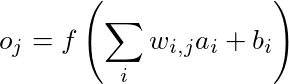Keras: Python Keras Text Classification
Sumber: https://realpython.com/python-keras-text-classification/
Bayangkan kita bisa mengetahui mood orang-orang di Internet. Mungkin kita tidak tertarik secara keseluruhan, tetapi cukup happy melihat orang bahagia di platform media sosial favorit kita. Setelah tutorial ini, kita akan diperlengkapi untuk melakukan ini. Saat melakukan ini, kita akan memahami kemajuan di (deep) neural network saat ini dan bagaimana penerapannya pada teks.
Membaca mood dari teks dengan machine learning dikenal dengan analisis sentimen, dan itu adalah salah satu kasus penggunaan yang menonjol dalam klasifikasi teks. Ini masuk ke bidang penelitian yang sangat aktif dari natural language processing (NLP). Kasus penggunaan umum lainnya dari klasifikasi teks termasuk deteksi spam, penandaan otomatis atas permintaan pelanggan, dan kategorisasi teks ke dalam topik yang ditentukan. Jadi, bagaimana kita bisa melakukan ini?
Memilih Dataset
Sebelum kita mulai, mari kita lihat data apa yang kita miliki. Pergi dan unduh kumpulan data dari Sentiment Labelled Sentences Data Set dari UCI Machine Learning Repository https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Sentiment+Labelled+Sentences
Repositori ini adalah sumber yang bagus untuk data set machine learning jika kita ingin mencoba beberapa algoritma. Kumpulan data ini mencakup review berlabel dari IMDb, Amazon, dan Yelp. Setiap ulasan ditandai dengan skor 0 untuk sentimen negatif atau 1 untuk sentimen positif.
Ekstrak folder ke folder data, lanjut dengan load data dengan Pandas:
import pandas as pd
filepath_dict = {'yelp': '/home/onno/TensorFlow/data/sentiment_analysis/yelp_labelled.txt',
'amazon': '/home/onno/TensorFlow/data/sentiment_analysis/amazon_cells_labelled.txt',
'imdb': '/home/onno/TensorFlow/data/sentiment_analysis/imdb_labelled.txt'}
df_list = []
for source, filepath in filepath_dict.items():
df = pd.read_csv(filepath, names=['sentence', 'label'], sep='\t')
df['source'] = source # Add another column filled with the source name
df_list.append(df)
df = pd.concat(df_list)
print(df.iloc[0])
Hasilnya kira-kira sebagai berikut,
sentence Wow... Loved this place. label 1 source yelp Name: 0, dtype: object
Ini terlihat benar. Dengan kumpulan data ini, kita dapat melatih model untuk memprediksi sentimen dari sebuah kalimat. Luangkan waktu sejenak untuk memikirkan bagaimana kita akan memprediksi data.
Salah satu cara kita dapat melakukan ini adalah dengan menghitung frekuensi setiap kata dalam setiap kalimat dan menghubungkan penghitungan ini kembali ke seluruh rangkaian kata dalam dataset. Kita akan mulai dengan mengambil data dan membuat kosa kata dari semua kata dalam semua kalimat. Kumpulan teks juga disebut corpus di NLP.
Vocabulary dalam hal ini adalah daftar kata-kata yang ada dalam teks di mana setiap kata memiliki indeks sendiri. Ini memungkinkan kita membuat vektor untuk sebuah kalimat. Kita kemudian akan mengambil kalimat yang ingin kita vektorisasi, dan kita menghitung setiap kemunculannya dalam kosa kata. Vektor yang dihasilkan akan dengan panjang kosakata dan jumlah untuk setiap kata dalam vocabulary.
Vektor yang dihasilkan biasa disebut feature vector. Dalam feature vector, setiap dimensi dapat berupa fitur numerik atau kategorikal, seperti misalnya tinggi bangunan, harga saham, atau, dalam kasus ini, hitungan kata dalam vocabulary. Feature Vector ini adalah bagian penting dalam data science dan machine learning, karena model yang ingin kita latih tergantung pada mereka.
Mari kita ilustrasikan ini dengan cepat. Bayangkan kita memiliki dua kalimat berikut:
sentences = ['John likes ice cream', 'John hates chocolate.']
Selanjutnya, kita dapat menggunakan CountVectorizer yang disediakan oleh scikit-learn library untuk membuat vektor kalimat. Library ini akan mengambil kata-kata dari setiap kalimat dan menciptakan vocabulary dari semua kata unik dalam kalimat. Vocabulary ini kemudian dapat digunakan untuk membuat feature vector dari jumlah kata:
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
vectorizer = CountVectorizer(min_df=0, lowercase=False) vectorizer.fit(sentences) vectorizer.vocabulary_
Hasilnya:
{'John': 0, 'chocolate': 1, 'cream': 2, 'hates': 3, 'ice': 4, 'likes': 5}
Vocabulary ini juga berfungsi sebagai indeks setiap kata. Sekarang, kita dapat mengambil setiap kalimat dan mendapatkan kemunculan kata berdasarkan vocabulary sebelumnya. Vocabulary terdiri dari semua lima kata dalam kalimat ini, masing-masing mewakili satu kata dalam Vocabulary. Ketika kita mengambil dua kalimat sebelumnya dan mengubahnya dengan CountVectorizer maka kita akan mendapatkan vektor yang mewakili jumlah setiap kata dari kalimat:
vectorizer.transform(sentences).toarray()
Hasilnya:
array([[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0]])
Sekarang, kita dapat melihat vektor fitur yang dihasilkan untuk setiap kalimat berdasarkan vocabulary sebelumnya. Misalnya, jika kita melihat item pertama, kita dapat melihat bahwa kedua vektor memiliki 1 di sana. Ini berarti bahwa kedua kalimat memiliki satu kemunculan John, yang berada pada tempat pertama dalam Vocabulary.
Ini dianggap model Bag-of-words (BOW), yang merupakan cara umum dalam NLP untuk membuat vektor dari teks. Setiap dokumen direpresentasikan sebagai vektor. Kita dapat menggunakan vektor ini sekarang sebagai feature vector untuk model machine learning. Ini membawa kita ke bagian selanjutnya, mendefinisikan model dasar.
Mendefinisikan Model Baseline
Saat kita bekerja dengan machine learning, satu langkah penting adalah menentukan model dasar. Ini biasanya melibatkan model sederhana, yang kemudian digunakan sebagai perbandingan dengan model yang lebih maju yang ingin kita uji. Dalam hal ini, kita akan menggunakan model dasar untuk membandingkannya dengan metode yang lebih maju yang melibatkan (deep) neural network.
Pertama, kita akan membagi data menjadi set training dan testing yang akan memungkinkan kita untuk mengevaluasi akurasi dan melihat apakah model kita dapat digeneralisasikan dengan baik. Ini berarti apakah model tersebut mampu berkinerja baik pada data yang belum pernah dilihat sebelumnya. Ini adalah cara untuk melihat apakah modelnya overfitting (cocok).
Overfitting adalah ketika model dilatih terlalu baik pada data training. Kita ingin menghindari overfitting, karena ini berarti model sebagian besar hanya menghafal data pelatihan. Ini akan menjelaskan akurasi yang besar dengan data training tetapi akurasi yang rendah dalam data testing.
Kita mulai dengan mengambil data set Yelp yang kita ekstrak dari kumpulan data gabungan. Dari sana, kita mengambil kalimat dan label. Nilai .values mengembalikan array NumPy daripada objek series Pandas yang dalam konteks ini akan lebih mudah digunakan:
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
df_yelp = df[df['source'] == 'yelp']
sentences = df_yelp['sentence'].values
y = df_yelp['label'].values
sentences_train, sentences_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
sentences, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=1000)
Di sini kita akan menggunakan lagi model BOW sebelumnya untuk membuat vektor kalimat. Kita dapat menggunakan lagi CountVectorizer untuk tugas ini. Karena kita mungkin tidak memiliki data pengujian yang tersedia selama testing, kikta dapat membuat Vocabulary hanya menggunakan data training. Dengan menggunakan Vocabulary ini, kita dapat membuat feature vector untuk setiap kalimat dari rangkaian training dan testing:
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer vectorizer = CountVectorizer() vectorizer.fit(sentences_train) X_train = vectorizer.transform(sentences_train) X_test = vectorizer.transform(sentences_test) X_train
Hasilnya:
<750x1714 sparse matrix of type '<class 'numpy.int64'>'
with 7368 stored elements in Compressed Sparse Row format>
Kita dapat melihat bahwa feature vector yang dihasilkan memiliki 750 sampel yang merupakan jumlah sampel training yang kita miliki setelah split train-test. Setiap sampel memiliki 1714 dimensi yang merupakan ukuran Vocabulary. Kita juga dapat melihat bahwa kita mendapatkan matriks sparce (yang banyak nol-nya). Ini adalah tipe data yang dioptimalkan untuk matriks dengan hanya beberapa elemen non-zero (tidak nol). Untuk menghemat memory, kita hanya akan memperhatikan elemen yang non-zero saja.
CountVectorizer melakukan tokenization yang memisahkan kalimat menjadi satu set token seperti yang kita lihat sebelumnya dalam Vocabulary. Ini juga menghilangkan tanda baca dan karakter khusus dan dapat menerapkan preprocessing lainnya untuk setiap kata. Jika mau, kita dapat menggunakan tokenizer khusus dari perpustakaan NLTK dengan CountVectorizer atau menggunakan sejumlah penyesuaian yang dapat kita eksplorasi untuk meningkatkan kinerja model kita.
Catatan: Ada banyak parameter tambahan untuk CountVectorizer() yang kita lupakan untuk digunakan di sini, seperti menambahkan ngram, karena tujuan awalnya adalah untuk membangun model baseline sederhana. Tokeb pattern itu sendiri default ke token_pattern = ’(?U)\b \w\w+\b’, yang merupakan pola regex yang mengatakan, "sebuah kata adalah 2 atau lebih karakter kata Unicode yang dikelilingi oleh batas kata.".
Model klasifikasi yang akan kita gunakan adalah regresi logistik yang merupakan model linier sederhana namun kuat yang secara matematis merupakan bentuk regresi antara 0 dan 1 berdasarkan feature vector input. Dengan menentukan nilai cutoff (secara default 0,5), model regresi digunakan untuk klasifikasi. Anda dapat menggunakan library scikit-learn yang menyediakan classifier LogisticRegression:
Model klasifikasi yang akan kita gunakan adalah regresi logistik yang merupakan model linier sederhana namun kuat yang secara matematis merupakan bentuk regresi antara 0 dan 1 berdasarkan feature vector input. Dengan menentukan nilai cutoff (secara default 0,5), model regresi digunakan untuk klasifikasi. Anda dapat menggunakan library scikit-learn yang menyediakan classifier LogisticRegression:
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
classifier = LogisticRegression()
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
score = classifier.score(X_test, y_test)
print("Accuracy:", score)
Hasilnya:
Accuracy: 0.796
Kita dapat melihat bahwa logistic regression mencapai 79,6% yang mengesankan, tetapi mari kita lihat bagaimana kinerja model ini pada set data lain yang kita miliki. Dalam skrip ini, kita melakukan dan mengevaluasi seluruh proses untuk setiap set data yang kita miliki:
for source in df['source'].unique():
df_source = df[df['source'] == source]
sentences = df_source['sentence'].values
y = df_source['label'].values
sentences_train, sentences_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
sentences, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=1000)
vectorizer = CountVectorizer()
vectorizer.fit(sentences_train)
X_train = vectorizer.transform(sentences_train)
X_test = vectorizer.transform(sentences_test)
classifier = LogisticRegression()
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
score = classifier.score(X_test, y_test)
print('Accuracy for {} data: {:.4f}'.format(source, score))
Here’s the result:
Accuracy for yelp data: 0.7960 Accuracy for amazon data: 0.7960 Accuracy for imdb data: 0.7487
Bagus! Kita dapat melihat bahwa model yang cukup sederhana ini menghasilkan akurasi yang cukup baik. Akan menarik untuk melihat apakah kita dapat memperbaiki model ini. Pada bagian selanjutnya, kita akan mengenal (Deep) Neural Network dan bagaimana menerapkannya pada klasifikasi teks.
(Deep) Neural Networks
Kita mungkin telah mengalami beberapa kekaguman dan ketakutan terkait dengan kecerdasan buatan dan deep learning. Kita mungkin telah menemukan beberapa artikel yang membingungkan atau TED talk yang khawatir membicarakan pendekatan singularitas atau mungkin kita melihat robot backflipping dan kita bertanya-tanya apakah kehidupan di belantara sebetulnya demikian menarik.
Pada catatan yang lebih ringan, semua peneliti AI sepakat bahwa mereka tidak setuju satu sama lain ketika AI akan melebihi kinerja tingkat Manusia. Dalam tulisan ini kita masih punya waktu.
Jadi kita mungkin penasaran bagaimana neural network bekerja. Jika kita sudah terbiasa dengan neural network, jangan ragu untuk beralih ke bagian yang melibatkan Keras. Juga, ada buku Deep Learning yang bagus dari Ian Goodfellow jika kita ingin menggali lebih dalam tentang matematika. Kita dapat membaca seluruh buku online secara gratis. Pada bagian ini kita akan mendapatkan gambaran tentang neural network dan cara kerja dalamnya, dan nanti kita akan melihat cara menggunakan neural network dengan library Keras yang luar biasa.
Dalam artikel ini, kita tidak perlu khawatir tentang singularitas, tetapi (deep) neural networks memainkan peran penting dalam perkembangan terbaru dalam AI. Semuanya dimulai dengan makalah terkenal pada 2012 oleh Geoffrey Hinton dan timnya, yang mengungguli semua model sebelumnya dalam Tantangan ImageNet yang terkenal.
Tantangannya bisa dianggap sebagai Piala Dunia dalam computer vision yang melibatkan pengklasifikasian satu set besar gambar berdasarkan label yang diberikan. Geoffrey Hinton dan timnya berhasil mengalahkan model-model sebelumnya dengan menggunakan convolution neural network (CNN), yang akan kita bahas dalam tutorial ini juga.
Sejak itu, neural network telah bergerak ke beberapa bidang yang melibatkan klasifikasi, regresi dan bahkan model generatif. Bidang yang paling umum termasuk penglihatan komputer, pengenalan suara dan natural language processing (NLP).
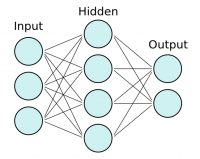
Neural Networks, atau kadang-kadang disebut Artificial Neural Network (ANN) / Jaringan Saraf Tiruan (JST) atau feedforward neural network, adalah jaringan komputasi yang secara samar-samar terinspirasi oleh jaringan saraf di otak manusia. Mereka terdiri dari neuron (juga disebut node) yang terhubung seperti pada grafik di bawah ini.
Kita mulai dengan memiliki lapisan neuron input tempat kita memberi masukan di feature vector kita dan nilai tersebut kemudian diumpankan (feed forward) ke lapisan tersembunyi. Pada setiap koneksi, kita memasukan nilai untuk dimajukan, kemudian nilai dikalikan dengan bobot dan ditambahkan bias. Ini terjadi pada setiap koneksi dan pada akhirnya kita mencapai lapisan output dengan satu atau lebih node output.
Jika kita ingin memiliki klasifikasi biner, kita dapat menggunakan satu simpul, tetapi jika kita memiliki beberapa kategori, kita harus menggunakan banyak simpul untuk setiap kategori.
Kita dapat memiliki lapisan tersembunyi sebanyak yang kita inginkan. Sebetulnya, neural networks dengan lebih dari satu lapisan tersembunyi dianggap sebagai deep neural networks. Jangan khawatir: kita tidak akan sampai di sini ke kedalaman matematika tentang neural network. Tetapi jika kita ingin mendapatkan pemahaman visual intuitif tentang matematika yang terlibat, anda dapat melihat Playlist YouTube https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLZHQObOWTQDNU6R1_67000Dx_ZCJB-3pi oleh Grant Sanderson. Rumus dari satu layer ke yang berikutnya adalah persamaan pendek ini:
Mari kita perlahan membongkar apa yang terjadi di sini. Kita lihat, kita berurusan di sini hanya dengan dua lapisan. Layer dengan node a berfungsi sebagai input untuk layer dengan node o. Untuk menghitung nilai untuk setiap simpul keluaran, kita harus mengalikan setiap simpul masukan dengan bobot w dan menambahkan bias b.
Semua itu harus dijumlahkan dan diteruskan ke fungsi f. Fungsi ini dianggap sebagai fungsi aktivasi dan ada berbagai fungsi berbeda yang dapat digunakan tergantung pada lapisan atau masalahnya. Umumnya umum untuk menggunakan rectified linear unit (ReLU) untuk lapisan hidden, fungsi sigmoid untuk lapisan output dalam masalah klasifikasi biner, atau fungsi softmax untuk lapisan output dari masalah klasifikasi multi-kelas.
Kita mungkin sudah bertanya-tanya bagaimana bobot dihitung, dan ini jelas merupakan bagian terpenting dari neural networks, tetapi juga bagian yang paling sulit. Algoritma dimulai dengan menginisialisasi bobot dengan nilai acak dan mereka kemudian dilatih dengan metode yang disebut backpropagation.
Ini dilakukan dengan menggunakan metode optimisasi (juga disebut optimizer) seperti gradient descent untuk mengurangi kesalahan antara output yang dihitung dan yang diinginkan (juga disebut output target). Kesalahan ditentukan oleh fungsi kerugian (loss function) yang kerugiannya (loss-nya) ingin kami perkecil dengan optimizer. Seluruh proses terlalu luas untuk dibahas di sini, tetapi saya akan merujuk lagi ke playlist Grant Sanderson dan buku Deep Learning oleh Ian Goodfellow.
Yang harus kita ketahui adalah bahwa ada berbagai metode pengoptimalan yang dapat kita gunakan, tetapi pengoptimal yang paling umum saat ini digunakan adalah Adam yang memiliki kinerja yang baik dalam berbagai masalah.
Kita juga dapat menggunakan fungsi loss yang berbeda, tetapi dalam tutorial ini kita hanya akan memerlukan cross entropy loss function atau lebih khusus, binary cross entropy yang digunakan untuk masalah klasifikasi biner. Pastikan untuk bereksperimen dengan berbagai metode dan tool yang tersedia. Beberapa peneliti bahkan mengklaim dalam sebuah artikel baru-baru ini bahwa pilihan untuk metode berkinerja terbaik berbatasan dengan alchemy. Alasannya adalah bahwa banyak metode tidak dijelaskan dengan baik dan terdiri dari banyak penyesuaian dan testing.
Pengenalan Keras
Keras adalah pembelajaran mendalam dan API neural networks oleh François Chollet yang mampu berjalan di atas Tensorflow (Google), Theano atau CNTK (Microsoft). Mengutip buku bagus dari François Chollet, Deep Learning with Python:
"Keras is a model-level library, providing high-level building blocks for developing deep-learning models. It doesn’t handle low-level operations such as tensor manipulation and differentiation. Instead, it relies on a specialized, well-optimized tensor library to do so, serving as the backend engine of Keras (Source)"
Ini adalah cara yang bagus untuk mulai bereksperimen dengan neural network tanpa harus menerapkan setiap lapisan oleh kita sendiri. Misalnya Tensorflow adalah library machine learning yang hebat, tetapi kita harus menerapkan banyak kode boilerplate agar model bisa jalan.
Install Keras
Sebelum menginstall Keras, kita perlu Tensorflow, Theano, atau CNTK. Dalam tutorial ini kita akan menggunakan Tensorflow jadi lihat panduan instalasi mereka, tetapi jangan ragu untuk menggunakan salah satu framework yang paling cocok untuk anda. Keras dapat diinstal menggunakan PyPI dengan perintah berikut:
$ pip install keras
Kita dapat memilih backend yang ingin kita miliki dengan membuka file konfigurasi Keras yang dapat kita temukan di sini:
$HOME/.keras/keras.json
Jika anda adalah pengguna Windows, anda harus mengganti $HOME dengan %USERPROFILE%. File konfigurasi akan terlihat sebagai berikut:
{
"image_data_format": "channels_last",
"epsilon": 1e-07,
"floatx": "float32",
"backend": "tensorflow"
}
Kita dapat mengubah backend field menjadi "theano", "tensorflow" atau "cntk", mengingat kita telah menginstal backend pada mesin yang kita gunakan. Untuk lebih jelasnya lihat dokumentasi Keras backends.
Anda mungkin memperhatikan bahwa kita menggunakan data float32 dalam file konfigurasi. Alasan untuk ini adalah bahwa neural network sering digunakan dalam GPU, dan hambatan komputasi adalah memori. Dengan menggunakan 32 bit, kita dapat mengurangi beban memori dan kami tidak kehilangan terlalu banyak informasi dalam proses.
Model Keras anda yang pertama
Now you are finally ready to experiment with Keras. Keras supports two main types of models. You have the Sequential model API which you are going to see in use in this tutorial and the functional API which can do everything of the Sequential model but it can be also used for advanced models with complex network architectures.
The Sequential model is a linear stack of layers, where you can use the large variety of available layers in Keras. The most common layer is the Dense layer which is your regular densely connected neural network layer with all the weights and biases that you are already familiar with.
Let’s see if we can achieve some improvement to our previous logistic regression model. You can use the X_train and X_test arrays that you built in our earlier example.
Before we build our model, we need to know the input dimension of our feature vectors. This happens only in the first layer since the following layers can do automatic shape inference. In order to build the Sequential model, you can add layers one by one in order as follows:
>>> from keras.models import Sequential >>> from keras import layers
>>> input_dim = X_train.shape[1] # Number of features
>>> model = Sequential() >>> model.add(layers.Dense(10, input_dim=input_dim, activation='relu')) >>> model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) Using TensorFlow backend.
Before you can start with the training of the model, you need to configure the learning process. This is done with the .compile() method. This method specifies the optimizer and the loss function.
Additionally, you can add a list of metrics which can be later used for evaluation, but they do not influence the training. In this case, we want to use the binary cross entropy and the Adam optimizer you saw in the primer mentioned before. Keras also includes a handy .summary() function to give an overview of the model and the number of parameters available for training:
>>> model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', ... optimizer='adam', ... metrics=['accuracy']) >>> model.summary() _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=====================================================
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 10) 17150 _________________________________________________________________ dense_2 (Dense) (None, 1) 11
=====================================================
Total params: 17,161 Trainable params: 17,161 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________
You might notice that we have 8575 parameters for the first layer and another 6 in the next one. Where did those come from?
See, we have 1714 dimensions for each feature vector, and then we have 5 nodes. We need weights for each feature dimension and each node which accounts for 1714 * 5 = 8570 parameters, and then we have another 5 times an added bias for each node, which gets us the 8575 parameters. In the final node, we have another 5 weights and one bias, which gets us to 6 parameters.
Neat! You are almost there. Now it is time to start your training with the .fit() function.
Since the training in neural networks is an iterative process, the training won’t just stop after it is done. You have to specify the number of iterations you want the model to be training. Those completed iterations are commonly called epochs. We want to run it for 100 epochs to be able to see how the training loss and accuracy are changing after each epoch.
Another parameter you have to your selection is the batch size. The batch size is responsible for how many samples we want to use in one epoch, which means how many samples are used in one forward/backward pass. This increases the speed of the computation as it need fewer epochs to run, but it also needs more memory, and the model may degrade with larger batch sizes. Since we have a small training set, we can leave this to a low batch size:
>>> history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, ... epochs=100, ... verbose=False, ... validation_data=(X_test, y_test) ... batch_size=10)
Now you can use the .evaluate() method to measure the accuracy of the model. You can do this both for the training data and testing data. We expect that the training data has a higher accuracy then for the testing data. Tee longer you would train a neural network, the more likely it is that it starts overfitting.
Note that if you rerun the .fit() method, you’ll start off with the computed weights from the previous training. Make sure to compile the model again before you start training the model again. Now let’s evaluate the accuracy model:
>>> loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train, verbose=False) >>> print("Training Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) >>> loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=False) >>> print("Testing Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) Training Accuracy: 1.0000 Testing Accuracy: 0.7960
You can already see that the model was overfitting since it reached 100% accuracy for the training set. But this was expected since the number of epochs was fairly large for this model. However, the accuracy of the testing set has already surpassed our previous logistic Regression with BOW model, which is a great step further in terms of our progress.
To make your life easier, you can use this little helper function to visualize the loss and accuracy for the training and testing data based on the History callback. This callback, which is automatically applied to each Keras model, records the loss and additional metrics that can be added in the .fit() method. In this case, we are only interested in the accuracy. This helper function employs the matplotlib plotting library:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.style.use('ggplot')
def plot_history(history):
acc = history.history['acc'] val_acc = history.history['val_acc'] loss = history.history['loss'] val_loss = history.history['val_loss'] x = range(1, len(acc) + 1)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(x, acc, 'b', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(x, val_acc, 'r', label='Validation acc')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(x, loss, 'b', label='Training loss')
plt.plot(x, val_loss, 'r', label='Validation loss')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.legend()
To use this function, simply call plot_history() with the collected accuracy and loss inside the history dictionary:
>>> plot_history(history)
loss accuracy baseline model Accuracy and loss for baseline model
You can see that we have trained our model for too long since the training set reached 100% accuracy. A good way to see when the model starts overfitting is when the loss of the validation data starts rising again. This tends to be a good point to stop the model. You can see this around 20-40 epochs in this training.
Note: When training neural networks, you should use a separate testing and validation set. What you would usually do is take the model with the highest validation accuracy and then test the model with the testing set.
This makes sure that you don’t overfit the model. Using the validation set to choose the best model is a form of data leakage (or “cheating”) to get to pick the result that produced the best test score out of hundreds of them. Data leakage happens when information outside the training data set is used in the model.
In this case, our testing and validation set are the same, since we have a smaller sample size. As we have covered before, (deep) neural networks perform best when you have a very large number of samples. In the next part, you’ll see a different way to represent words as vectors. This is a very exciting and powerful way to work with words where you’ll see how to represent words as dense vectors. What Is a Word Embedding?
Text is considered a form of sequence data similar to time series data that you would have in weather data or financial data. In the previous BOW model, you have seen how to represent a whole sequence of words as a single feature vector. Now you will see how to represent each word as vectors. There are various ways to vectorize text, such as:
Words represented by each word as a vector Characters represented by each character as a vector N-grams of words/characters represented as a vector (N-grams are overlapping groups of multiple succeeding words/characters in the text)
In this tutorial, you’ll see how to deal with representing words as vectors which is the common way to use text in neural networks. Two possible ways to represent a word as a vector are one-hot encoding and word embeddings. One-Hot Encoding
The first way to represent a word as a vector is by creating a so-called one-hot encoding, which is simply done by taking a vector of the length of the vocabulary with an entry for each word in the corpus.
In this way, you have for each word, given it has a spot in the vocabulary, a vector with zeros everywhere except for the corresponding spot for the word which is set to one. As you might imagine, this can become a fairly large vector for each word and it does not give any additional information like the relationship between words.
Let’s say you have a list of cities as in the following example:
>>> cities = ['London', 'Berlin', 'Berlin', 'New York', 'London'] >>> cities ['London', 'Berlin', 'Berlin', 'New York', 'London']
You can use scikit-learn and the LabelEncoder to encode the list of cities into categorical integer values like here:
>>> from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
>>> encoder = LabelEncoder() >>> city_labels = encoder.fit_transform(cities) >>> city_labels array([1, 0, 0, 2, 1])
Using this representation, you can use the OneHotEncoder provided by scikit-learn to encode the categorical values we got before into a one-hot encoded numeric array. OneHotEncoder expects each categorical value to be in a separate row, so you’ll need to reshape the array, then you can apply the encoder:
>>> from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
>>> encoder = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False) >>> city_labels = city_labels.reshape((5, 1)) >>> encoder.fit_transform(city_labels) array([[0., 1., 0.],
[1., 0., 0.],
[1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1.],
[0., 1., 0.]])
You can see that categorical integer value represents the position of the array which is 1 and the rest is 0. This is often used when you have a categorical feature which you cannot represent as a numeric value but you still want to be able to use it in machine learning. One use case for this encoding is of course words in a text but it is most prominently used for categories. Such categories can be for example city, department, or other categories. Word Embeddings
This method represents words as dense word vectors (also called word embeddings) which are trained unlike the one-hot encoding which are hardcoded. This means that the word embeddings collect more information into fewer dimensions.
Note that the word embeddings do not understand the text as a human would, but they rather map the statistical structure of the language used in the corpus. Their aim is to map semantic meaning into a geometric space. This geometric space is then called the embedding space.
This would map semantically similar words close on the embedding space like numbers or colors. If the embedding captures the relationship between words well, things like vector arithmetic should become possible. A famous example in this field of study is the ability to map King - Man + Woman = Queen.
How can you get such a word embedding? You have two options for this. One way is to train your word embeddings during the training of your neural network. The other way is by using pretrained word embeddings which you can directly use in your model. There you have the option to either leave these word embeddings unchanged during training or you train them also.
Now you need to tokenize the data into a format that can be used by the word embeddings. Keras offers a couple of convenience methods for text preprocessing and sequence preprocessing which you can employ to prepare your text.
You can start by using the Tokenizer utility class which can vectorize a text corpus into a list of integers. Each integer maps to a value in a dictionary that encodes the entire corpus, with the keys in the dictionary being the vocabulary terms themselves. You can add the parameter num_words, which is responsible for setting the size of the vocabulary. The most common num_words words will be then kept. I have the testing and training data prepared from the previous example:
>>> from keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
>>> tokenizer = Tokenizer(num_words=5000) >>> tokenizer.fit_on_texts(sentences_train)
>>> X_train = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(sentences_train) >>> X_test = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(sentences_test)
>>> vocab_size = len(tokenizer.word_index) + 1 # Adding 1 because of reserved 0 index
>>> print(sentences_train[2]) >>> print(X_train[2]) Of all the dishes, the salmon was the best, but all were great. [11, 43, 1, 171, 1, 283, 3, 1, 47, 26, 43, 24, 22]
The indexing is ordered after the most common words in the text, which you can see by the word the having the index 1. It is important to note that the index 0 is reserved and is not assigned to any word. This zero index is used for padding, which I’ll introduce in a moment.
Unknown words (words that are not in the vocabulary) are denoted in Keras with word_count + 1 since they can also hold some information. You can see the index of each word by taking a look at the word_index dictionary of the Tokenizer object:
>>> for word in ['the', 'all', 'happy', 'sad']: ... print('{}: {}'.format(word, tokenizer.word_index[word])) the: 1 all: 43 happy: 320 sad: 450
Note: Pay close attention to the difference between this technique and the X_train that was produced by scikit-learn’s CountVectorizer.
With CountVectorizer, we had stacked vectors of word counts, and each vector was the same length (the size of the total corpus vocabulary). With Tokenizer, the resulting vectors equal the length of each text, and the numbers don’t denote counts, but rather correspond to the word values from the dictionary tokenizer.word_index.
One problem that we have is that each text sequence has in most cases different length of words. To counter this, you can use pad_sequence() which simply pads the sequence of words with zeros. By default, it prepends zeros but we want to append them. Typically it does not matter whether you prepend or append zeros.
Additionally you would want to add a maxlen parameter to specify how long the sequences should be. This cuts sequences that exceed that number. In the following code, you can see how to pad sequences with Keras:
>>> from keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
>>> maxlen = 100
>>> X_train = pad_sequences(X_train, padding='post', maxlen=maxlen) >>> X_test = pad_sequences(X_test, padding='post', maxlen=maxlen)
>>> print(X_train[0, :]) [ 1 10 3 282 739 25 8 208 30 64 459 230 13 1 124 5 231 8
58 5 67 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
The first values represent the index in the vocabulary as you have learned from the previous examples. You can also see that the resulting feature vector contains mostly zeros, since you have a fairly short sentence. In the next part you will see how to work with word embeddings in Keras. Keras Embedding Layer
Notice that, at this point, our data is still hardcoded. We have not told Keras to learn a new embedding space through successive tasks. Now you can use the Embedding Layer of Keras which takes the previously calculated integers and maps them to a dense vector of the embedding. You will need the following parameters:
input_dim: the size of the vocabulary output_dim: the size of the dense vector input_length: the length of the sequence
With the Embedding layer we have now a couple of options. One way would be to take the output of the embedding layer and plug it into a Dense layer. In order to do this you have to add a Flatten layer in between that prepares the sequential input for the Dense layer:
from keras.models import Sequential from keras import layers
embedding_dim = 50
model = Sequential() model.add(layers.Embedding(input_dim=vocab_size,
output_dim=embedding_dim,
input_length=maxlen))
model.add(layers.Flatten()) model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='relu')) model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.summary()
The result will be as follows:
_________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=====================================================
embedding_8 (Embedding) (None, 100, 50) 87350 _________________________________________________________________ flatten_3 (Flatten) (None, 5000) 0 _________________________________________________________________ dense_13 (Dense) (None, 10) 50010 _________________________________________________________________ dense_14 (Dense) (None, 1) 11
=====================================================
Total params: 137,371 Trainable params: 137,371 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________
You can now see that we have 87350 new parameters to train. This number comes from vocab_size times the embedding_dim. These weights of the embedding layer are initialized with random weights and are then adjusted through backpropagation during training. This model takes the words as they come in the order of the sentences as input vectors. You can train it with the following:
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train,
epochs=20,
verbose=False,
validation_data=(X_test, y_test),
batch_size=10)
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train, verbose=False) print("Training Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=False) print("Testing Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) plot_history(history)
The result will be as follows:
Training Accuracy: 0.5100 Testing Accuracy: 0.4600
loss accuracy first model Accuracy and loss for first model
This is typically a not very reliable way to work with sequential data as you can see in the performance. When working with sequential data you want to focus on methods that look at local and sequential information instead of absolute positional information.
Another way to work with embeddings is by using a MaxPooling1D/AveragePooling1D or a GlobalMaxPooling1D/GlobalAveragePooling1D layer after the embedding. You can think of the pooling layers as a way to downsample (a way to reduce the size of) the incoming feature vectors.
In the case of max pooling you take the maximum value of all features in the pool for each feature dimension. In the case of average pooling you take the average, but max pooling seems to be more commonly used as it highlights large values.
Global max/average pooling takes the maximum/average of all features whereas in the other case you have to define the pool size. Keras has again its own layer that you can add in the sequential model:
from keras.models import Sequential from keras import layers
embedding_dim = 50
model = Sequential() model.add(layers.Embedding(input_dim=vocab_size,
output_dim=embedding_dim,
input_length=maxlen))
model.add(layers.GlobalMaxPool1D()) model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='relu')) model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.summary()
The result will be as follows:
_________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=====================================================
embedding_9 (Embedding) (None, 100, 50) 87350 _________________________________________________________________ global_max_pooling1d_5 (Glob (None, 50) 0 _________________________________________________________________ dense_15 (Dense) (None, 10) 510 _________________________________________________________________ dense_16 (Dense) (None, 1) 11
=====================================================
Total params: 87,871 Trainable params: 87,871 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________
The procedure for training does not change:
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train,
epochs=50,
verbose=False,
validation_data=(X_test, y_test),
batch_size=10)
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train, verbose=False) print("Training Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=False) print("Testing Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) plot_history(history)
The result will be as follows:
Training Accuracy: 1.0000 Testing Accuracy: 0.8050
loss accurcay max pooling Accuracy and loss for max pooling model
You can already see some improvements in our models. Next you’ll see how we can employ pretrained word embeddings and if they help us with our model. Using Pretrained Word Embeddings
We just saw an example of jointly learning word embeddings incorporated into the larger model that we want to solve.
An alternative is to use a precomputed embedding space that utilizes a much larger corpus. It is possible to precompute word embeddings by simply training them on a large corpus of text. Among the most popular methods are Word2Vec developed by Google and GloVe (Global Vectors for Word Representation) developed by the Stanford NLP Group.
Note that those are different approaches with the same goal. Word2Vec achieves this by employing neural networks and GloVe achieves this with a co-occurrence matrix and by using matrix factorization. In both cases you are dealing with dimensionality reduction, but Word2Vec is more accurate and GloVe is faster to compute.
In this tutorial, you’ll see how to work with the GloVe word embeddings from the Stanford NLP Group as their size is more manageable than the Word2Vec word embeddings provided by Google. Go ahead and download the 6B (trained on 6 billion words) word embeddings from here (822 MB).
You can find other word embeddings also on the main GloVe page. You can find the pretrained Word2Vec embeddings by Google here. If you want to train your own word embeddings, you can do so efficiently with the gensim Python package which uses Word2Vec for calculation. More details on how to do this here.
Now that we got you covered, you can start using the word embeddings in your models. You can see in the next example how you can load the embedding matrix. Each line in the file starts with the word and is followed by the embedding vector for the particular word.
This is a large file with 400000 lines, with each line representing a word followed by its vector as a stream of floats. For example, here are the first 50 characters of the first line:
$ head -n 1 data/glove_word_embeddings/glove.6B.50d.txt | cut -c-50
the 0.418 0.24968 -0.41242 0.1217 0.34527 -0.04445
Since you don’t need all words, you can focus on only the words that we have in our vocabulary. Since we have only a limited number of words in our vocabulary, we can skip most of the 40000 words in the pretrained word embeddings:
import numpy as np
def create_embedding_matrix(filepath, word_index, embedding_dim):
vocab_size = len(word_index) + 1 # Adding again 1 because of reserved 0 index embedding_matrix = np.zeros((vocab_size, embedding_dim))
with open(filepath) as f:
for line in f:
word, *vector = line.split()
if word in word_index:
idx = word_index[word]
embedding_matrix[idx] = np.array(
vector, dtype=np.float32)[:embedding_dim]
return embedding_matrix
You can use this function now to retrieve the embedding matrix:
>>> embedding_dim = 50 >>> embedding_matrix = create_embedding_matrix( ... 'data/glove_word_embeddings/glove.6B.50d.txt', ... tokenizer.word_index, embedding_dim)
Wonderful! Now you are ready to use the embedding matrix in training. Let’s go ahead and use the previous network with global max pooling and see if we can improve this model. When you use pretrained word embeddings you have the choice to either allow the embedding to be updated during training or only use the resulting embedding vectors as they are.
First, let’s have a quick look how many of the embedding vectors are nonzero:
>>> nonzero_elements = np.count_nonzero(np.count_nonzero(embedding_matrix, axis=1)) >>> nonzero_elements / vocab_size 0.9507727532913566
This means 95.1% of the vocabulary is covered by the pretrained model, which is a good coverage of our vocabulary. Let’s have a look at the performance when using the GlobalMaxPool1D layer:
model = Sequential() model.add(layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim,
weights=[embedding_matrix],
input_length=maxlen,
trainable=False))
model.add(layers.GlobalMaxPool1D()) model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='relu')) model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.summary()
The result will be as follows:
_________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=====================================================
embedding_10 (Embedding) (None, 100, 50) 87350 _________________________________________________________________ global_max_pooling1d_6 (Glob (None, 50) 0 _________________________________________________________________ dense_17 (Dense) (None, 10) 510 _________________________________________________________________ dense_18 (Dense) (None, 1) 11
=====================================================
Total params: 87,871 Trainable params: 521 Non-trainable params: 87,350 _________________________________________________________________
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train,
epochs=50,
verbose=False,
validation_data=(X_test, y_test),
batch_size=10)
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train, verbose=False) print("Training Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=False) print("Testing Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) plot_history(history)
The result will be as follows:
Training Accuracy: 0.7500 Testing Accuracy: 0.6950
loss accuracy embedding untrained Accuracy and loss for untrained word embeddings
Since the word embeddings are not additionally trained, it is expected to be lower. But let’s now see how this performs if we allow the embedding to be trained by using trainable=True:
model = Sequential() model.add(layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim,
weights=[embedding_matrix],
input_length=maxlen,
trainable=True))
model.add(layers.GlobalMaxPool1D()) model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='relu')) model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.summary()
The result will be as follows:
_________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=====================================================
embedding_11 (Embedding) (None, 100, 50) 87350 _________________________________________________________________ global_max_pooling1d_7 (Glob (None, 50) 0 _________________________________________________________________ dense_19 (Dense) (None, 10) 510 _________________________________________________________________ dense_20 (Dense) (None, 1) 11
=====================================================
Total params: 87,871 Trainable params: 87,871 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train,
epochs=50,
verbose=False,
validation_data=(X_test, y_test),
batch_size=10)
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train, verbose=False) print("Training Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=False) print("Testing Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) plot_history(history)
The result will be as follows:
Training Accuracy: 1.0000 Testing Accuracy: 0.8250
loss accuracy embedding trained Accuracy and Loss for pretrained word embeddings
You can see that it is most effective to allow the embeddings to be trained. When dealing with large training sets it can boost the training process to be much faster than without. In our case it seemed to help but not by much. This does not have to be because of pretrained word embeddings.
Now it is time to focus on a more advanced neural network model to see if it is possible to boost the model and give it the leading edge over the previous models. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
Convolutional neural networks or also called convnets are one of the most exciting developments in machine learning in recent years.
They have revolutionized image classification and computer vision by being able to extract features from images and using them in neural networks. The properties that made them useful in image processing makes them also handy for sequence processing. You can imagine a CNN as a specialized neural network that is able to detect specific patterns.
If it is just another neural network, what differentiates it from what you have previously learned?
A CNN has hidden layers which are called convolutional layers. When you think of images, a computer has to deal with a two dimensional matrix of numbers and therefore you need some way to detect features in this matrix. These convolutional layers are able to detect edges, corners and other kinds of textures which makes them such a special tool. The convolutional layer consists of multiple filters which are slid across the image and are able to detect specific features.
This is the very core of the technique, the mathematical process of convolution. With each convolutional layer the network is able to detect more complex patterns. In the Feature Visualization by Chris Olah you can get a good intuition what these features can look like.
When you are working with sequential data, like text, you work with one dimensional convolutions, but the idea and the application stays the same. You still want to pick up on patterns in the sequence which become more complex with each added convolutional layer.
In the next figure you can see how such a convolution works. It starts by taking a patch of input features with the size of the filter kernel. With this patch you take the dot product of the multiplied weights of the filter. The one dimensional convnet is invariant to translations, which means that certain sequences can be recognized at a different position. This can be helpful for certain patterns in the text: one dimensional convolution 1D Convolution (Image source)
Now let’s have a look how you can use this network in Keras. Keras offers again various Convolutional layers which you can use for this task. The layer you’ll need is the Conv1D layer. This layer has again various parameters to choose from. The ones you are interested in for now are the number of filters, the kernel size, and the activation function. You can add this layer in between the Embedding layer and the GlobalMaxPool1D layer:
embedding_dim = 100
model = Sequential() model.add(layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim, input_length=maxlen)) model.add(layers.Conv1D(128, 5, activation='relu')) model.add(layers.GlobalMaxPooling1D()) model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='relu')) model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.summary()
The result will be as follows:
_________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=====================================================
embedding_13 (Embedding) (None, 100, 100) 174700 _________________________________________________________________ conv1d_2 (Conv1D) (None, 96, 128) 64128 _________________________________________________________________ global_max_pooling1d_9 (Glob (None, 128) 0 _________________________________________________________________ dense_23 (Dense) (None, 10) 1290 _________________________________________________________________ dense_24 (Dense) (None, 1) 11
=====================================================
Total params: 240,129 Trainable params: 240,129 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train,
epochs=10,
verbose=False,
validation_data=(X_test, y_test),
batch_size=10)
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train, verbose=False) print("Training Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=False) print("Testing Accuracy: {:.4f}".format(accuracy)) plot_history(history)
The result will be as follows:
Training Accuracy: 1.0000 Testing Accuracy: 0.7700
loss accuracy convolution model Accuracy and loss for convolutional neural network
You can see that 80% accuracy seems to be tough hurdle to overcome with this data set and a CNN might not be well equipped. The reason for such a plateau might be that:
There are not enough training samples The data you have does not generalize well Missing focus on tweaking the hyperparameters
CNNs work best with large training sets where they are able to find generalizations where a simple model like logistic regression won’t be able. Hyperparameters Optimization
One crucial steps of deep learning and working with neural networks is hyperparameter optimization.
As you saw in the models that we have used so far, even with simpler ones, you had a large number of parameters to tweak and choose from. Those parameters are called hyperparameters. This is the most time consuming part of machine learning and sadly there are no one-fits-all solutions ready.
When you have a look at the competitions on Kaggle, one of the largest places to compete against other fellow data scientists, you can see that many of the winning teams and models have gone through a lot of tweaking and experimenting until they reached their prime. So don’t get discouraged when it gets tough and you reach a plateau, but rather think about the ways you could optimize the model or the data.
One popular method for hyperparameter optimization is grid search. What this method does is it takes lists of parameters and it runs the model with each parameter combination that it can find. It is the most thorough way but also the most computationally heavy way to do this. Another common way, random search, which you’ll see in action here, simply takes random combinations of parameters.
In order to apply random search with Keras, you will need to use the KerasClassifier which serves as a wrapper for the scikit-learn API. With this wrapper you are able to use the various tools available with scikit-learn like cross-validation. The class that you need is RandomizedSearchCV which implements random search with cross-validation. Cross-validation is a way to validate the model and take the whole data set and separate it into multiple testing and training data sets.
There are various types of cross-validation. One type is the k-fold cross-validation which you’ll see in this example. In this type the data set is partitioned into k equal sized sets where one set is used for testing and the rest of the partitions are used for training. This enables you to run k different runs, where each partition is once used as a testing set. So, the higher k is the more accurate the model evaluation is, but the smaller each testing set is.
First step for KerasClassifier is to have a function that creates a Keras model. We will use the previous model, but we will allow various parameters to be set for the hyperparameter optimization:
def create_model(num_filters, kernel_size, vocab_size, embedding_dim, maxlen):
model = Sequential()
model.add(layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim, input_length=maxlen))
model.add(layers.Conv1D(num_filters, kernel_size, activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.GlobalMaxPooling1D())
model.add(layers.Dense(10, activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
Next, you want to define the parameter grid that you want to use in training. This consists of a dictionary with each parameters named as in the previous function. The number of spaces on the grid is 3 * 3 * 1 * 1 * 1, where each of those numbers is the number of different choices for a given parameter.
You can see how this could get computationally expensive very quickly, but luckily both grid search and random search are embarrassingly parallel, and the classes come with an n_jobs parameter that lets you test grid spaces in parallel. The parameter grid is initialized with the following dictionary:
param_grid = dict(num_filters=[32, 64, 128],
kernel_size=[3, 5, 7],
vocab_size=[5000],
embedding_dim=[50],
maxlen=[100])
Now you are already ready to start running the random search. In this example we iterate over each data set and then you want to preprocess the data in the same way as previously. Afterwards you take the previous function and add it to the KerasClassifier wrapper class including the number of epochs.
The resulting instance and the parameter grid are then used as the estimator in the RandomSearchCV class. Additionally, you can choose the number of folds in the k-folds cross-validation, which is in this case 4. You have seen most of the code in this snippet before in our previous examples. Besides the RandomSearchCV and KerasClassifier, I have added a little block of code handling the evaluation:
from keras.wrappers.scikit_learn import KerasClassifier from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
- Main settings
epochs = 20 embedding_dim = 50 maxlen = 100 output_file = 'data/output.txt'
- Run grid search for each source (yelp, amazon, imdb)
for source, frame in df.groupby('source'):
print('Running grid search for data set :', source)
sentences = df['sentence'].values
y = df['label'].values
# Train-test split
sentences_train, sentences_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
sentences, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=1000)
# Tokenize words tokenizer = Tokenizer(num_words=5000) tokenizer.fit_on_texts(sentences_train) X_train = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(sentences_train) X_test = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(sentences_test)
# Adding 1 because of reserved 0 index vocab_size = len(tokenizer.word_index) + 1
# Pad sequences with zeros X_train = pad_sequences(X_train, padding='post', maxlen=maxlen) X_test = pad_sequences(X_test, padding='post', maxlen=maxlen)
# Parameter grid for grid search
param_grid = dict(num_filters=[32, 64, 128],
kernel_size=[3, 5, 7],
vocab_size=[vocab_size],
embedding_dim=[embedding_dim],
maxlen=[maxlen])
model = KerasClassifier(build_fn=create_model,
epochs=epochs, batch_size=10,
verbose=False)
grid = RandomizedSearchCV(estimator=model, param_distributions=param_grid,
cv=4, verbose=1, n_iter=5)
grid_result = grid.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Evaluate testing set test_accuracy = grid.score(X_test, y_test)
# Save and evaluate results
prompt = input(f'finished {source}; write to file and proceed? [y/n]')
if prompt.lower() not in {'y', 'true', 'yes'}:
break
with open(output_file, 'a') as f:
s = ('Running {} data set\nBest Accuracy : '
'{:.4f}\n{}\nTest Accuracy : {:.4f}\n\n')
output_string = s.format(
source,
grid_result.best_score_,
grid_result.best_params_,
test_accuracy)
print(output_string)
f.write(output_string)
This takes a while which is a perfect chance to go outside to get some fresh air or even go on a hike, depending on how many models you want to run. Let’s take a look what we have got:
Running amazon data set Best Accuracy : 0.8122 {'vocab_size': 4603, 'num_filters': 64, 'maxlen': 100, 'kernel_size': 5, 'embedding_dim': 50} Test Accuracy : 0.8457
Running imdb data set Best Accuracy : 0.8161 {'vocab_size': 4603, 'num_filters': 128, 'maxlen': 100, 'kernel_size': 5, 'embedding_dim': 50} Test Accuracy : 0.8210
Running yelp data set Best Accuracy : 0.8127 {'vocab_size': 4603, 'num_filters': 64, 'maxlen': 100, 'kernel_size': 7, 'embedding_dim': 50} Test Accuracy : 0.8384
Interesting! For some reason the testing accuracy is higher than the training accuracy which might be because there is a large variance in the scores during cross-validation. We can see that we were still not able to break much through the dreaded 80%, which seems to be a natural limit for this data with its given size. Remember that we have a small data set and convolutional neural networks tend to perform the best with large data sets.
Another method for CV is the nested cross-validation (shown here) which is used when the hyperparameters also need to be optimized. This is used because the resulting non-nested CV model has a bias toward the data set which can lead to an overly optimistic score. You see, when doing hyperparameter optimization as we did in the previous example, we are picking the best hyperparameters for that specific training set but this does not mean that these hyperparameters generalize the best. Conclusion
There you have it: you have learned how to work with text classification with Keras, and we have gone from a bag-of-words model with logistic regression to increasingly more advanced methods leading to convolutional neural networks.
You should be now familiar with word embeddings, why they are useful, and also how to use pretrained word embeddings for your training. You have also learned how to work with neural networks and how to use hyperparameter optimization to squeeze more performance out of your model.
One big topic which we have not covered here left for another time was recurrent neural networks, more specifically LSTM and GRU. Those are other powerful and popular tools to work with sequential data like text or time series. Other interesting developments are currently in neural networks that employ attention which are under active research and seem to be a promising next step since LSTM tend to be heavy on the computation.
You have now an understanding of a crucial cornerstone in natural language processing which you can use for text classification of all sorts. Sentiment analysis is the most prominent example for this, but this includes many other applications such as:
Spam detection in emails Automatic tagging of texts Categorization of news articles with predefined topics
You can use this knowledge and the models that you have trained on an advanced project as in this tutorial to employ sentiment analysis on a continuous stream of twitter data with Kibana and Elasticsearch. You could also combine sentiment analysis or text classification with speech recognition like in this handy tutorial using the SpeechRecognition library in Python.
Referensi
- https://realpython.com/python-keras-text-classification/
- http://colah.github.io/posts/2014-07-NLP-RNNs-Representations/