Difference between revisions of "Orange: Rank"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| − | + | Pemeringkatan atribut dalam klasifikasi atau regresi data. | |
==Input== | ==Input== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
Reduced Data: dataset with selected attributes | Reduced Data: dataset with selected attributes | ||
| − | + | Widget Rank mempertimbangkan kumpulan data berlabel kelas (klasifikasi atau regresi) dan menilai atribut sesuai dengan korelasinya dengan kelas. Peringkat juga menerima model untuk penilaian, seperti linear regression, logistic regression, random forest, SGD, dll. | |
[[File:Rank-stamped.png|center|200px|thumb]] | [[File:Rank-stamped.png|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
* FCBF (Fast Correlation Based Filter): entropy-based measure, which also identifies redundancy due to pairwise correlations between features | * FCBF (Fast Correlation Based Filter): entropy-based measure, which also identifies redundancy due to pairwise correlations between features | ||
| − | + | Selain itu, kita dapat menghubungkan learner tertentu yang memungkinkan penilaian feature berdasarkan seberapa penting mereka dalam model yang dibuat learner (mis. Linear Regression / Logistic Regression, Random Forest, SGD). | |
==Example: Attribute Ranking and Selection== | ==Example: Attribute Ranking and Selection== | ||
| − | + | Di bawah ini, kita telah menggunakan Rank widget segera setelah File widget untuk mengurangi set atribut data dan hanya menyertakan yang paling informatif: | |
[[File:Rank-Select-Schema.png|center|200px|thumb]] | [[File:Rank-Select-Schema.png|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
| − | + | Perhatikan bagaimana widget menghasilkan set data yang hanya menyertakan atribut dengan skor terbaik: | |
| − | |||
[[File:Rank-Select-Widgets.png|center|200px|thumb]] | [[File:Rank-Select-Widgets.png|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
Revision as of 10:05, 31 January 2020
Sumber: https://docs.biolab.si//3/visual-programming/widgets/data/rank.html
Pemeringkatan atribut dalam klasifikasi atau regresi data.
Input
Data: input dataset Scorer: models for feature scoring
Output
Reduced Data: dataset with selected attributes
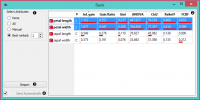
Widget Rank mempertimbangkan kumpulan data berlabel kelas (klasifikasi atau regresi) dan menilai atribut sesuai dengan korelasinya dengan kelas. Peringkat juga menerima model untuk penilaian, seperti linear regression, logistic regression, random forest, SGD, dll.
- Select attributes from the data table.
- Data table with attributes (rows) and their scores by different scoring methods (columns)
- Produce a report.
- If ‘Send Automatically’ is ticked, the widget automatically communicates changes to other widgets.
Scoring method
Information Gain: the expected amount of information (reduction of entropy)
- Gain Ratio: a ratio of the information gain and the attribute’s intrinsic information, which reduces the bias towards multivalued features that occurs in information gain
- Gini: the inequality among values of a frequency distribution
- ANOVA: the difference between average vaules of the feature in different classes
- Chi2: dependence between the feature and the class as measure by the chi-square statistic
- ReliefF: the ability of an attribute to distinguish between classes on similar data instances
- FCBF (Fast Correlation Based Filter): entropy-based measure, which also identifies redundancy due to pairwise correlations between features
Selain itu, kita dapat menghubungkan learner tertentu yang memungkinkan penilaian feature berdasarkan seberapa penting mereka dalam model yang dibuat learner (mis. Linear Regression / Logistic Regression, Random Forest, SGD).
Example: Attribute Ranking and Selection
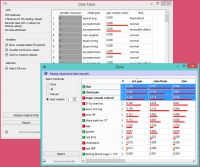
Di bawah ini, kita telah menggunakan Rank widget segera setelah File widget untuk mengurangi set atribut data dan hanya menyertakan yang paling informatif:
Perhatikan bagaimana widget menghasilkan set data yang hanya menyertakan atribut dengan skor terbaik:
Example: Feature Subset Selection for Machine Learning
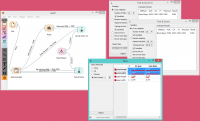
What follows is a bit more complicated example. In the workflow below, we first split the data into a training set and a test set. In the upper branch, the training data passes through the Rank widget to select the most informative attributes, while in the lower branch there is no feature selection. Both feature selected and original datasets are passed to their own Test & Score widgets, which develop a Naive Bayes classifier and score it on a test set.
For datasets with many features, a naive Bayesian classifier feature selection, as shown above, would often yield a better predictive accuracy.