5G Daftar Istilah
Revision as of 06:36, 29 December 2022 by Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs)
Berbagai istilah yang digunakan dalam 5G dilihat di
https://www.mpirical.com/glossary/
Berikut adalah beberapa yang digunakan disini yang di beri keterangan dalam bahasa Indonesia.
| Istilah | Istilah Panjang | Penjelasan |
|---|---|---|
| 3GPP | Third Generation Partnership Project | 3GPP dibentuk pada Desember 1998 sebagai kesepakatan kerjasama yang mempertemukan sejumlah badan standar telekomunikasi. Badan standar ini disebut sebagai Mitra Organisasi. Tujuan awal 3GPP adalah untuk menghasilkan spesifikasi teknis yang dapat diterapkan secara global untuk sistem seluler generasi ketiga berdasarkan jaringan inti GSM yang berkembang dan teknologi akses radio UTRA (Universal Terrestrial Radio Access). Ini kemudian diubah untuk memasukkan pemeliharaan dan pengembangan standar GSM termasuk GPRS dan EDGE (Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution). Perkembangan jaringan lebih lanjut dikaitkan dengan 3GPP termasuk evolusi manajemen layanan melalui IMS, peningkatan kecepatan data di UTRA melalui HSPA+ dan yang terbaru, pekerjaan yang terkait dengan LTE, LTE Advanced dan LTE Advanced Pro. |
| 4G | Fourth Generation | 4G adalah istilah yang diberikan untuk sistem komunikasi seluler generasi keempat, yang menawarkan kecepatan data tingkat lanjut secara signifikan di semua jaringan pembawa berbasis IP. Teknologi utama dibalik 4G adalah LTE (Long Term Evolution), meskipun jaringan HSPA (High Speed Packet Access) dan jaringan berbasis WiMAX juga dapat diberi label 4G. |
| 5G | Fifth Generation | 5G adalah istilah yang diberikan untuk teknologi komunikasi seluler generasi kelima. Pekerjaan dimulai dalam 3GPP pada spesifikasi Rilis 15 pertama untuk 5G, yang disebut arsitektur NexGen (Next Generation) pada Desember 2016. Pekerjaan standardisasi 5G NR (New Radio) juga sedang dalam proses pengembangan, dengan tahap pertama penyebaran 5G yang diharapkan berdasarkan Rilis 15 jatuh tempo pada tahun 2020. |
| 5GC | 5G Core Network | 5G Core (3GPP) mencakup berbagai fungsi: AUSF (Authentication Server Function), AMF (Core Access and Mobility Management Function), DN (Data Network), DSF (Data Storage Network Function), NRF (NF Repository Function), PCF (Policy Control Function), SMF (Session Management Function), UDM (Unified Data Management) dan UPF (User Plane Function). |
| 5GMM | 5GS Mobility Management | Protokol ini menyediakan prosedur untuk mengontrol mobilitas ketika UE menggunakan jaringan akses NG-RAN dan/atau non-3GPP. |
| 5G NAS | 5G Non Access Stratum | 5G NAS (Non-Access Stratum) mencakup prosedur yang terkait dengan 5GMM (5GS Mobility Management) dan 5GSM (5GS Session Management) pada 5GS (5G system). |
| 5G RAN | 5G Radio Access Network | 5G Radio Access Network mengidentifikasi jaringan akses radio yang terhubung ke 5GC (5G Core). Contohnya termasuk 5G New Radio dan sistem radio dengan New Radio extensions. |
| AMF | Authentication Management Field | AMF adalah istilah yang digunakan dalam arsitektur UMTS AKA (Authentication and Key Agreement). AMF adalah nilai 16 bit yang digunakan untuk mengatur acceptable synchronization window di UE (Peralatan Pengguna) dan jaringan. |
| AUSF | Authentication Server Function | Authentication Server Function adalah bagian dari Arsitektur 3GPP 5G. Ini digunakan untuk memfasilitasi proses 5G security. |
| eNB | Evolved Node B | eNB berfungsi sebagai base station di dalam E-UTRAN, mengakhiri air interface di sisi jaringan. Akibatnya, eNB bertanggung jawab untuk semua radio resource management, serta alokasi lalu lintas pengguna ke downlink/uplink, keamanan dan menyampaikan sinyal NAS (Non Access Stratum) ke MME (Mobility Management Entity). eNB juga mampu melakukan prosedur serah terima antar eNB melalui X2 interface. |
| EPC | Evolved Packet Core | Evolusi core network dimulai dengan Rilis 4. Ini memberikan titik awal untuk pengenalan IP ke dalam domain CS core network serta peningkatan untuk memungkinkan layanan real time dan non real time berhasil diintegrasikan ke dalam media transportasi umum . Dalam Rilis 8 dari standar 3GPP, fungsionalitas core network dibuat lebih rata dengan sebagian besar kecerdasan yang diperlukan untuk mendukung pengiriman layanan ditempatkan di dalam domain seperti IMS. Akibatnya EPC terdiri dari MME (Mobility Management Entity) yang melakukan banyak fungsi mobilitas yang secara tradisional disediakan oleh SGSN seperti prosedur paging, keamanan dan Idle Mode. EPC juga mencakup S-GW (Serving Gateway), yang menggantikan fungsi User Plane dari SGSN, serta PDN-GW (Packet Data Network Gateway), yang menghentikan user plane di dalam EPC. |
| E-UTRAN | Evolved – Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network | The E-UTRAN is the LTE RAN, forming part of the overall Evolved Packet System. |
| FDD | Frequency Division Duplex | Frequency Division Duplex is employed in radio systems to provide an uplink and downlink radio channel between the network and the user. The frequencies separated by a duplex spacing. Users tune between the uplink and downlink frequencies to transmit and receive respectively. |
| gNB | Next Generation Node B | The gNB is a 3GPP 5G Next Generation base station which supports the 5G New Radio. |
| GUMMEI | Globally Unique MME Identifier | The GUTI (Globally Unique Temporary Identity) has two main components, the GUMMEI (Globally Unique MME Identifier) that uniquely identifies the MME that allocated the GUTI and the M-TMSI (M-Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity) that provides for an unambiguous identity of the UE within this MME. |
| GUTI | Globally Unique Temporary ID | In LTE the GUTI is allocated to the UE by the MME and has two components. These are the GUMMEI (Globally Unique MME ID) and the M-TMSI (MME-TMSI). While the GUMMEI identifies the MME, the M-TMSI identifies the UE within the MME. |
| GTP-U | GPRS Tunnelling Protocol User | GPRS Tunnelling Protocol – User plane messages are exchanged between GSN (Gateway Support Node) pairs or GSN/ RNC (Radio Network Controller) pairs in a path. The user plane messages are used to carry user data packets, and signalling messages for path management and error indication. The GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTP) is a group of IP-based communications protocols used within GSM, UMTS, LTE and 5G NR radio networks. GTP-U is used to carry user data inside mobile networks. |
| IMSI | International Mobile Subscriber Identity | The International Mobile Subscriber Identity is a unique identifier allocated to each mobile subscriber in a GSM, UMTS, LTE and 5G network. It consists of a MCC (Mobile Country Code), a MNC (Mobile Network Code) and a MSIN (Mobile Subscriber Identification Number). |
| IoT | Internet of Things | The Internet of Things is best described as the interconnection of billions of devices, often in everyday objects, which will send and receive data. The term is often associated with key verticals such as Automotive, Utilities and Healthcare enabling smart and efficient services to be supported. Examples from these verticals may include, fleet tracking, smart meters and remote health monitoring. |
| LAI | Location Area Identity | The Location Area Identity uniquely identifies a LA (Location Area) within any PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network). It is comprised of the MCC (Mobile Country Code), MNC (Mobile Network Code) and the LAC (Location Area Code). |
| LTE | Long Term Evolution | Standardized in 3GPP Release 8, LTE introduces a network which is based purely on IP as the transport mechanism. That is, all traffic, including voice, will be passed across the E-UTRAN as an IP datagram. Moreover, all of the network nodes within LTE use IP to carry signalling between one another. Termed the EPS (Evolved Packet System), the end to end LTE network is comprised of the E-UTRAN (Evolved – Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network) and the EPC (Evolved Packet Core). |
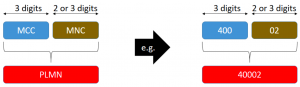
| MCC | Mobile Country Code | The Mobile Country Code is a three digit number uniquely identifying a given country. It is utilized within numerous identities across 3GPP mobile networks, including the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity), LAI (Location Area Identity) and GUTI (Globally Unique Temporary ID).
Mobile Country Code is used in wireless telephone networks such as GSM, CDMA, WCDMA or LTE in order to identify mobile user belongs to which country. MCC consists of 3 decimal digits. |
| MIMO | Multiple Input Multiple Output | The ever increasing requirement for higher data rates and improved QoS across wireless links has generated the need to improve the spectral efficiency and reliability of radio communication. One way to achieve this is through the use of multiple antennas at each end of the transmission link. This technique is known as MIMO. |
| MME | Mobility Management Entity | The MME is responsible for mobility and session management procedures in the EPC. As such, the MME communicates with the mobile via NAS (Non Access Stratum) signalling and communicates with the HSS through Diameter. Key responsibilities include ECM (EPS Connection Management), EMM (EPS Mobility Management), gateway selection, NAS security and handover assistance. |
| MNC | Mobile Network Code | The Mobile Network Code is either a two or three digit number used to uniquely identify a given network from within a specified country ( MCC (Mobile Country Code)). The MNC is used as part of the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) and LAI (Location Area Identity) etc. |
| NAS | Non Access Stratum | The Non Access Stratum is a functional layer running between the UE (User Equipment) and the CN (Core Network). The layer supports traffic and signalling messages between the CN and UE (User Equipment). |
| NB-IoT | Narrow Band – Internet of Things | This is a standards based LPWA (Low Power Wide Area) technology developed to enable a wide range of devices to connect within The Internet of Things. The technology supports a number of key features including low power consumption, radio spectrum efficiency and low cost. The technology can co-exist with existing 3GPP based 2G, 3G and 4G technologies and also benefits from the security features found within these network |
| NGAP | NG Application Protocol | NGAP is found on the N2 reference point between the gNB and the AMF (Core Access and Mobility and Management Function) in order to support both UE and non UE associated services. This includes operations such as configuration updates, UE context transfer, PDU Session resource management and also support for mobility procedures. NGAP is also used to convey downlink and uplink NAS (Non Access Stratum) messages as a payload, as well as support CM Idle and CM Connected operations such as Paging and UE Context release. |
| PFCP | Packet Forwarding Control Protocol (PFCP) | Packet Forwarding Control Protocol (PFCP) is a 3GPP protocol used on the Sx/N4 interface between the control plane and the user plane function, specified in TS 29.244.[1] It is one of the main protocols introduced in the 5G Next Generation Mobile Core Network (aka 5GC[2]), but also used in the 4G/LTE EPC to implement the Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS).[3] PFCP and the associated interfaces seek to formalize the interactions between different types of functional elements used in the Mobile Core Networks as deployed by most operators providing 4G, as well as 5G, services to mobile subscribers |
| PHY | Physical Link | A Physical Link is the connection between devices. |
| PLMN | Public Land Mobile Network | A Public Land Mobile Network is a generic name for all mobile wireless networks that use land based radio transmitters or base stations. Public Land Mobile Network Identifier or with abbreviated version PLMN is a combination of MCC and MNC. It is unique value and globally used to identify the mobile network that a user subscribed. |
| PRACH | Physical Random Access Channel | The Random Access procedure is used in various scenarios, including initial access, handover, or re-establishment. Like other 3GPP systems the random access procedure provides a method for contention and non-contention based access. The PRACH (Physical Random Access Channel) includes RA (Random Access) preambles generated from Zadoff-Chu sequences. |
| S1AP | S1 Application Protocol | S1AP is used between the eNB and the MME in order to support operations such as E-RAB (E-UTRAN Radio Access Bearer) Management, transfer of UE Context information, NAS Signalling transport, Paging and EPC based mobility. |
| SBI | Service Based Interface | SBI is the term given to the API based communication that can take place between two VNFs (Virtualized Network Functions) within the 5G SBA (Service Based Architecture). A given VNF can utilise an API call over the SBI in order to invoke a particular service or service operation. |
| SCTP | Stream Control Transmission Protocol | SCTP provides sequential, reliable delivery of higher layer data, using logical streams to separate this functionality and hence avoid head of line blocking. An SCTP connection between two network nodes e.g. eNB (Evolved Node B) to MME (Mobility Management Entity) is termed an SCTP Association, which can feature flow control and multihoming as standard capabilities. SCTP provides much of the same functionality as TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), without the inherent drawbacks that TCP can suffer from. |
| SGW-U | Serving Gateway User plane function | The SGW-U is the user data plane ingress and egress point of the E-UTRAN side of the EPC when control and user plane separation is in place. As such, when the subscriber moves around the E-UTRAN, their point of attachment to the EPC remains fixed at the SGW-U (unless the network decides that a SGW-U relocation is required). A single subscriber may be supported by multiple SGW-U if connectivity to multiple PDNs are in place. Additional responsibilities include lawful interception of subscriber traffic, inter-operator accounting, as well as downlink data buffering whilst the subscriber is paged. |
| TAC | Tracking Area Code | An element of the TAI which serves to uniquely identify the Tracking Area. Tracking Area is a logical concept of an area where a user can move around without updating the MME. The network allocates a list with one or more TAs to the user. In certain operation modes, the UE may move freely in all TAs of the list without updating the MME. You can think of 'Tracking Area' as 'Routing Area' in UMTS. |
| TAI | Timing Advance Index | The MS (Mobile Station) performing uplink or downlink packet transfer, will receive a packet uplink or downlink assignment message. This message will contain the MS assigned TAI and the PTCCH (Packet Timing Control Channel). The TAI specifies which PTCCH subchannel is to be used by the MS. |
| TDD | Time Division Duplex | In a Time Division Duplex system a common carrier is shared between the uplink and downlink, the resource being switched in time. Users are allocated one or more timeslots for uplink and downlink transmission. The main advantage of TDD operation is that it allows asymmetric flow which is more suited to data transmission. |
| TMSI | Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity | In order to ensure subscriber identity confidentiality the VLR (Visitor Location Register) and SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node) may allocate TMSI (Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identities) to visiting mobile subscribers. The VLR and SGSN must be capable of correlating an allocated TMSI with the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) of the MS (Mobile Station) to which it is allocated. A MS may be allocated two TMSI, one for services provided through the VLR, and the other known as the P-TMSI (Packet TMSI) for services provided through the SGSN. |
| UE | User Equipment | The UMTS Subscriber or UE (User Equipment) is a combination of ME (Mobile Equipment) and SIM / USIM (Subscriber Identity Module / UMTS Subscriber Identity Module). |
| UMTS | Universal Mobile Telecommunications System | A 3G mobile communication system which supports improved data rates over GSM and subsequently provides an enhanced range of multimedia services. UMTS has increased convergence between telecommunications, IT (Information technology), media and content industries to deliver new services and create fresh revenue generating opportunities. UMTS delivers low cost, high capacity mobile communications, offering data rates as high as 2Mbps (under ideal conditions) with global roaming and other advanced capabilities. The specifications defining UMTS are formulated by the 3GPP. |
| RRC | Radio Recource Control | RRC is a sublayer of Layer 3 on the UMTS radio interface; it exists in the control plane only and provides an information transfer service to NAS (Non Access Stratum) signalling. RRC is also responsible for controlling the configuration of the UMTS radio interface, facilitating the establishment and management of radio bearers, mobility management and security. A sublayer of Layer 3 on the UMTS radio interface; it exists in the control plane only and provides information transfer service to the NAS (Non Access Stratum). RRC is responsible for controlling the configuration of UMTS radio interface Layers 1 and 2. |
| WiFi | Wireless Fidelity | WiFi is an interoperability standard developed by the WiFi Alliance and issued to those manufacturers whose IEEE 802.11 equipment has passed a suite of basic interoperability tests. Equipment passing these tests carries the WiFi logo. |
| WiMAX | World wide Interoperability for Microwave Access | WiMAX is a mobile broadband technology standardized by the IEEE 802.16m working group. Although WiMAX is a potential option for supporting 4G, it has seen mixed success around the globe, with many service providers adopting LTE as an alternative. |
| X2AP | X2 Application Protocol | X2AP is a control protocol found between eNBs on the X2 control plane. Main functions of X2AP include X2 based mobility, as well as X2 “Global Procedures”. The former is largely associated with eNB (Evolved Node B) controlled handover procedures whereas the latter deals with the establishment and management of the X2 connection. |