Difference between revisions of "Orange: Linear Projection"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| − | + | Metode proyeksi linier dengan analisis data eksploratif. | |
==Input== | ==Input== | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
Components: projection vectors | Components: projection vectors | ||
| − | + | Widget ini menampilkan proyeksi linear class-labeled data. Ini mendukung berbagai jenis proyeksi seperti circular, linear discriminant analysis, principal component analysis, dan custom projection. | |
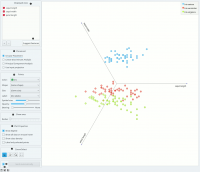
| − | + | Pertimbangkan, sebagai permulaan, proyeksi dataset Iris yang ditunjukkan di bawah ini. Perhatikan bahwa lebar sepal dan panjang sepal yang sudah memisahkan Iris setosa dari dua lainnya, sedangkan panjang petal adalah atribut terbaik memisahkan Iris versicolor dari Iris virginica. | |
[[File:Linear-projection-stamped.png|center|200px|thumb]] | [[File:Linear-projection-stamped.png|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
Revision as of 12:02, 3 February 2020
Sumber: https://docs.biolab.si//3/visual-programming/widgets/visualize/linearprojection.html
Metode proyeksi linier dengan analisis data eksploratif.
Input
Data: input dataset Data Subset: subset of instances Projection: custom projection vectors
Output
Selected Data: instances selected from the plot Data: data with an additional column showing whether a point is selected Components: projection vectors
Widget ini menampilkan proyeksi linear class-labeled data. Ini mendukung berbagai jenis proyeksi seperti circular, linear discriminant analysis, principal component analysis, dan custom projection.
Pertimbangkan, sebagai permulaan, proyeksi dataset Iris yang ditunjukkan di bawah ini. Perhatikan bahwa lebar sepal dan panjang sepal yang sudah memisahkan Iris setosa dari dua lainnya, sedangkan panjang petal adalah atribut terbaik memisahkan Iris versicolor dari Iris virginica.
- Axes in the projection that are displayed and other available axes.
- Optimize your projection by using Suggest Features. This feature scores attributes by average classification accuracy and returns the top scoring attributes with a simultaneous visualization update.
- Choose the type of projection.
- Axes inside a circle are hidden. Circle radius can be be changed using a slider.
- Adjust plot properties:
- Set jittering to prevent the dots from overlapping (especially for discrete attributes).
- Show legend displays a legend on the right. Click and drag the legend to move it.
- Show class density colors the graph by class (see the screenshot below).
- Label only selected points allows you to select individual data instances and label them.
- Select, zoom, pan and zoom to fit are the options for exploring the graph. Manual selection of data instances works as an angular/square selection tool. Double click to move the projection. Scroll in or out for zoom.
- If Send automatically is ticked, changes are communicated automatically. Alternatively, press Send.
- Save Image saves the created image to your computer in a .svg or .png format. Produce a report.
Contoh
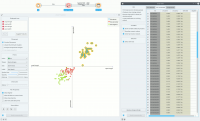
The Linear Projection widget works just like other visualization widgets. Below, we connected it to the File widget to see the set projected on a 2-D plane. Then we selected the data for further analysis and connected it to the Data Table widget to see the details of the selected subset.
Referensi
Koren Y., Carmel L. (2003). Visualization of labeled data using linear transformations. In Proceedings of IEEE Information Visualization 2003, (InfoVis’03). Available here.
Boulesteix A.-L., Strimmer K. (2006). Partial least squares: a versatile tool for the analysis of high-dimensional genomic data. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 8(1), 32-44. Abstract here.