Difference between revisions of "OS: Build in Monitoring Tool"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) (→iostat) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) (→iostat) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
z Turn on or off color/mono | z Turn on or off color/mono | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==htop== | ||
| + | |||
| + | seperti top, tapi agak lebih "user friendly". Instalasi htop menggunakan perintah | ||
| + | |||
| + | sudo apt-get install htop | ||
| + | |||
| + | menjalankan htop menggunakan perintah | ||
| + | |||
| + | htop | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==psacct atau acct== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * ac command prints the statistics of user logins/logouts (connect time) in hours. | ||
| + | * lastcomm command prints the information of previously executed commands of user. | ||
| + | * accton commands is used to turn on/off process for accounting. | ||
| + | * sa command summarizes information of previously executed commands. | ||
| + | * last and lastb commands show listing of last logged in users. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | apt install acct | ||
| + | |||
| + | restart | ||
| + | |||
| + | /etc/init.d/acct status | ||
| + | /etc/init.d/acct start | ||
| + | /etc/init.d/acct status | ||
| + | |||
| + | accounting | ||
| + | |||
| + | ac | ||
| + | ac -d | ||
| + | ac -p | ||
| + | ac onno | ||
| + | ac -d onno | ||
| + | |||
| + | execute command | ||
| + | |||
| + | sa | ||
| + | sa -u | ||
| + | sa -m | ||
| + | sa -c | ||
| + | |||
| + | last command | ||
| + | |||
| + | lastcomm onno | ||
| + | lastcomm ls | ||
==ps== | ==ps== | ||
| Line 147: | Line 194: | ||
ps -auxf | sort -nr -k 3 | head -10 | ps -auxf | sort -nr -k 3 | head -10 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==pstree== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | pstree is a small, command line (i.e., all-text mode) program that displays the processes (i.e., executing instances of programs) on the system in the form of a tree diagram. It differs from the much more commonly used (and more complex) ps program in a number of respects, including that the latter shows the processes in a list rather than a tree diagram but provides more detailed information about them. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tree Diagrams | ||
| + | |||
| + | A tree diagram is a way of showing the ancestral relationships among processes (or other entities) by connecting them with short lines that indicate for each process the process from which it originated (i.e., its parent) and any processes that it created (i.e., its children). This type of diagram differs from the usual image of a tree in that the root is at the top and the branches point downwards. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Similar inverted tree diagrams are commonly used to illustrate the hierarchical filesystems of Linux and other Unix-like operating systems, which begin with the root directory (represented by a forward slash) off from which branch the second tier directories such as /bin, /boot, /etc, /home, /mount and /sbin. | ||
| + | |||
| + | One of the advantages of pstree as compared with ps is that it makes it easier to terminate a series of related processes (i.e., all of the descendants of a particular process). This is because pstree makes it immediately clear which process is the parent, and all that is necessary is to terminate the parent in order to extinguish all of its descendant processes. That is, it is not necessary to manually search through a list to find and individually terminate each process as would be necessary using ps. The kill command is commonly used to terminate a crashed or otherwise misbehaving program or process. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syntax | ||
| + | |||
| + | The basic syntax for pstree is: | ||
| + | |||
| + | pstree [options] [pid or username] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The square brackets indicate that the items in them are optional. If pstree is used without any options or arguments, that is, by typing | ||
| + | |||
| + | pstree | ||
| + | |||
| + | and then pressing the ENTER key, the result is a tree diagram that shows all of the processes currently on the system. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | init─┬─NetworkManager─┬─dhclient | ||
| + | │ ├─dnsmasq | ||
| + | │ └─3*[{NetworkManager}] | ||
| + | ├─accounts-daemon───2*[{accounts-daemon}] | ||
| + | ├─acpid | ||
| + | ├─apache2───5*[apache2] | ||
| + | ├─at-spi-bus-laun─┬─dbus-daemon | ||
| + | │ └─3*[{at-spi-bus-laun}] | ||
| + | ├─at-spi2-registr───{at-spi2-registr} | ||
| + | ├─avahi-daemon───avahi-daemon | ||
| + | ├─bamfdaemon───3*[{bamfdaemon}] | ||
| + | ├─bluetoothd | ||
| + | ├─colord───{colord} | ||
| + | ├─console-kit-dae───64*[{console-kit-dae}] | ||
| + | ├─cron | ||
| + | ├─cups-browsed | ||
| + | ├─cupsd───dbus | ||
==vmstat== | ==vmstat== | ||
| Line 269: | Line 363: | ||
iostat | iostat | ||
| + | |||
| + | Agar dapat jalan dengan baik kita perlu install | ||
| + | |||
| + | apt install sysstat | ||
| + | |||
Contoh output | Contoh output | ||
| Line 280: | Line 379: | ||
sda 4.41 56.67 52.68 3183588 2959436 | sda 4.41 56.67 52.68 3183588 2959436 | ||
sdb 4.44 28.00 43.68 1572868 2454036 | sdb 4.44 28.00 43.68 1572868 2454036 | ||
| − | |||
==mpstat== | ==mpstat== | ||
| Line 296: | Line 394: | ||
10:04:53 AM 0 22.14 0.18 1.07 1.26 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.00 75.32 | 10:04:53 AM 0 22.14 0.18 1.07 1.26 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.00 75.32 | ||
10:04:53 AM 1 21.89 0.09 1.00 1.28 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 75.72 | 10:04:53 AM 1 21.89 0.09 1.00 1.28 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 75.72 | ||
| + | |||
| + | mpstat merupakan bagian dari sysstat install menggunakan | ||
| + | |||
| + | sudo apt-get install sysstat | ||
==pmap== | ==pmap== | ||
| Line 346: | Line 448: | ||
* shared: 15184K jumlah alamat memory dari proses ini yang di sharing dengan proses yang lain. | * shared: 15184K jumlah alamat memory dari proses ini yang di sharing dengan proses yang lain. | ||
| + | ==netstat== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Perintah netstat menampilkan informasi tentang sambungan jaringan, tabel routing, statistik interface, sambungan masquerade, dan keanggotaan multicast. Contoh penggunaannya: | ||
| + | |||
| + | netstat -nr | ||
| + | |||
| + | Contoh output: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kernel IP routing table | ||
| + | Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface | ||
| + | 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.222 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0 | ||
| + | 169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 | ||
| + | 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 | ||
| + | 192.168.13.0 192.168.0.33 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Melihat IP dan socket yang saling terhubung | ||
| + | |||
| + | netstat -an | ||
| + | |||
| + | Contoh output | ||
| + | |||
| + | Active Internet connections (servers and established) | ||
| + | Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:873 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:139 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:10000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:445 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:59669 173.194.38.149:443 ESTABLISHED | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:34229 69.171.235.16:80 ESTABLISHED | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:33922 69.171.235.16:80 ESTABLISHED | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:34049 69.171.235.16:80 ESTABLISHED | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:34252 69.171.235.16:80 ESTABLISHED | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:34097 69.171.235.16:80 ESTABLISHED | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:50100 192.168.0.7:9090 ESTABLISHED | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:38858 111.95.240.27:443 ESTABLISHED | ||
| + | tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:34076 69.171.235.16:80 ESTABLISHED | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==ss== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Perintah ss digunakan untuk dump statistik socket. ss memungkinkan untuk melihat informasi yang mirip dengan netstat. Cara mengunakannya | ||
| + | |||
| + | ss | ||
| + | |||
| + | Contoh tampilan | ||
| + | |||
| + | State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port | ||
| + | ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.3:55530 111.94.248.38:https | ||
| + | ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.3:59669 173.194.38.149:https | ||
| + | ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.3:34229 69.171.235.16:http | ||
| + | ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.3:33922 69.171.235.16:http | ||
| + | ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.3:34049 69.171.235.16:http | ||
| + | ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.3:34252 69.171.235.16:http | ||
| + | ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.3:34097 69.171.235.16:http | ||
| + | ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.3:50100 192.168.0.7:9090 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==iptraf== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Perintah iptraf adalah IP LAN monitor yang berwarna warni. iptraf menampilkan berbagai statistik jaringan termasuk TCP info, UDP count, informasi ICMP dan OSPF, info load Ethernet, statistik node, cek IP. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Instalasi iptraf menggunakan perintah | ||
| + | |||
| + | apt-get install iptraf | ||
| + | |||
| + | Menjalankan iptraf menggunakan perintah | ||
| + | |||
| + | iptraf | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hasilnya kira-kira | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Iptraf1.png|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Iptraf2.png|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Iptraf3.png|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Iptraf4.png|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Iptraf5.png|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Iptraf6.png|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
| − | + | ==Referensi== | |
| − | + | * http://activedoc.opensuse.org/book/opensuse-system-analysis-and-tuning-guide | |
| + | * http://activedoc.opensuse.org/book/opensuse-system-analysis-and-tuning-guide/part-ii-system-monitoring | ||
| + | * http://activedoc.opensuse.org/book/opensuse-system-analysis-and-tuning-guide/chapter-2-system-monitoring-utilities | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Pranala Menarik== | |
| − | + | * [[Linux]] | |
| + | * [[Ubuntu]] | ||
| + | * [[Sistem Operasi]] | ||
| + | * [[Linux: Instalasi Sistem Operasi]] | ||
| + | * [[Linux: Skema Partisi di Linux]] | ||
| + | * [[Kernel]] | ||
| + | * [[Compile Kernel]] | ||
| + | * [[Compile Kernel: Konfigurasi Kernel]] | ||
| + | * [[Kernel: Anatomi Kernel Source]] | ||
| + | * [[OS: Linux Kernel]] | ||
| + | * [[OS: Parameter Kernel Default]] | ||
| + | * [[OS: Kernel Scheduler]] | ||
| + | * [[OS: Complete Teori Tuning Kernel Scheduler]] | ||
| + | * [[OS: Complete Teori Tuning I/O Performance]] | ||
| + | * [[OS: Tuning Kernel Scheduler]] | ||
| + | * [[OS: Tuning Completely Fair Queueing CFQ I/O scheduler]] | ||
| + | * [[OS: Tuning Completely Fair scheduler CFS]] | ||
| + | * [[OS: Build in Monitoring Tool]] | ||
| + | * [[Linux Benchmarking]] | ||
| + | * [[OS: Benchmarking menggunakan UnixBench]] | ||
| + | * [[OS: Benchmarking menggunakan LLCBench]] | ||
| + | * [[OS: Mengerti System Call]] | ||
| + | * [[OS: Membuat Kernel Modul]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:05, 29 March 2022
Sumber: http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/top-linux-monitoring-tools.html
Apakah anda butuh melihat performance Linux? coba gunakan built-in command dan beberapa tool tambahan berikut. Kebanyakan distribusi linux di persenjatai oleh banyak sekali tool untuk melakukan monitoring. Tool ini memberikan informasi tentang aktifitas sistem. Kita dapat menggunakan tool ini untuk melihat masalah dalam performance sistem.
Perintah di bawah ini akan dapat membantu analisa sistem dan debugging server seperti:
- Menemukan bottlenecks.
- Disk (storage) bottlenecks.
- CPU dan memory bottlenecks.
- Network bottlenecks.
top
top menyediakan, dinamis real-time dari proses dalam sistem berjalan. Hal ini dapat menampilkan berbagai informasi, termasuk ringkasan kondisi sistem dan task yang saat ini sedang dikelola oleh kernel Linux. top akan mengupdate secara automatis setiap detik. Secara default, top akan menampilkan task yang paling memakan CPU.
Top juga memiliki kemampuan terbatas untuk memanipulasi proses. Kedua operasi dan informasi yang ditampilkan dapat dikonfigurasi, dan setiap detail konfigurasi dapat dibuat untuk bertahan saat restart.
Secara default, proses yang ditunjukkan diurutkan berdasarkan persentase penggunaan CPU, memberikan pandangan yang mudah ke dalam proses yang paling mengkonsumsi sumber daya.
top - 08:39:14 up 14:18, 3 users, load average: 1.09, 1.04, 1.08
Tasks: 190 total, 2 running, 188 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
Cpu(s): 52.7%us, 3.1%sy, 0.0%ni, 44.2%id, 0.0%wa, 0.0%hi, 0.0%si, 0.0%st
Mem: 2011972k total, 1631164k used, 380808k free, 53628k buffers
Swap: 779148k total, 161836k used, 617312k free, 337676k cached
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
3068 onno 20 0 1384m 495m 19m R 98 25.2 316:17.21 firefox
1267 root 20 0 170m 19m 4952 S 7 1.0 10:25.66 Xorg
2235 onno 20 0 1390m 63m 9088 S 5 3.3 5:03.61 compiz
2896 onno 20 0 513m 13m 6052 S 2 0.7 0:23.35 gnome-terminal
13162 root 20 0 17432 1364 952 R 0 0.1 0:00.07 top
1 root 20 0 24584 2008 1028 S 0 0.1 0:00.88 init
2 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0 0.0 0:00.00 kthreadd
3 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0 0.0 0:04.95 ksoftirqd/0
6 root RT 0 0 0 0 S 0 0.0 0:00.00 migration/0
7 root RT 0 0 0 0 S 0 0.0 0:00.24 watchdog/0
Hot key top yang sering digunakan
t Tampilkan informasi rangkuman off dan on. m Tampilkan informasi memory off dan on. A Urutkan tampilan berdasarkan konsumen sumber daya sistem yang paling besar. f Masuk ke layar konfigurasi interaktif pada top. o Enable agar kita dapat memilih secara interaktif dalam top. r Lakukan perintah renice. k Lakukan perintah kill. z Turn on or off color/mono
htop
seperti top, tapi agak lebih "user friendly". Instalasi htop menggunakan perintah
sudo apt-get install htop
menjalankan htop menggunakan perintah
htop
psacct atau acct
- ac command prints the statistics of user logins/logouts (connect time) in hours.
- lastcomm command prints the information of previously executed commands of user.
- accton commands is used to turn on/off process for accounting.
- sa command summarizes information of previously executed commands.
- last and lastb commands show listing of last logged in users.
apt install acct
restart
/etc/init.d/acct status /etc/init.d/acct start /etc/init.d/acct status
accounting
ac ac -d ac -p ac onno ac -d onno
execute command
sa sa -u sa -m sa -c
last command
lastcomm onno lastcomm ls
ps
ps mengambil snapshot dari kelompok proses terpilih yang aktif. Secara default kelompok ini terbatas pada proses yang dimiliki oleh pengguna saat ini dan terkait dengan terminal yang sama.
Hal ini dapat memberikan informasi lebih rinci tentang proses yang terjadi daripada top, tapi tidak dinamis.
Untuk memilih semua proses gunakan -A atau -e:
ps -A ps -e
Contoh keluaran
PID TTY TIME CMD
1 ? 00:00:00 init
2 ? 00:00:00 kthreadd
3 ? 00:00:05 ksoftirqd/0
6 ? 00:00:00 migration/0
7 ? 00:00:00 watchdog/0
8 ? 00:00:00 migration/1
...
...
12400 ? 00:00:00 btrfs-worker-2
12403 ? 00:00:00 btrfs-endio-met
12508 ? 00:00:00 kworker/0:0
12723 ? 00:00:00 kworker/1:0
13329 ? 00:00:00 kworker/1:2
13541 pts/2 00:00:00 ps
ps tidak berbeda jauh dengan top tapi memberikan lebih banyak informasi. Untuk memberikan Long Format output:
ps -Al
Untuk mengaktifkan extra full mode, ini akan memperlihatkan command line argumen yang dikirimkan ke proses
ps -AlF
Untuk melihat thread ( LWP dan NLWP)
ps -AlFH
Untuk melihat thread setelah di proses
ps -AlLm
Untuk melihat semua proses yang ada di server
ps ax ps axu
Print proses tree
ps -ejH ps axjf pstree
Print informasi security
ps -eo euser,ruser,suser,fuser,f,comm,label ps axZ ps -eM
Lihat semua proses yang jalan sebagai User www-data
ps -U www-data -u www-data u
Set output dalam format yang user-defined
ps -eo pid,tid,class,rtprio,ni,pri,psr,pcpu,stat,wchan:14,comm ps axo stat,euid,ruid,tty,tpgid,sess,pgrp,ppid,pid,pcpu,comm ps -eopid,tt,user,fname,tmout,f,wchan
Display hanya proses ID dari firefox
ps -C firefox -o pid= ps -C soffice.bin -o pid= pgrep firefox pgrep soffice.bin
Tampilkan nama dari PID 55977
ps -p 55977 -o comm=
Tampilkan top 10 proses yang mengkonsumsi memory
ps -auxf | sort -nr -k 4 | head -10
Tampilkan top 10 proses yang mengkonsumsi CPU
ps -auxf | sort -nr -k 3 | head -10
pstree
pstree is a small, command line (i.e., all-text mode) program that displays the processes (i.e., executing instances of programs) on the system in the form of a tree diagram. It differs from the much more commonly used (and more complex) ps program in a number of respects, including that the latter shows the processes in a list rather than a tree diagram but provides more detailed information about them.
Tree Diagrams
A tree diagram is a way of showing the ancestral relationships among processes (or other entities) by connecting them with short lines that indicate for each process the process from which it originated (i.e., its parent) and any processes that it created (i.e., its children). This type of diagram differs from the usual image of a tree in that the root is at the top and the branches point downwards.
Similar inverted tree diagrams are commonly used to illustrate the hierarchical filesystems of Linux and other Unix-like operating systems, which begin with the root directory (represented by a forward slash) off from which branch the second tier directories such as /bin, /boot, /etc, /home, /mount and /sbin.
One of the advantages of pstree as compared with ps is that it makes it easier to terminate a series of related processes (i.e., all of the descendants of a particular process). This is because pstree makes it immediately clear which process is the parent, and all that is necessary is to terminate the parent in order to extinguish all of its descendant processes. That is, it is not necessary to manually search through a list to find and individually terminate each process as would be necessary using ps. The kill command is commonly used to terminate a crashed or otherwise misbehaving program or process.
Syntax
The basic syntax for pstree is:
pstree [options] [pid or username]
The square brackets indicate that the items in them are optional. If pstree is used without any options or arguments, that is, by typing
pstree
and then pressing the ENTER key, the result is a tree diagram that shows all of the processes currently on the system.
init─┬─NetworkManager─┬─dhclient
│ ├─dnsmasq
│ └─3*[{NetworkManager}]
├─accounts-daemon───2*[{accounts-daemon}]
├─acpid
├─apache2───5*[apache2]
├─at-spi-bus-laun─┬─dbus-daemon
│ └─3*[{at-spi-bus-laun}]
├─at-spi2-registr───{at-spi2-registr}
├─avahi-daemon───avahi-daemon
├─bamfdaemon───3*[{bamfdaemon}]
├─bluetoothd
├─colord───{colord}
├─console-kit-dae───64*[{console-kit-dae}]
├─cron
├─cups-browsed
├─cupsd───dbus
vmstat
vmstat (Statistik Virtual Memory) mengeluarkan laporan seketika tentang proses dalam sistem, memori, paging, block I/O, interupsi dan aktivitas CPU.
Meskipun tidak dinamis seperti top, kita dapat menentukan interval sampling, yang memungkinkan kita mengamati aktivitas sistem mendekati real time.
vmstat 3
Contoh output:
procs -----------memory---------- ---swap-- -----io---- -system-- ----cpu---- r b swpd free buff cache si so bi bo in cs us sy id wa 3 0 160988 93024 64376 609380 1 2 42 47 11 129 21 1 76 1 2 0 160988 75440 52892 640592 0 0 19168 0 963 760 91 4 0 5 2 0 160988 75208 38260 658948 0 0 16316 198 887 661 85 3 2 11 1 1 160988 75304 31272 663872 0 0 16584 4 1055 1014 92 5 0 4 1 1 160988 76816 30100 667352 0 0 4 55416 1349 3649 51 8 0 41
Dapatkan penggunaan memory
vmstat -m
Dapatkan informasi tentang penggunaan page memory yang aktif / tidak aktif.
vmstat -a
sar
sar (Sistem Reporter Activity) mengumpulkan dan melaporkan informasi tentang aktivitas sistem saat ini. sar dapat di instalasi melalui perintah
apt-get install sysstat
Dan edit file
vi /etc/default/sysstat
agar
ENABLED="true"
Kemudian restart sysstat
/etc/init.d/sysstat restart
setelah data di koleksi. Untuk melihat network counter, ketik
sar -n DEV | more
Untuk melihat network counter dari sa24
sar -n DEV -f /var/log/sa/sa24 | more
Kita juga dapat melihat penggunan secara real time menggunakan sar
sar 2 5
Contoh keluaran
Linux 3.2.0-29-generic (openbts28) 03/23/2013 _x86_64_ (2 CPU) 09:59:20 AM CPU %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle 09:59:22 AM all 50.63 0.00 1.51 0.00 0.00 47.86 09:59:24 AM all 51.00 0.00 1.75 0.75 0.00 46.50 09:59:26 AM all 50.63 0.00 2.26 0.00 0.00 47.12 09:59:28 AM all 49.62 0.00 2.52 0.00 0.00 47.86 09:59:30 AM all 50.38 0.00 2.02 1.26 0.00 46.35 Average: all 50.45 0.00 2.01 0.40 0.00 47.14
Alat ini merupakan alternatif yang berguna untuk mencoba untuk membuat laporan berkala tentang aktivitas sistem dari top.
w
Perintah w menampilkan informasi tentang user yang saat ini sedang on di mesin, dan proses yang mereka gunakan.
Perintah yang dapat digunakan
w w username
Contoh keluaran
09:06:42 up 14:46, 3 users, load average: 1.04, 1.08, 1.05 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT onno tty7 Fri18 14:46m 11:55 0.28s gnome-session --session=ubuntu onno pts/1 :0 Fri18 1:08m 1.38s 1.38s bash onno pts/2 :0 06:05 0.00s 0.48s 25.80s gnome-terminal
uptime
Perintah uptime dapat digunakan untuk melihat berapa lama sistem telah berjalan, waktu sekarang di komputer, berapa user yang sedang log on, beban sistem 1, 5 dan 15 menit terakhir.
uptime
hasilnya kurang lebih
08:47:21 up 14:27, 3 users, load average: 1.16, 1.09, 1.07
Load akan berubah dari satu sistem ke sistem lain. Untuk sistem dengan 1 CPU maka load 1-3 cukup optimal. Untuk sebuah sistem SMP maka load 6-10 masih dapat di terima.
free
Perintah ini menampilkan jumlah memory yang digunakan secara fisik dan swap memory yang ada di sistem, juga buffer yang digunakan oleh kernel.
free
Contoh output
total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 2011972 1847148 164824 0 47088 592660 -/+ buffers/cache: 1207400 804572 Swap: 779148 162108 617040
iostat
Perintah iostat melaporkan statistik CPU dan input/output dari device, partisi maupun network file system (NFS)
iostat
Agar dapat jalan dengan baik kita perlu install
apt install sysstat
Contoh output
Linux 3.2.0-29-generic (openbts28) 03/23/2013 _x86_64_ (2 CPU)
avg-cpu: %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle
21.76 0.14 1.04 1.28 0.00 75.79
Device: tps kB_read/s kB_wrtn/s kB_read kB_wrtn
sda 4.41 56.67 52.68 3183588 2959436
sdb 4.44 28.00 43.68 1572868 2454036
mpstat
Perintah mpstat menampilkan aktifitas masing-masing processor yang tersedia. Processor 0 sebagai yang pertama. Untuk menampilkan rata-rata pengunakan CPU per processor, ketik:
mpstat -P ALL
Contoh output:
Linux 3.2.0-29-generic (openbts28) 03/23/2013 _x86_64_ (2 CPU) 10:04:53 AM CPU %usr %nice %sys %iowait %irq %soft %steal %guest %idle 10:04:53 AM all 22.02 0.14 1.03 1.27 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 75.52 10:04:53 AM 0 22.14 0.18 1.07 1.26 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.00 75.32 10:04:53 AM 1 21.89 0.09 1.00 1.28 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 75.72
mpstat merupakan bagian dari sysstat install menggunakan
sudo apt-get install sysstat
pmap
Perintah pmap melaporkan memory map dari sebuah proses. Gunakan perintah ini untuk melihat bottleneck di memory. Ketik
pmap -d PID
Untuk menampilkan informasi memory proses untuk PID # 15070, ketik:
pmap -d 15070
Contoh output:
15070: /usr/lib/libreoffice/program/soffice.bin --writer --splash-pipe=6 Address Kbytes Mode Offset Device Mapping 0000000000400000 4 r-x-- 0000000000000000 008:00002 soffice.bin 0000000000600000 4 r---- 0000000000000000 008:00002 soffice.bin 0000000000601000 4 rw--- 0000000000001000 008:00002 soffice.bin 0000000001d4d000 19612 rw--- 0000000000000000 000:00000 [ anon ] 00007fc830000000 140 rw--- 0000000000000000 000:00000 [ anon ] 00007fc830023000 65396 ----- 0000000000000000 000:00000 [ anon ] 00007fc834718000 32 r-x-- 0000000000000000 008:00002 libmcnttype.so 00007fc834720000 2044 ----- 0000000000008000 008:00002 libmcnttype.so 00007fc83491f000 4 r---- 0000000000007000 008:00002 libmcnttype.so 00007fc834920000 4 rw--- 0000000000008000 008:00002 libmcnttype.so 00007fc834921000 72 r-x-- 0000000000000000 008:00002 gnome-keyring-pkcs11.so 00007fc834933000 2044 ----- 0000000000012000 008:00002 gnome-keyring-pkcs11.so 00007fc834b32000 8 r---- 0000000000011000 008:00002 gnome-keyring-pkcs11.so 00007fc834b34000 4 rw--- 0000000000013000 008:00002 gnome-keyring-pkcs11.so ... ... 00007fc872ccd000 4 r-xs- 0000000000000000 008:00002 .execoooxQzg4m (deleted) 00007fc872cce000 4 rw-s- 0000000000000000 008:00002 .execoooxQzg4m (deleted) 00007fc872ccf000 4 rw--- 0000000000000000 000:00000 [ anon ] 00007fc872cd0000 12 r---- 0000000000000000 008:00002 user 00007fc872cd3000 4 r--s- 0000000000000000 008:00002 user 00007fc872cd4000 80 rw--- 0000000000000000 000:00000 [ anon ] 00007fc872ce8000 4 r---- 0000000000022000 008:00002 ld-2.15.so 00007fc872ce9000 8 rw--- 0000000000023000 008:00002 ld-2.15.so 00007fff36b4d000 132 rw--- 0000000000000000 000:00000 [ stack ] 00007fff36bff000 4 r-x-- 0000000000000000 000:00000 [ anon ] ffffffffff600000 4 r-x-- 0000000000000000 000:00000 [ anon ] mapped: 1105764K writeable/private: 97360K shared: 15184K
Kalimat terakhir sangat penting:
- mapped: 1105764K total memory yang di map ke file.
- writeable/private: 97360K jumlah alamat memory private.
- shared: 15184K jumlah alamat memory dari proses ini yang di sharing dengan proses yang lain.
netstat
Perintah netstat menampilkan informasi tentang sambungan jaringan, tabel routing, statistik interface, sambungan masquerade, dan keanggotaan multicast. Contoh penggunaannya:
netstat -nr
Contoh output:
Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.222 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0 169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 192.168.13.0 192.168.0.33 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
Melihat IP dan socket yang saling terhubung
netstat -an
Contoh output
Active Internet connections (servers and established) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:873 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:139 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:10000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:445 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:59669 173.194.38.149:443 ESTABLISHED tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:34229 69.171.235.16:80 ESTABLISHED tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:33922 69.171.235.16:80 ESTABLISHED tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:34049 69.171.235.16:80 ESTABLISHED tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:34252 69.171.235.16:80 ESTABLISHED tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:34097 69.171.235.16:80 ESTABLISHED tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:50100 192.168.0.7:9090 ESTABLISHED tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:38858 111.95.240.27:443 ESTABLISHED tcp 0 0 192.168.0.3:34076 69.171.235.16:80 ESTABLISHED
ss
Perintah ss digunakan untuk dump statistik socket. ss memungkinkan untuk melihat informasi yang mirip dengan netstat. Cara mengunakannya
ss
Contoh tampilan
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.3:55530 111.94.248.38:https ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.3:59669 173.194.38.149:https ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.3:34229 69.171.235.16:http ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.3:33922 69.171.235.16:http ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.3:34049 69.171.235.16:http ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.3:34252 69.171.235.16:http ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.3:34097 69.171.235.16:http ESTAB 0 0 192.168.0.3:50100 192.168.0.7:9090
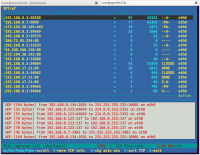
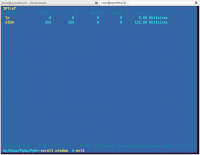
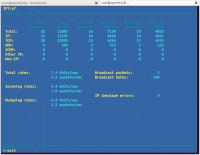
iptraf
Perintah iptraf adalah IP LAN monitor yang berwarna warni. iptraf menampilkan berbagai statistik jaringan termasuk TCP info, UDP count, informasi ICMP dan OSPF, info load Ethernet, statistik node, cek IP.
Instalasi iptraf menggunakan perintah
apt-get install iptraf
Menjalankan iptraf menggunakan perintah
iptraf
Hasilnya kira-kira
Referensi
- http://activedoc.opensuse.org/book/opensuse-system-analysis-and-tuning-guide
- http://activedoc.opensuse.org/book/opensuse-system-analysis-and-tuning-guide/part-ii-system-monitoring
- http://activedoc.opensuse.org/book/opensuse-system-analysis-and-tuning-guide/chapter-2-system-monitoring-utilities
Pranala Menarik
- Linux
- Ubuntu
- Sistem Operasi
- Linux: Instalasi Sistem Operasi
- Linux: Skema Partisi di Linux
- Kernel
- Compile Kernel
- Compile Kernel: Konfigurasi Kernel
- Kernel: Anatomi Kernel Source
- OS: Linux Kernel
- OS: Parameter Kernel Default
- OS: Kernel Scheduler
- OS: Complete Teori Tuning Kernel Scheduler
- OS: Complete Teori Tuning I/O Performance
- OS: Tuning Kernel Scheduler
- OS: Tuning Completely Fair Queueing CFQ I/O scheduler
- OS: Tuning Completely Fair scheduler CFS
- OS: Build in Monitoring Tool
- Linux Benchmarking
- OS: Benchmarking menggunakan UnixBench
- OS: Benchmarking menggunakan LLCBench
- OS: Mengerti System Call
- OS: Membuat Kernel Modul