Difference between revisions of "VoIP: Instalasi MCUWeb"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) (New page: 1. Getting mcuWeb.sar 1.1 Download binary from sourceforge The binary release of the application can be found on sourceforge at http://sourceforge.net/projects/mcumediaserver/files/mcumed...) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | Sumber: http://www.medooze.com/products/mcu/open-source-installation.aspx | |
| − | + | ||
| + | ==Getting mcuWeb.sar== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Download binary from sourceforge=== | ||
The binary release of the application can be found on sourceforge at http://sourceforge.net/projects/mcumediaserver/files/mcumediaserver/ | The binary release of the application can be found on sourceforge at http://sourceforge.net/projects/mcumediaserver/files/mcumediaserver/ | ||
| Line 6: | Line 9: | ||
Please note that the binary file is not released for every subversion commit. If you want to use the very latest version in the repository, you will have to compile it from sources as described in the next chapter. | Please note that the binary file is not released for every subversion commit. If you want to use the very latest version in the repository, you will have to compile it from sources as described in the next chapter. | ||
| − | + | ===Compile it from source=== | |
First you need to download the apache xmlrpc library and make sure that you have sailfin installed in your server. Obviously java JDK and ant are also needed. | First you need to download the apache xmlrpc library and make sure that you have sailfin installed in your server. Obviously java JDK and ant are also needed. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 45: | ||
ant -Dj2ee.server.home=/usr/local/sailfin -Dlibs.CopyLibs.classpath=/usr/share/netbeans/java4/ant/extra/org-netbeans-modules-java-j2seproject-copylibstask.jar | ant -Dj2ee.server.home=/usr/local/sailfin -Dlibs.CopyLibs.classpath=/usr/share/netbeans/java4/ant/extra/org-netbeans-modules-java-j2seproject-copylibstask.jar | ||
| − | + | ==Deployment in an SIP Application Server== | |
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Using Sailfin SIP Aplication Server=== | ||
SailFin is based on robust and scalable SIP servlets technology open sourced by Ericsson on top of a deployment-quality, Java EE-based GlassFish by Sun. JSR 289 updates the SIP Servlets API and defines a standard application programming model to mix SIP Servlets and Java EE components. | SailFin is based on robust and scalable SIP servlets technology open sourced by Ericsson on top of a deployment-quality, Java EE-based GlassFish by Sun. JSR 289 updates the SIP Servlets API and defines a standard application programming model to mix SIP Servlets and Java EE components. | ||
| Line 172: | Line 176: | ||
Login into the Sailfin admin consoling available in http://[ip]:4848/ | Login into the Sailfin admin consoling available in http://[ip]:4848/ | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [[Image:Login 800x472.jpg|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
User: admin. | User: admin. | ||
| Line 178: | Line 183: | ||
If you want to to change the http listening port you can do it under Configuration > http-listener-1 | If you want to to change the http listening port you can do it under Configuration > http-listener-1 | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [[Image:Listener 800x472.jpg|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
It is also possible to change also the listening ports for the SIP protocol that will be listening on the default 5060 one to avoid conflicts with anyother SIP server running in the same server (as Asterisk). First we will change the SIP port assigned to the container under Configuration > Sip container | It is also possible to change also the listening ports for the SIP protocol that will be listening on the default 5060 one to avoid conflicts with anyother SIP server running in the same server (as Asterisk). First we will change the SIP port assigned to the container under Configuration > Sip container | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [[Image:Listener2 800x472.jpg|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
Change the following values | Change the following values | ||
| Line 189: | Line 196: | ||
And then the set the listening port under Configuration > SIP Listener > sip-listener-1 | And then the set the listening port under Configuration > SIP Listener > sip-listener-1 | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [[Image:Listener3 800x472.jpg|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
And under Configuration > SIP Listener > sip-listener-2 | And under Configuration > SIP Listener > sip-listener-2 | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [[Image:Listener4 800x472.jpg|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
Now we will install the mcuWeb application in the Sailfin server.Go to Applications > Converged Sip Modules and click deploy | Now we will install the mcuWeb application in the Sailfin server.Go to Applications > Converged Sip Modules and click deploy | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [[Image:Deploy 800x472.jpg|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
Choose the local file and deploy it | Choose the local file and deploy it | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [[Image:Deploy2 800x472.jpg|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
The mcuWeb interface will be ready under http://[ip]/mcuWeb | The mcuWeb interface will be ready under http://[ip]/mcuWeb | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Mcuweb 800x536.jpg|center|200px|thumb]] | |
| − | + | ===Using Mobicents SIP Application Server=== | |
Mobicents SIP Servlets is a modern communications middleware platform and implements the latest SIP Servlet v1.1 (JSR 289) standard. It can be plugged into any Application Server container (currently 7.X and JBoss 7.X) and also offers High Availability and Failover. It also supoprts SIP over websockets. | Mobicents SIP Servlets is a modern communications middleware platform and implements the latest SIP Servlet v1.1 (JSR 289) standard. It can be plugged into any Application Server container (currently 7.X and JBoss 7.X) and also offers High Availability and Failover. It also supoprts SIP over websockets. | ||
| Line 234: | Line 245: | ||
Once deployed you will ned to setup the SIP servlet routing to make the mcuWeb application handle the sip traffic. This is done via the mobicents sip servlet management console available at http://ip:port/sip-servlets-management | Once deployed you will ned to setup the SIP servlet routing to make the mcuWeb application handle the sip traffic. This is done via the mobicents sip servlet management console available at http://ip:port/sip-servlets-management | ||
| − | + | ==SIP Server integration== | |
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Asterisk integration=== | ||
First, enable general video support in the sip configuration. | First, enable general video support in the sip configuration. | ||
| Line 261: | Line 273: | ||
[from-sip-external] | [from-sip-external] | ||
exten => _3XX,1,Dial(SIP/${EXTEN}@mcuWeb,,) | exten => _3XX,1,Dial(SIP/${EXTEN}@mcuWeb,,) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Referensi== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * http://www.medooze.com/products/mcu/open-source-installation.aspx | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Pranala Menarik== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[VoIP]] | ||
| + | * [[OpenBTS]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Latar Belakang=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[Menjadikan VoIP dan 4G Legal]] | ||
| + | * [[Sekitar VoIP Rakyat]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Dasar Hukum Internet Telepon]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Beberapa Skenario Topologi]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Pilihan Teknologi Internet Telepon]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Pengkodean Suara di Jaringan Komputer]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Konsep Video Conference]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Untuk Pemula=== | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Kebutuhan Peralatan dan Software]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Internet Telepon PC ke PC]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Untuk Peneliti / Pencoba=== | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Bandwidth Internet Telepon]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Softswitch / Server Internet Telepon]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Repository Software Internet Telepon]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Menghubungkan PSTN dan Selular]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Untuk Operator=== | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Server Video Conference]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Software dan peralatan client Internet Telepon]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Penggunaan DAHDI]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Hardware Client VoIP]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Hardware Server VoIP]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Interkoneksi dan Alokasi Nomor Telepon]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Peering Antar Operator VoIP]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Menghubungkan PSTN dan Selular]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Trunk]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Topik Lanjut=== | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: ENUM untuk pengenalan nomor telepon di Internet Telepon]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Teknik Evaluasi Internet Telepon]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Troubleshooting]] | ||
| + | * [[VoIP: Video Conference Server]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Buku Teknologi VoIP=== | ||
| + | * [[Onno W. Purbo]], "VoIP Cikal Bakal Telkom Rakyat", Infokomputer, 2007. | ||
| + | * http://125.160.17.21/speedyorari/index.php?dir=ebook-voip | ||
| + | * http://opensource.telkomspeedy.com/speedyorari/index.php?dir=ebook-voip | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category: VoIP]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Internet Telepon]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:03, 8 January 2014
Sumber: http://www.medooze.com/products/mcu/open-source-installation.aspx
Getting mcuWeb.sar
Download binary from sourceforge
The binary release of the application can be found on sourceforge at http://sourceforge.net/projects/mcumediaserver/files/mcumediaserver/
Please note that the binary file is not released for every subversion commit. If you want to use the very latest version in the repository, you will have to compile it from sources as described in the next chapter.
Compile it from source
First you need to download the apache xmlrpc library and make sure that you have sailfin installed in your server. Obviously java JDK and ant are also needed.
# # External source code checkout # svn checkout svn://svn.code.sf.net/p/mcumediaserver/code/trunk/ medooze
The next step is to retreive the latest version from the reopository.
Edit the project properties to match your library directories. In /usr/local/src/medooze/XmlRpcMcuClient/nbproject/project.properties:
file.reference.commons-logging-1.1.jar=/usr/local/apache-xmlrpc-3.1.3/lib/commons-logging-1.1.jar file.reference.ws-commons-util-1.0.2.jar=/usr/local/apache-xmlrpc-3.1.3/lib/ws-commons-util-1.0.2.jar file.reference.xmlrpc-client-3.1.3.jar=/usr/local/apache-xmlrpc-3.1.3/lib/xmlrpc-client-3.1.3.jar file.reference.xmlrpc-common-3.1.3.jar=/usr/local/apache-xmlrpc-3.1.3/lib/xmlrpc-common-3.1.3.jar
In /usr/local/src/medooze/mcuWeb/nbproject/project.properties:
file.reference.commons-logging-1.1.jar=/usr/local/apache-xmlrpc-3.1.3/lib/commons-logging-1.1.jar file.reference.ssa-api.jar=/usr/local/sailfin/lib/ssa-api.jar file.reference.ws-commons-util-1.0.2.jar=/usr/local//apache-xmlrpc-3.1.3/lib/ws-commons-util-1.0.2.jar file.reference.xmlrpc-client-3.1.3.jar=/usr/local/apache-xmlrpc-3.1.3/lib/xmlrpc-client-3.1.3.jar file.reference.xmlrpc-common-3.1.3.jar=/usr/local/apache-xmlrpc-3.1.3/lib/xmlrpc-common-3.1.3.jar file.reference.XmlRpcMcuClient.jar=../XmlRpcMcuClient/dist/XmlRpcMcuClient.jar
And now compile both projects:
cd /usr/local/src/medooze/XmlRpcMcuClient ant cd /usr/local/src/medooze/mcuWeb ant -Dj2ee.server.home=/usr/local/sailfin -Dlibs.CopyLibs.classpath=/usr/share/netbeans/java4/ant/extra/org-netbeans-modules-java-j2seproject-copylibstask.jar
Deployment in an SIP Application Server
Using Sailfin SIP Aplication Server
SailFin is based on robust and scalable SIP servlets technology open sourced by Ericsson on top of a deployment-quality, Java EE-based GlassFish by Sun. JSR 289 updates the SIP Servlets API and defines a standard application programming model to mix SIP Servlets and Java EE components. Installing Sailfin
The first step is to download and install sun JDK 1.6 and install the Sailfin server.
# #Installing Sailfin # cd /usr/local wget http://download.java.net/javaee5/sailfin/v2_branch/promoted/Linux/sailfin-installer-v2-b31g-linux.jar java -Xmx256m -jar sailfin-installer-v2-b31g-linux.jar cd sailfin chmod -R +x lib/ant/bin lib/ant/bin/ant -f setup.xml
Once installed, we will add a start script. Create a new mcuWeb file under /etc/init.d and copy the following.
#! /bin/sh
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: mcuWeb
# Required-Start:
# Required-Stop:
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: mcuWeb startup script
# Description: mcuWeb startup script
### END INIT INFO
# Author: Sergio Garcia Murillo “sergio.garcia@fontventa.com”
PATH=/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin
DESC="Start Sailfin domian domain1"
NAME="asadmin"
DAEMON=/usr/local/sailfin/bin/$NAME
START_ARGS="start-domain domain1"
STOP_ARGS="stop-domain domain1"
PIDFILE=/var/run/$NAME.pid
SCRIPTNAME=/etc/init.d/$NAME
# Exit if the package is not installed
[ -x "$DAEMON" ] || exit 0
# Read configuration variable file if it is present
[ -r /etc/default/$NAME ] && . /etc/default/$NAME
#
# Function that starts the daemon/service
#
do_start()
{
# Return
# 0 if daemon has been started
# 1 if daemon was already running
# 2 if daemon could not be started
$DAEMON $START_ARGS || return 2
}
#
# Function that stops the daemon/service
#
do_stop()
{
# Return
# 0 if daemon has been stopped
# 1 if daemon was already stopped
# 2 if daemon could not be stopped
$DAEMON $STOP_ARGS || return 2
}
case "$1" in
start)
[ "$VERBOSE" != no ] && echo "Starting $DESC" "$NAME"
do_start
case "$?" in
0|1) [ "$VERBOSE" != no ] && echo "Done" ;;
2) [ "$VERBOSE" != no ] && echo "Failed" ;;
esac
;;
stop)
[ "$VERBOSE" != no ] && echo "Stopping $DESC" "$NAME"
do_stop
case "$?" in
0|1) [ "$VERBOSE" != no ] && echo "Done" ;;
2) [ "$VERBOSE" != no ] && echo "Failed" ;;
esac
;;
restart|force-reload)
#
# If the "reload" option is implemented then remove the
# 'force-reload' alias
#
echo "Restarting $DESC" "$NAME"
do_stop
case "$?" in
0|1)
do_start
case "$?" in
0) echo "Done" ;;
1) echo "Old process is still running" ;; # Old process is still running
*) echo "Failed to start" ;; # Failed to start
esac
;;
*)
# Failed to stop
echo "Failed"
;;
esac
;;
*)
#echo "Usage: $SCRIPTNAME {start|stop|restart|reload|force-reload}" >&2
echo "Usage: $SCRIPTNAME {start|stop|restart|force-reload}" >&2
exit 3
;;
esac
Let’s configure the service to start automatically at the desired runleves and start the default Sailfin domain:
chmod 777 /etc/init.d/mcuWeb /sbin/chkconfig --level 35 mcuWeb on service mcuWeb start
Configure Sailfin and deploy mcuWeb
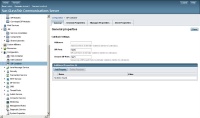
Login into the Sailfin admin consoling available in http://[ip]:4848/
User: admin. Default password: adminadmin
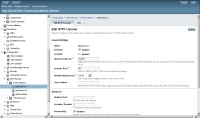
If you want to to change the http listening port you can do it under Configuration > http-listener-1
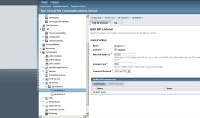
It is also possible to change also the listening ports for the SIP protocol that will be listening on the default 5060 one to avoid conflicts with anyother SIP server running in the same server (as Asterisk). First we will change the SIP port assigned to the container under Configuration > Sip container
Change the following values
Sip Port: 5070 Secure Sip Port: 5071
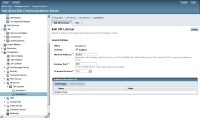
And then the set the listening port under Configuration > SIP Listener > sip-listener-1
And under Configuration > SIP Listener > sip-listener-2
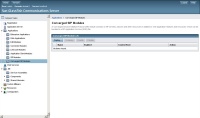
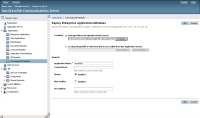
Now we will install the mcuWeb application in the Sailfin server.Go to Applications > Converged Sip Modules and click deploy
Choose the local file and deploy it
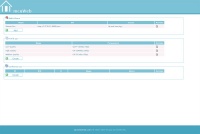
The mcuWeb interface will be ready under http://[ip]/mcuWeb
Using Mobicents SIP Application Server
Mobicents SIP Servlets is a modern communications middleware platform and implements the latest SIP Servlet v1.1 (JSR 289) standard. It can be plugged into any Application Server container (currently 7.X and JBoss 7.X) and also offers High Availability and Failover. It also supoprts SIP over websockets.
Installing MSS 2.0
The first step is to download and install sun JDK 1.6 and mss 2.0.
# #Installing Mobicents # cd /usr/local wget http://sourceforge.net/projects/mobicents/files/Mobicents%20Sip%20Servlets/Mobicents%20Sip%20Servlets%202.0.0.FINAL/mss-2.0.0.FINAL-jboss-as-7.1.2.Final-1349104459.zip/download unzip mss-2.0.0.FINAL-jboss-as-7.1.2.Final-1349104459.zip mv mss-2.0.0.FINAL-jboss-as-7.1.2.Final-1349104459 mss-2.0.0
To run mss server just:
# cd /usr/local/mss-2.0.0/bin/ ./standalone.sh -c standalone-sip.xml -b
Deploy mcuWeb and configure routing
In order to deploy the mcuWeb into Mobicents Sip Servlet, all is needed is to rename the mcuWeb.sar file to mcuWeb.war and copy to the autopdeploy directory
cp mcuWeb.sar /usr/local/mss-2.0.0/standalone/deployments/mcuWeb.war
Once deployed you will ned to setup the SIP servlet routing to make the mcuWeb application handle the sip traffic. This is done via the mobicents sip servlet management console available at http://ip:port/sip-servlets-management
SIP Server integration
Asterisk integration
First, enable general video support in the sip configuration.
videosupport=yes
Add the SIP Application Server as a peer to the sip configuration. Add the following should be added to the sip.conf or to the sip_custom.conf. Make sure to change IP and port to match your actual deployment.
[mcuWeb] videosupport=yes type=peer host=127.0.0.1 port=5070 canreinvite=no disallow=all allow=ulaw allow=alaw allow=speex allow=h263 allow=h263p allow=h264
The only step left is to forward the desired extensions to be used as conferences to the Sailfin server in the dialplan. For example to forward all 3XX extensions just add the following to the extension.conf or to the extension_custom.conf. Change the context to match your current default or custom content.
[from-sip-external]
exten => _3XX,1,Dial(SIP/${EXTEN}@mcuWeb,,)
Referensi
Pranala Menarik
Latar Belakang
- Menjadikan VoIP dan 4G Legal
- Sekitar VoIP Rakyat
- VoIP: Dasar Hukum Internet Telepon
- VoIP: Beberapa Skenario Topologi
- VoIP: Pilihan Teknologi Internet Telepon
- VoIP: Pengkodean Suara di Jaringan Komputer
- VoIP: Konsep Video Conference
Untuk Pemula
Untuk Peneliti / Pencoba
- VoIP: Bandwidth Internet Telepon
- VoIP: Softswitch / Server Internet Telepon
- VoIP: Repository Software Internet Telepon
- VoIP: Menghubungkan PSTN dan Selular
Untuk Operator
- VoIP: Server Video Conference
- VoIP: Software dan peralatan client Internet Telepon
- VoIP: Penggunaan DAHDI
- VoIP: Hardware Client VoIP
- VoIP: Hardware Server VoIP
- VoIP: Interkoneksi dan Alokasi Nomor Telepon
- VoIP: Peering Antar Operator VoIP
- VoIP: Menghubungkan PSTN dan Selular
- VoIP: Trunk
Topik Lanjut
- VoIP: ENUM untuk pengenalan nomor telepon di Internet Telepon
- VoIP: Teknik Evaluasi Internet Telepon
- VoIP: Troubleshooting
- VoIP: Video Conference Server
Buku Teknologi VoIP
- Onno W. Purbo, "VoIP Cikal Bakal Telkom Rakyat", Infokomputer, 2007.
- http://125.160.17.21/speedyorari/index.php?dir=ebook-voip
- http://opensource.telkomspeedy.com/speedyorari/index.php?dir=ebook-voip