Difference between revisions of "4G Mobile Core"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) (Created page with "The 4G Mobile Core, which 3GPP officially refers to as the Evolved Packet Core (EPC), consists of five main components, the first three of which run in the Control Plane (CP)...") |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | 4G Mobile Core, yang secara resmi disebut oleh 3GPP sebagai Evolved Packet Core (EPC), terdiri dari lima komponen utama, tiga yang pertama berjalan di Control Plane (CP) dan dua yang kedua berjalan di User Plane (UP). | |
| − | |||
| − | HSS (Home Subscriber Server): | + | * MME (Mobility Management Entity): Melacak dan mengelola pergerakan UE di seluruh RAN. Ini termasuk merekam saat UE tidak aktif. |
| − | + | * HSS (Home Subscriber Server):Melacak dan mengelola pergerakan UE di seluruh RAN. Ini termasuk merekam saat UE tidak aktif. | |
| − | PCRF (Policy & Charging Rules Function): Tracks and manages policy rules and records billing data on subscriber traffic. | + | * PCRF (Policy & Charging Rules Function): Tracks and manages policy rules and records billing data on subscriber traffic. |
| − | + | * SGW (Serving Gateway): Forwards IP packets to and from the RAN. Anchors the Mobile Core end of the bearer service to a (potentially mobile) UE, and so is involved in handovers from one base station to another. | |
| − | SGW (Serving Gateway): Forwards IP packets to and from the RAN. Anchors the Mobile Core end of the bearer service to a (potentially mobile) UE, and so is involved in handovers from one base station to another. | + | * PGW (Packet Gateway): Essentially an IP router, connecting the Mobile Core to the external Internet. Supports additional access-related functions, including policy enforcement, traffic shaping, and charging. |
| − | |||
| − | PGW (Packet Gateway): Essentially an IP router, connecting the Mobile Core to the external Internet. Supports additional access-related functions, including policy enforcement, traffic shaping, and charging. | ||
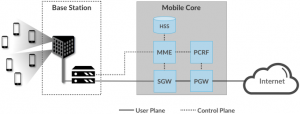
Although specified as distinct components, in practice the SGW (RAN-facing) and PGW (Internet-facing) are often combined in a single device, commonly referred to as an S/PGW. The end result is illustrated in Figure 14. | Although specified as distinct components, in practice the SGW (RAN-facing) and PGW (Internet-facing) are often combined in a single device, commonly referred to as an S/PGW. The end result is illustrated in Figure 14. | ||
| − | + | [[File:Slide20.png|center|300px|thumb|Gambar 14. 4G Mobile Core (Evolved Packet Core).]] | |
| − | |||
Note that 3GPP is flexible in how the Mobile Core components are deployed to serve a geographic area. For example, a single MME/PGW pair might serve a metropolitan area, with SGWs deployed across ~10 edge sites spread throughout the city, each of which serves ~100 base stations. But alternative deployment configurations are allowed by the spec. | Note that 3GPP is flexible in how the Mobile Core components are deployed to serve a geographic area. For example, a single MME/PGW pair might serve a metropolitan area, with SGWs deployed across ~10 edge sites spread throughout the city, each of which serves ~100 base stations. But alternative deployment configurations are allowed by the spec. | ||
Revision as of 12:58, 26 October 2022
4G Mobile Core, yang secara resmi disebut oleh 3GPP sebagai Evolved Packet Core (EPC), terdiri dari lima komponen utama, tiga yang pertama berjalan di Control Plane (CP) dan dua yang kedua berjalan di User Plane (UP).
- MME (Mobility Management Entity): Melacak dan mengelola pergerakan UE di seluruh RAN. Ini termasuk merekam saat UE tidak aktif.
- HSS (Home Subscriber Server):Melacak dan mengelola pergerakan UE di seluruh RAN. Ini termasuk merekam saat UE tidak aktif.
- PCRF (Policy & Charging Rules Function): Tracks and manages policy rules and records billing data on subscriber traffic.
- SGW (Serving Gateway): Forwards IP packets to and from the RAN. Anchors the Mobile Core end of the bearer service to a (potentially mobile) UE, and so is involved in handovers from one base station to another.
- PGW (Packet Gateway): Essentially an IP router, connecting the Mobile Core to the external Internet. Supports additional access-related functions, including policy enforcement, traffic shaping, and charging.
Although specified as distinct components, in practice the SGW (RAN-facing) and PGW (Internet-facing) are often combined in a single device, commonly referred to as an S/PGW. The end result is illustrated in Figure 14.
Note that 3GPP is flexible in how the Mobile Core components are deployed to serve a geographic area. For example, a single MME/PGW pair might serve a metropolitan area, with SGWs deployed across ~10 edge sites spread throughout the city, each of which serves ~100 base stations. But alternative deployment configurations are allowed by the spec.