Difference between revisions of "Orange: k-Means"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) (→Contoh) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Sumber: https://docs.biolab.si//3/visual-programming/widgets/unsupervised/kmeans.html | Sumber: https://docs.biolab.si//3/visual-programming/widgets/unsupervised/kmeans.html | ||
| − | + | Widget k-Means mengelompokan item / data menggunakan algoritma k-Means clustering. | |
| − | + | ==Input== | |
| − | + | Data: input dataset | |
| − | + | ==Output== | |
| − | + | Data: dataset with cluster index as a class attribute | |
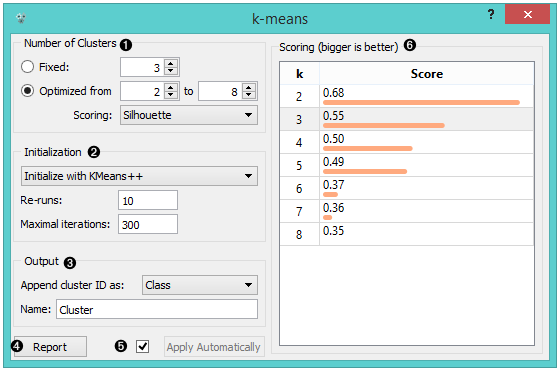
| − | + | Widget k-Means menerapkan algoritma k-Means clustering ke data dan mengeluarkan dataset baru di mana indeks cluster digunakan sebagai atribut class. Atribut class yang original, jika ada, dipindahkan ke atribut meta. Skor hasil pengelompokan untuk berbagai k juga ditampilkan di widget k-Means. | |
| − | [[File:KMeans-stamped.png|center| | + | [[File:KMeans-stamped.png|center|600px|thumb]] |
| − | + | * Select the number of clusters. | |
| − | + | ** Fixed: algorithm clusters data in a specified number of clusters. | |
| − | + | ** Optimized: widget shows clustering scores for the selected cluster range: | |
| − | + | *** Silhouette (contrasts average distance to elements in the same cluster with the average distance to elements in other clusters) | |
| − | + | *** Inter-cluster distance (measures distances between clusters,normally between centroids) | |
| − | + | *** Distance to centroids (measures distances to the arithmetic means of clusters) | |
| − | + | * Select the initialization method (the way the algorithm begins clustering): | |
| − | + | ** k-Means++ (first center is selected randomly, subsequent are chosen from the remaining points with probability proportioned to squared distance from the closest center) | |
| − | + | ** Random initialization (clusters are assigned randomly at first and then updated with further iterations) Re-runs (how many times the algorithm is run from random initial positions; the result with the lowest within-cluster sum of squares will be used) and maximal iterations (the maximum number of iterations within each algorithm run) can be set manually. | |
| − | + | * The widget outputs a new dataset with appended cluster information. Select how to append cluster information (as class, feature or meta attribute) and name the column. | |
| − | + | * If Apply Automatically is ticked, the widget will commit changes automatically. Alternatively, click Apply. | |
| − | + | * Produce a report. | |
| − | + | * Check scores of clustering results for various k. | |
==Contoh== | ==Contoh== | ||
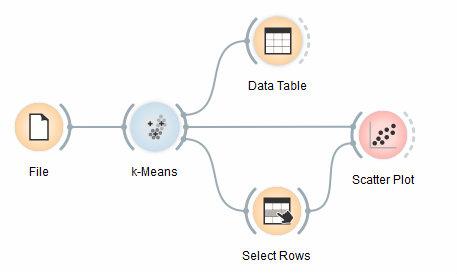
| − | + | Kita akan mengexplorasi Widget k-Means melalui schema / workflow berikut. | |
| − | [[File:K-MeansClustering-Schema.png.jpeg|center| | + | [[File:K-MeansClustering-Schema.png.jpeg|center|600px|thumb]] |
| − | + | Pertama, kita memuat dataset Iris, membaginya menjadi tiga cluster dan menampilkannya di widget Data Table, di mana kita bisa mengamati instance mana yang masuk ke cluster mana. Bagian yang menarik adalah Widget Scatter Plot dan Widget Select Rows. | |
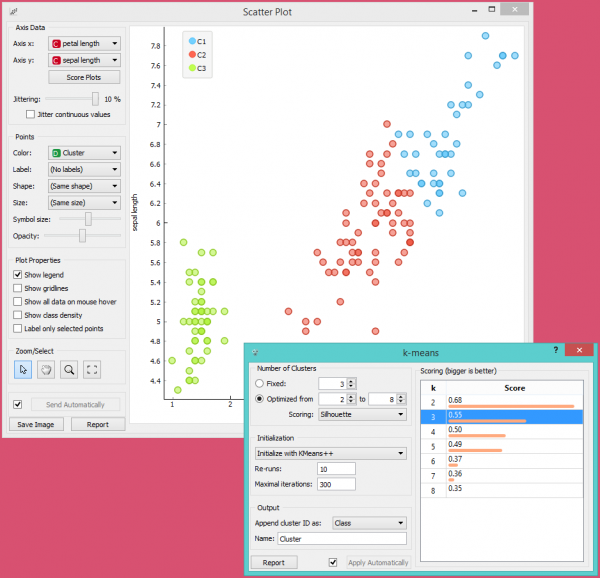
| − | + | Karena Widget k-Means menambahkan cluster index sebagai atribut class, Widget Scatter Plot akan mewarnai titik-titik sesuai dengan kelompoknya. | |
| − | [[File:KMeans-Scatterplot.png|center| | + | [[File:KMeans-Scatterplot.png|center|600px|thumb]] |
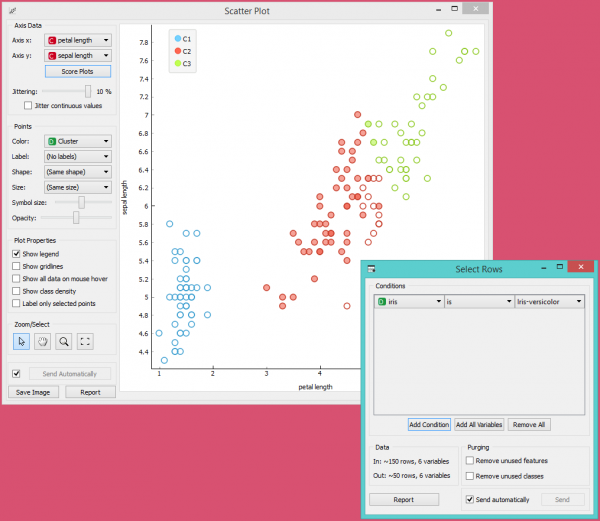
| − | + | Yang kita akan benar-benar tertarik adalah seberapa baik cluster yang dilakukan oleh (unsupervised) clustering algorithm cocok dengan class aktual dalam data. Oleh karena itu, kita menggunakan widget Select Rows, di mana kami dapat memilih class-class individual dan menandai titik-titik terkait di widget Scatter Plot. Kecocokan yang sempurna terjadi pada setosa, dan cukup bagus untuk dua class lainnya. | |
| − | [[File:K-MeansClustering-Example.png|center| | + | [[File:K-MeansClustering-Example.png|center|600px|thumb]] |
| − | + | Kita mungkin telah memperhatikan bahwa kita membiarkan Remove unused values/attributes dan Remove unused classes di widget Select Rows tidak dicentang. Ini penting: jika widget k-Means memodifikasi atribut, widget k-Means menampilkan daftar instance yang dimodifikasi dan widget Scatter Plot jadi tidak dapat membandingkannya dengan data original. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Mungkin cara yang lebih sederhana untuk menguji kecocokan antara cluster dan class original adalah dengan menggunakan widget Distributions. | ||
| + | [[File:K-MeansClustering-Example2.png|center|600px|thumb]] | ||
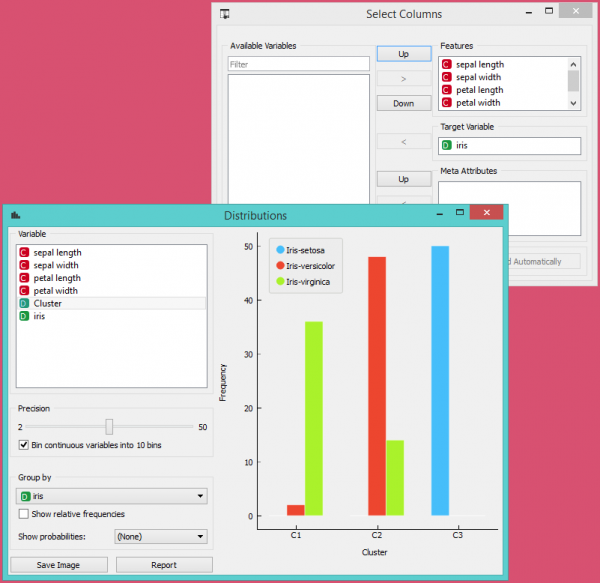
| + | Satu-satunya masalah (kecil) di sini adalah bahwa widget Scatter Plot hanya memvisualisasikan atribut normal (dan bukan meta). Kita menyelesaikan masalah ini dengan menggunakan widget Select Columns: kita mengembalikan class Iris original sebagai class dan menempatkan cluster index sebagai atribut. | ||
| + | Kecocokan yang sempurna untuk setosa: semua contoh setosa berada di cluster ketiga (biru). 48 versicolors berada di cluster kedua (merah), sedangkan dua di yang pertama. Untuk virginica, 36 berada di kelompok pertama dan 14 di kelompok kedua. | ||
==Referensi== | ==Referensi== | ||
Latest revision as of 09:56, 14 April 2020
Sumber: https://docs.biolab.si//3/visual-programming/widgets/unsupervised/kmeans.html
Widget k-Means mengelompokan item / data menggunakan algoritma k-Means clustering.
Input
Data: input dataset
Output
Data: dataset with cluster index as a class attribute
Widget k-Means menerapkan algoritma k-Means clustering ke data dan mengeluarkan dataset baru di mana indeks cluster digunakan sebagai atribut class. Atribut class yang original, jika ada, dipindahkan ke atribut meta. Skor hasil pengelompokan untuk berbagai k juga ditampilkan di widget k-Means.
- Select the number of clusters.
- Fixed: algorithm clusters data in a specified number of clusters.
- Optimized: widget shows clustering scores for the selected cluster range:
- Silhouette (contrasts average distance to elements in the same cluster with the average distance to elements in other clusters)
- Inter-cluster distance (measures distances between clusters,normally between centroids)
- Distance to centroids (measures distances to the arithmetic means of clusters)
- Select the initialization method (the way the algorithm begins clustering):
- k-Means++ (first center is selected randomly, subsequent are chosen from the remaining points with probability proportioned to squared distance from the closest center)
- Random initialization (clusters are assigned randomly at first and then updated with further iterations) Re-runs (how many times the algorithm is run from random initial positions; the result with the lowest within-cluster sum of squares will be used) and maximal iterations (the maximum number of iterations within each algorithm run) can be set manually.
- The widget outputs a new dataset with appended cluster information. Select how to append cluster information (as class, feature or meta attribute) and name the column.
- If Apply Automatically is ticked, the widget will commit changes automatically. Alternatively, click Apply.
- Produce a report.
- Check scores of clustering results for various k.
Contoh
Kita akan mengexplorasi Widget k-Means melalui schema / workflow berikut.
Pertama, kita memuat dataset Iris, membaginya menjadi tiga cluster dan menampilkannya di widget Data Table, di mana kita bisa mengamati instance mana yang masuk ke cluster mana. Bagian yang menarik adalah Widget Scatter Plot dan Widget Select Rows.
Karena Widget k-Means menambahkan cluster index sebagai atribut class, Widget Scatter Plot akan mewarnai titik-titik sesuai dengan kelompoknya.
Yang kita akan benar-benar tertarik adalah seberapa baik cluster yang dilakukan oleh (unsupervised) clustering algorithm cocok dengan class aktual dalam data. Oleh karena itu, kita menggunakan widget Select Rows, di mana kami dapat memilih class-class individual dan menandai titik-titik terkait di widget Scatter Plot. Kecocokan yang sempurna terjadi pada setosa, dan cukup bagus untuk dua class lainnya.
Kita mungkin telah memperhatikan bahwa kita membiarkan Remove unused values/attributes dan Remove unused classes di widget Select Rows tidak dicentang. Ini penting: jika widget k-Means memodifikasi atribut, widget k-Means menampilkan daftar instance yang dimodifikasi dan widget Scatter Plot jadi tidak dapat membandingkannya dengan data original.
Mungkin cara yang lebih sederhana untuk menguji kecocokan antara cluster dan class original adalah dengan menggunakan widget Distributions.
Satu-satunya masalah (kecil) di sini adalah bahwa widget Scatter Plot hanya memvisualisasikan atribut normal (dan bukan meta). Kita menyelesaikan masalah ini dengan menggunakan widget Select Columns: kita mengembalikan class Iris original sebagai class dan menempatkan cluster index sebagai atribut.
Kecocokan yang sempurna untuk setosa: semua contoh setosa berada di cluster ketiga (biru). 48 versicolors berada di cluster kedua (merah), sedangkan dua di yang pertama. Untuk virginica, 36 berada di kelompok pertama dan 14 di kelompok kedua.