Difference between revisions of "Orange: Lift Curve"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| − | + | Mengukur performance sebuah classifier yang dipilih terhadap random classifier. | |
==Input== | ==Input== | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Evaluation Results: results of testing classification algorithms | Evaluation Results: results of testing classification algorithms | ||
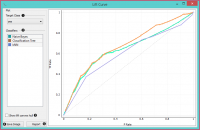
| − | + | Lift curve menunjukkan hubungan antara jumlah instance yang diprediksi positif dan yang memang positif dan dengan demikian mengukur kinerja classifier yang dipilih terhadap classifier random. Graph dibangun dengan jumlah kasus kumulatif (dalam urutan probabilitas menurun) pada sumbu x dan jumlah kumulatif true positif pada sumbu y. Lift Curve sering digunakan dalam pengelompokan populasi, misalnya, memplot jumlah pelanggan yang merespons terhadap jumlah semua pelanggan yang dihubungi. Kita juga dapat menentukan optimal classifier dan threshold-nya dari graph. | |
[[File:LiftCurve-stamped.png|center|200px|thumb]] | [[File:LiftCurve-stamped.png|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
Revision as of 05:01, 7 March 2020
Sumber: https://docs.biolab.si//3/visual-programming/widgets/evaluate/liftcurve.html
Mengukur performance sebuah classifier yang dipilih terhadap random classifier.
Input
Evaluation Results: results of testing classification algorithms
Lift curve menunjukkan hubungan antara jumlah instance yang diprediksi positif dan yang memang positif dan dengan demikian mengukur kinerja classifier yang dipilih terhadap classifier random. Graph dibangun dengan jumlah kasus kumulatif (dalam urutan probabilitas menurun) pada sumbu x dan jumlah kumulatif true positif pada sumbu y. Lift Curve sering digunakan dalam pengelompokan populasi, misalnya, memplot jumlah pelanggan yang merespons terhadap jumlah semua pelanggan yang dihubungi. Kita juga dapat menentukan optimal classifier dan threshold-nya dari graph.
- Choose the desired Target class. The default class is chosen alphabetically.
- If test results contain more than one classifier, the user can choose which curves she or he wants to see plotted. Click on a classifier to select or deselect the curve.
- Show lift convex hull plots a convex hull over lift curves for all classifiers (yellow curve). The curve shows the optimal classifier (or combination thereof) for each desired TP/P rate.
- Press Save Image if you want to save the created image to your computer in a .svg or .png format.
- Produce a report.
- 2-D pane with P rate (population) as x-axis and TP rate (true positives) as a y-axis. The diagonal line represents the behavior of a random classifier. Click and drag to move the pane and scroll in or out to zoom. Click on the “A” sign at the bottom left corner to realign the pane.
Note! The perfect classifier would have a steep slope towards 1 until all classes are guessed correctly and then run straight along 1 on y-axis to (1,1).
Contoh
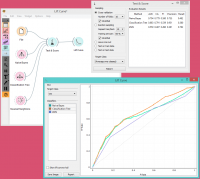
At the moment, the only widget which gives the right type of the signal needed by the Lift Curve is Test & Score.
In the example below, we try to see the prediction quality for the class ‘survived’ on the Titanic dataset. We compared three different classifiers in the Test Learners widget and sent them to Lift Curve to see their performance against a random model. We see the Tree classifier is the best out of the three, since it best aligns with lift convex hull. We also see that its performance is the best for the first 30% of the population (in order of descending probability), which we can set as the threshold for optimal classification.
Referensi
Handouts of the University of Notre Dame on Data Mining - Lift Curve. Available here.
Referensi