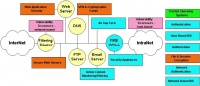
SECURITY: Cyber Security Technology Map (en)
Network security has become essential knowledge for those who want to seriously engage in Internet activities. Unfortunately, technology has evolved to such a complex degree that it demands network security professionals to learn extensively to fully understand the entire concept & technology of network security. To facilitate the learning process, it is advisable to pay close attention to the attached image containing a technology map of network security. A very good reference on this can be found at http://www.sans.org.
Generally, the topology of computer network consists of a public Internet network that spreads across the world and an Intranet network located internally in companies/institutions. Between InterNet and IntraNet, there is usually a De-Militarized Zone (DMZ) restricted by a Filtering Router towards the Internet, and a Firewall towards the IntraNet. In the De-Militarized Zone (DMZ), various servers are typically installed, such as, Mail Server, FTP Server, Web Server, and DNS Server.
Based on the network topology above, we can divide network security technology into four (4) major parts, namely:
Let's look at the technologies that are part of these four (4) sections, in general,
Penetration Testing, consists of:
- Active Content Monitoring / Filtering, usually placed on the mail server in the DMZ.
- Intrusion Detection - Host Based, usually placed on servers in both IntraNet and DMZ.
- Firewall, acts as an intermediary between IntraNet, DMZ, and InterNet.
- Intrusion Detection - Network Based, usually used to monitor IntraNet.
- Authorization, run in the IntraNet.
- Air Gap Technology, operated in the De-Militarized Zone (DMZ).
- Network Authentication, operated in the IntraNet.
- Security Appliances, usually in the form of hardware Firewall.
- Security Services: Penetration Testing, external companies providing services to us.
- Authentication, operated in the IntraNet.
Certificate Authority / PKI, supports other technologies & can be operated on servers in the IntraNet, consisting of:
- Certificate Authority, in both IntraNet and InterNet.
- File & Session Encryption, operated in the IntraNet.
- VPN & Cryptographic Communications, starts in the De-Militerized Zone and is used to penetrate the Internet to another IntraNet.
- Secure Web Servers, operated in the De-Militarized Zone (DMZ).
- Single Sign On, on servers.
- Web Application Security, on Web servers.
Vulnerability Testing, usually conducted by auditors or security managers, includes:
- Vulnerability Scanners - Host Based, operated on IntraNet servers.
- Real-Time Security Awareness, Response & Threat Management, used by security managers.
- Vulnerability Scanners - Network Based, operated on filtering routers directly connected to the InterNet.
Managed Security Services, part of the management (non-technical) support for network security. Issues include:
- Enterprise Security Policy Implementation.
- Managed Security Services.
- Enterprise Security Administration.
- Security Services: Policy Development.
- Trusted Operating Systems, installed on all computers.
- Anti D.D.O.D Tools.
Next, let's look at various concepts with more detailed explanations.
Penetration Testing
- Active Content Monitoring / Filtering. When you connect to the Internet, you risk computer viruses, malicious java / Active-X scripts, etc. This tool will check all content entering the network / computer, continuously updating its library.
- Intrusion Detection - Host Based. Host-based intrusion detection will monitor log files. It will respond with alarms or counter-attacks if a user attempts to access unauthorized data, files, or services.
- Firewall. A Firewall is a system or group of systems that enforce access control policy between two networks.
- Intrusion Detection - Network Based. Network-based intrusion detection will monitor the network and will respond with alarms when it identifies bad traffic patterns, such as scanning, denial of service attempts, and other attacks.
- Authorization. Authentication asks "who are you?". Authorization asks "do you have the right?". With authorization mechanisms, every user who wants to access resources must apply to the authorization server to obtain permission.
- Air Gap Technology. This type of hardware/software allows real-time data transfer between the Internet and the back-end without opening a hole in the firewall. Sometimes Air Gap solutions require physical disconnection from the external network. Air Gap disconnects all network protocols, restricts access to data at the application layer, and performs content analysis.
- Network Authentication. This tool uses several approaches to improve the system's ability to distinguish between those who are authorized and those who are not.
- Security Appliances. A combination of hardware/software that provides limited services, such as firewalls, network load management, etc. Because its operating system is very limited, it is easier to manage and not a target for hacker attacks like general-purpose UNIX or Windows NT.
- Security Services: Penetration Testing. Consulting organizations that simulate hacker attacks in the real world and social engineering attacks. They usually provide advice on how to improve defenses. They typically use network-based vulnerability scanning tools.
- Authentication. Authentication is a process that determines something or someone is who or what. The simplest form of authentication process is a logon password, unfortunately very vulnerable to theft. Another way to address this is by using tokens that allow a stricter authentication process.
Certificate Authority / PKI
- Certificate Authority. A Certificate Authority (CA) is an organization that issues and manages security credentials and public keys for encryption & decryption of messages. Certificates managed include public keys that strengthen authentication, privacy & non-repudiation.
- File & Session Encryption. Encryption is a process where data is changed in form so that it is difficult to open and understand by people who do not have the authority for it. Advanced computer algorithms are used in the encrypt & decrypt process when needed.
- VPN & Cryptographic Communications. Virtual Private Network (VPN) allows secure communication over the public Internet network. This is very cost-effective for companies with mobile workers or company branches, allowing communication without using expensive private telephone networks.
Secure Web Servers. A tool that allows us to provide web services in an engineered environment so that security holes are minimal.
- Single Sign On. A software package that helps users access several computers without having to remember many passwords. Single Sign On essentially does not change the underlying processes, but hides the differences through an additional layer of software.
- Web Application Security. Web application security will protect web applications and existing resources from threats on the Internet, such as, stealing company assets, credit card theft, defacing sites, etc. This is done by detecting/blocking hacking techniques in this area.
Vulnerability Testing
- Vulnerability Scanners - Host Based. Tool to check the system settings to determine whether they are appropriate/consistent with the company's security policy. This tool is commonly used by auditors.
- Real-Time Security Awareness, Response & Threat Management. RTSA allows a security manager to see what is happening in the company that uses many tools from multiple vendors in real-time through a console. RTSA helps reduce the number of personnel needed to monitor many devices.
- Vulnerability Scanners - Network Based. Software that can simulate the behavior of attackers and study about 600 possible weaknesses in the system being attacked.
Managed Security Services
- Enterprise Security Policy Implementation. EPSI allows security managers to automate every security step from a central console, starting from creating, editing, approving, publishing, distribution, education, compliance, reporting, and maintenance. This tool will enforce socialization, check employee understanding, record incidents, and measure compliance, which ultimately will help manage IT risks without burdening limited staff.
- Managed Security Services. Vendors offering managed security services assume that they will take over some percentage of the work as outsourced. In this way, administrators can do other work.
- Enterprise Security Administration. This tool administers enterprise-level security, ensuring that all users in an enterprise receive the same rights and obligations. This system is especially very useful for providing access for new users, and importantly, eliminating all access for employees who have left.
- Security Services: Policy Development. Consultants who assist in quickly developing security policies. They generally already have templates so that security policies can be implemented quickly, such as good email use, extranet to PKI.
- Trusted Operating Systems. Because all security mechanisms are highly dependent on the operating system, trusted O/S technology provides the only mechanism on O/S to withstand attacks.
- Anti D.D.O.D Tools. Anti Ddos tools will identify irregular usage on the network. If irregularities occur, the tool will attempt to check the legitimacy of access and recommend some preventive steps.