENDED
- OpenBTS: 2.8 Konfigurasi
- OpenBTS: 2.8 Konfigurasi Subscriber Registery
- OpenBTS: Database SQLite
Multi OpenBTS 2.8
Ettus E110
- OpenBTS: E110 Cara Login
- OpenBTS: E110 Install Image di MicroSD
- OpenBTS: E110 Cek Daughter Board
- OpenBTS: E110 Mengubah Master Clock
- OpenBTS: E110 Kalibrasi Clock
- OpenBTS: E110 Bekerja dengan opkg
- OpenBTS: E110 GNURadio
- OpenBTS: E110 Install UHD Image
- OpenBTS: E110 Instalasi OpenBTS
- OpenBTS: E110 Instalasi OpenBTS 2.6 NOT RECOMMENDED
- OpenBTS: E110 Instalasi OpenBTS 2.8 untuk MultiBTS
Power Amplifier
Lain Lain
- OpenBTS: Materi Magang di ICTWATCH
- OpenBTS: Seminar Outline
- OpenBTS: Workshop Outline
- Membuat Base Station GSM Open Source
- Teknologi Selular
- GSM: Daftar Channel Frekuensi
- Wireless Internet
- OpenBSC
- AirProbe
- Base station subsystem
- GSM
- Asterisk
- Mobile phone
Catatan Legal dan Pendukung
- Siapa Bilang OpenBTS Ilegal?
- OpenBTS: Catatan MNC dan MCC Indonesia
- OpenBTS: Catatan MNC dan MCC COOL
- OpenBTS : Alokasi Frekuensi Operator GSM Indonesia
- GSM: Daftar Channel Frekuensi
Catatan Sejarah
- 2011/04/30 - Workshop OpenBTS Pertama di Indonesia dilakukan di Univ Gajah Putih Takengon Aceh Tengah
- OpenBTS: Daftar Workshop atau Seminar yang pernah dilakukan
- OpenBTS: Daftar Artikel di Media
Dokumentasi Video
- http://youtu.be/8ogOcUSpINU (1/6)
- http://youtu.be/F5d7HGuhppk (2/6)
- http://youtu.be/90Jgq6bOgrQ (3/6)
- http://youtu.be/cNkx_qNqdfc (4/6)
- http://youtu.be/6LCuoeI57ak (5/6)
- http://youtu.be/-dEqcHoIlYk (6/6)