Difference between revisions of "Orange: Continuize"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
* Tentukan perlakuan variabel kategorikal non-biner. | * Tentukan perlakuan variabel kategorikal non-biner. | ||
| − | * | + | * Contoh di bagian ini akan menganggap bahwa kita memiliki status atribut diskrit dengan nilai rendah, sedang dan tinggi, yang terdaftar dalam urutan seperti itu. Pilihan untuk transformasi artibut tersebut adalah: |
| − | ** | + | ** Nilai pertama sebagai basis: variabel kategori bernilai-N akan ditransformasikan menjadi variabel numerik N-1, masing-masing berfungsi sebagai indikator untuk salah satu nilai original kecuali untuk nilai dasar. Nilai dasar adalah nilai pertama dalam daftar. Secara default, nilai-nilai tersebut disusun berdasarkan abjad; urutan mereka dapat diubah di Edit Domain. |
| − | ** | + | ** Dalam kasus di atas, status variabel bernilai tiga diubah menjadi dua variabel numerik, status = tengah dengan nilai 0 atau 1 yang menunjukkan apakah variabel original memiliki nilai tengah pada contoh tertentu, dan demikian pula, status = tinggi. |
| − | ** | + | ** Nilai yang paling sering sebagai basis: mirip dengan yang di atas, kecuali bahwa nilai yang paling sering digunakan sebagai basis. Jadi, jika nilai yang paling sering dalam contoh di atas adalah menengah, maka tengah dianggap sebagai basis dan dua variabel yang baru dibangun adalah status = rendah dan status = tinggi. |
| − | ** | + | ** Satu atribut per nilai: opsi ini untuk membuat satu variabel numerik per setiap nilai variabel original. Dalam kasus di atas, kita akan mendapatkan variabel status = rendah, status = menengah dan status = tinggi. |
| − | ** | + | ** Abaikan atribut multinomial: menghapus variabel kategori non-biner dari data. |
| − | ** | + | ** Perlakukan sebagai ordinal: mengubah variabel menjadi variabel numerik tunggal yang menyebutkan nilai orginal. Dalam kasus di atas, variabel baru akan memiliki nilai 0 untuk rendah, 1 untuk menengah dan 2 untuk tinggi. Sekali lagi perhatikan bahwa urutan nilai dapat diatur dalam Edit Domain. |
| − | ** | + | ** Membagi dengan jumlah nilai: sama seperti di atas, kecuali bahwa nilai-nilai dinormalisasi ke dalam rentang 0-1. Dalam contoh kami, nilai-nilai variabel baru adalah 0, 0,5 dan 1. |
* Define the treatment of continuous attributes. Besised the option to Leave them as they are, we can Normalize by span, which will subtract the lowest value found in the data and divide by the span, so all values will fit into [0, 1]. Option Normalize by standard deviation subtracts the average and divides by the standard deviation. | * Define the treatment of continuous attributes. Besised the option to Leave them as they are, we can Normalize by span, which will subtract the lowest value found in the data and divide by the span, so all values will fit into [0, 1]. Option Normalize by standard deviation subtracts the average and divides by the standard deviation. | ||
* Define the treatment of class attributes (outcomes, targets). Besides leaving it as it is, the available options mirror those for multinomial attributes, except for those that would split the outcome into multiple outcome variables. | * Define the treatment of class attributes (outcomes, targets). Besides leaving it as it is, the available options mirror those for multinomial attributes, except for those that would split the outcome into multiple outcome variables. | ||
Revision as of 09:28, 27 January 2020
Sumber: https://docs.biolab.si//3/visual-programming/widgets/data/continuize.html
Mengubah diskrit variable (attribute) menjadi numeric (“continuous”) dummy variable.
Input
Data: input data set
Output
Data: transformed data set
Continuize widget menerima set data dalam input dan output set data yang sama di mana variabel diskrit (termasuk variabel biner) diganti dengan continuous.
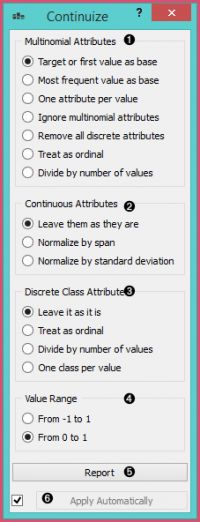
- Tentukan perlakuan variabel kategorikal non-biner.
- Contoh di bagian ini akan menganggap bahwa kita memiliki status atribut diskrit dengan nilai rendah, sedang dan tinggi, yang terdaftar dalam urutan seperti itu. Pilihan untuk transformasi artibut tersebut adalah:
- Nilai pertama sebagai basis: variabel kategori bernilai-N akan ditransformasikan menjadi variabel numerik N-1, masing-masing berfungsi sebagai indikator untuk salah satu nilai original kecuali untuk nilai dasar. Nilai dasar adalah nilai pertama dalam daftar. Secara default, nilai-nilai tersebut disusun berdasarkan abjad; urutan mereka dapat diubah di Edit Domain.
- Dalam kasus di atas, status variabel bernilai tiga diubah menjadi dua variabel numerik, status = tengah dengan nilai 0 atau 1 yang menunjukkan apakah variabel original memiliki nilai tengah pada contoh tertentu, dan demikian pula, status = tinggi.
- Nilai yang paling sering sebagai basis: mirip dengan yang di atas, kecuali bahwa nilai yang paling sering digunakan sebagai basis. Jadi, jika nilai yang paling sering dalam contoh di atas adalah menengah, maka tengah dianggap sebagai basis dan dua variabel yang baru dibangun adalah status = rendah dan status = tinggi.
- Satu atribut per nilai: opsi ini untuk membuat satu variabel numerik per setiap nilai variabel original. Dalam kasus di atas, kita akan mendapatkan variabel status = rendah, status = menengah dan status = tinggi.
- Abaikan atribut multinomial: menghapus variabel kategori non-biner dari data.
- Perlakukan sebagai ordinal: mengubah variabel menjadi variabel numerik tunggal yang menyebutkan nilai orginal. Dalam kasus di atas, variabel baru akan memiliki nilai 0 untuk rendah, 1 untuk menengah dan 2 untuk tinggi. Sekali lagi perhatikan bahwa urutan nilai dapat diatur dalam Edit Domain.
- Membagi dengan jumlah nilai: sama seperti di atas, kecuali bahwa nilai-nilai dinormalisasi ke dalam rentang 0-1. Dalam contoh kami, nilai-nilai variabel baru adalah 0, 0,5 dan 1.
- Define the treatment of continuous attributes. Besised the option to Leave them as they are, we can Normalize by span, which will subtract the lowest value found in the data and divide by the span, so all values will fit into [0, 1]. Option Normalize by standard deviation subtracts the average and divides by the standard deviation.
- Define the treatment of class attributes (outcomes, targets). Besides leaving it as it is, the available options mirror those for multinomial attributes, except for those that would split the outcome into multiple outcome variables.
- This option defines the ranges of new variables. In the above text, we supposed the range from 0 to 1.
- Produce a report.
- If Apply automatically is ticked, changes are committed automatically. Otherwise, you have to press Apply after each change.
Contoh
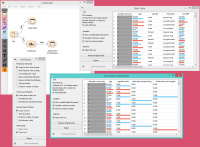
First, let’s see what is the output of the Continuize widget. We feed the original data (the Heart disease data set) into the Data Table and see how they look like. Then we continuize the discrete values and observe them in another Data Table.
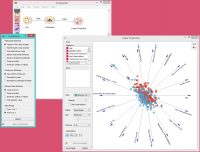
In the second example, we show a typical use of this widget - in order to properly plot the linear projection of the data, discrete attributes need to be converted to continuous ones and that is why we put the data through the Continuize widget before drawing it. The attribute “chest pain” originally had four values and was transformed into three continuous attributes; similar happened to gender, which was transformed into a single attribute “gender=female”.