Difference between revisions of "Pola radiasi"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) (New page: In the field of antenna design the term ''''''radiation pattern'''''' most commonly refers to the ''directional'' (angular) dependence of radiation from the antenna or ...) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | In the field of [[Antenna (radio)|antenna]] design the term ''''''radiation pattern'''''' most commonly refers to the ''directional'' (angular) dependence of radiation from the antenna or other source (synonyms: '''antenna pattern''', '''far-field pattern'''). | + | [[Image:Radiation-patterns.jpeg|right|200px|thumb|Radiation Patterns]] |
| + | In the field of [[Antenna (radio)|antenna]] design the term ''''''[[radiation pattern]]'''''' most commonly refers to the ''directional'' (angular) dependence of radiation from the antenna or other source (synonyms: '''antenna pattern''', '''far-field pattern'''). | ||
| − | Particularly in the fields of [[fiber optics]], [[laser]]s, and [[integrated optics]], the term radiation pattern, or '''near-field radiation pattern''', may also be used as a synonym for the '''near-field pattern''' or '''Fresnel pattern'''. This refers to the ''positional'' dependence of the electromagnetic field in the [[near-field|near-field, or Fresnel region]] of the source. The near-field pattern is most commonly defined over a plane placed in front of the source, or over a cylindrical or spherical surface enclosing it. | + | Particularly in the fields of [[fiber optics]], [[laser]]s, and [[integrated optics]], the term radiation pattern, or '''near-field radiation pattern''', may also be used as a synonym for the '''near-field pattern''' or '''Fresnel pattern'''. This refers to the ''positional'' dependence of the [[electromagnetic field]] in the [[near-field|near-field, or Fresnel region]] of the source. The near-field pattern is most commonly defined over a plane placed in front of the source, or over a cylindrical or spherical surface enclosing it. |
The far-field pattern of an antenna may be determined experimentally at an [[antenna measurement|antenna range]], or alternatively, the near-field pattern may be found using a '''[[Electromagnetic near-field scanner|near-field scanner]]''', and the radiation pattern deduced from it by computation. | The far-field pattern of an antenna may be determined experimentally at an [[antenna measurement|antenna range]], or alternatively, the near-field pattern may be found using a '''[[Electromagnetic near-field scanner|near-field scanner]]''', and the radiation pattern deduced from it by computation. | ||
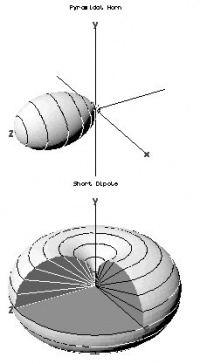
The far field radiation pattern may be represented graphically as a plot of one of a number of related variables, including; the field strength at a constant (large) radius (an '''amplitude pattern''' or '''field pattern'''), the power per unit solid angle ('''power pattern''') and the gain or [[directive gain]]. Very often, only the relative amplitude is plotted, normalized either to the amplitude on the antenna [[boresight]], or to the total radiated power. The plotted quantity may be shown on a linear scale, or in [[Decibel|dB]]. The plot is typically represented as a three dimensional graph (as at right), or as separate graphs in the [[vertical plane]] and [[horizontal plane]]. | The far field radiation pattern may be represented graphically as a plot of one of a number of related variables, including; the field strength at a constant (large) radius (an '''amplitude pattern''' or '''field pattern'''), the power per unit solid angle ('''power pattern''') and the gain or [[directive gain]]. Very often, only the relative amplitude is plotted, normalized either to the amplitude on the antenna [[boresight]], or to the total radiated power. The plotted quantity may be shown on a linear scale, or in [[Decibel|dB]]. The plot is typically represented as a three dimensional graph (as at right), or as separate graphs in the [[vertical plane]] and [[horizontal plane]]. | ||
Latest revision as of 07:10, 27 January 2010
In the field of antenna design the term 'radiation pattern' most commonly refers to the directional (angular) dependence of radiation from the antenna or other source (synonyms: antenna pattern, far-field pattern).
Particularly in the fields of fiber optics, lasers, and integrated optics, the term radiation pattern, or near-field radiation pattern, may also be used as a synonym for the near-field pattern or Fresnel pattern. This refers to the positional dependence of the electromagnetic field in the near-field, or Fresnel region of the source. The near-field pattern is most commonly defined over a plane placed in front of the source, or over a cylindrical or spherical surface enclosing it.
The far-field pattern of an antenna may be determined experimentally at an antenna range, or alternatively, the near-field pattern may be found using a near-field scanner, and the radiation pattern deduced from it by computation.
The far field radiation pattern may be represented graphically as a plot of one of a number of related variables, including; the field strength at a constant (large) radius (an amplitude pattern or field pattern), the power per unit solid angle (power pattern) and the gain or directive gain. Very often, only the relative amplitude is plotted, normalized either to the amplitude on the antenna boresight, or to the total radiated power. The plotted quantity may be shown on a linear scale, or in dB. The plot is typically represented as a three dimensional graph (as at right), or as separate graphs in the vertical plane and horizontal plane.