5G Daftar Istilah
Berbagai istilah yang digunakan dalam 5G dilihat di
https://www.mpirical.com/glossary/
Berikut adalah beberapa yang digunakan disini yang di beri keterangan dalam bahasa Indonesia.
| Istilah | Istilah Panjang | Penjelasan |
|---|---|---|
| GUMMEI | Globally Unique MME Identifier | The GUTI (Globally Unique Temporary Identity) has two main components, the GUMMEI (Globally Unique MME Identifier) that uniquely identifies the MME that allocated the GUTI and the M-TMSI (M-Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity) that provides for an unambiguous identity of the UE within this MME. |
| GUTI | Globally Unique Temporary ID | In LTE the GUTI is allocated to the UE by the MME and has two components. These are the GUMMEI (Globally Unique MME ID) and the M-TMSI (MME-TMSI). While the GUMMEI identifies the MME, the M-TMSI identifies the UE within the MME. |
| IMSI | International Mobile Subscriber Identity | The International Mobile Subscriber Identity is a unique identifier allocated to each mobile subscriber in a GSM, UMTS, LTE and 5G network. It consists of a MCC (Mobile Country Code), a MNC (Mobile Network Code) and a MSIN (Mobile Subscriber Identification Number). |
| LAI | Location Area Identity | The Location Area Identity uniquely identifies a LA (Location Area) within any PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network). It is comprised of the MCC (Mobile Country Code), MNC (Mobile Network Code) and the LAC (Location Area Code). |
| MCC | Mobile Country Code | The Mobile Country Code is a three digit number uniquely identifying a given country. It is utilized within numerous identities across 3GPP mobile networks, including the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity), LAI (Location Area Identity) and GUTI (Globally Unique Temporary ID). |
| MNC | Mobile Network Code | The Mobile Network Code is either a two or three digit number used to uniquely identify a given network from within a specified country ( MCC (Mobile Country Code)). The MNC is used as part of the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) and LAI (Location Area Identity) etc. |
| S1AP | S1 Application Protocol | S1AP is used between the eNB and the MME in order to support operations such as E-RAB (E-UTRAN Radio Access Bearer) Management, transfer of UE Context information, NAS Signalling transport, Paging and EPC based mobility. |
| TAC | Tracking Area Code | An element of the TAI which serves to uniquely identify the Tracking Area. |
| TAI | Timing Advance Index | The MS (Mobile Station) performing uplink or downlink packet transfer, will receive a packet uplink or downlink assignment message. This message will contain the MS assigned TAI and the PTCCH (Packet Timing Control Channel). The TAI specifies which PTCCH subchannel is to be used by the MS. |
| UE | User Equipment | The UMTS Subscriber or UE (User Equipment) is a combination of ME (Mobile Equipment) and SIM / USIM (Subscriber Identity Module / UMTS Subscriber Identity Module). |
Tracking Area
Tracking Area is a logical concept of an area where a user can move around without updating the MME. The network allocates a list with one or more TAs to the user. In certain operation modes, the UE may move freely in all TAs of the list without updating the MME. You can think of 'Tracking Area' as 'Routing Area' in UMTS.
Each eNobe broadcasts a special tracking area code (TAC) to indicate to which Tracking Area the eNodeB belong to and the TAC is unique within a PLMN. (Since PLMN is a unique number allocated to each of the system operator and TAC is a unique in a PLMN, if you combine these two numbers you would have a globally unique number. This number (PLMN + TAC) is called Tracking Area Identity (TAI)
UE stores a group of TAC and this group of TAC maintained in a UE is called Tracking Area List. UE does not need to go through Tracking Area Update procedure when it moves along this TAI.
Tracking Area Codes (TACs) or TAs: it is group of eNodeBs in one small area with maximum number of 100 eNodeBs. TAC and TAL planning is to determine the size of a TAC and TAL border. The TAC and TAL size is simply defined as the number of eNodeBs in the TAC or TACs in a TAL.
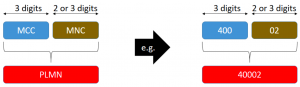
Public Land Mobile Network Identifier or with abbreviated version PLMN is a combination of MCC and MNC. It is unique value and globally used to identify the mobile network that a user subscribed.
MCC: Mobile Country Code is used in wireless telephone networks such as GSM, CDMA, WCDMA or LTE in order to identify mobile user belongs to which country. MCC consists of 3 decimal digits.
MNC Mobile Network Code The Mobile Network Code is either a two or three digit number used to uniquely identify a given network from within a specified country ( MCC (Mobile Country Code)). The MNC is used as part of the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) and LAI (Location Area Identity) etc.
SGW-U
Serving Gateway User plane function
The SGW-U is the user data plane ingress and egress point of the E-UTRAN side of the EPC when control and user plane separation is in place. As such, when the subscriber moves around the E-UTRAN, their point of attachment to the EPC remains fixed at the SGW-U (unless the network decides that a SGW-U relocation is required). A single subscriber may be supported by multiple SGW-U if connectivity to multiple PDNs are in place. Additional responsibilities include lawful interception of subscriber traffic, inter-operator accounting, as well as downlink data buffering whilst the subscriber is paged.
GTPU
GTP-U PROTOCOL
PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION The GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTP) is a group of IP-based communications protocols used within GSM, UMTS, LTE and 5G NR radio networks. GTP-U is used to carry user data inside mobile networks.
PFCP
Packet Forwarding Control Protocol (PFCP) is a 3GPP protocol used on the Sx/N4 interface between the control plane and the user plane function, specified in TS 29.244.[1] It is one of the main protocols introduced in the 5G Next Generation Mobile Core Network (aka 5GC[2]), but also used in the 4G/LTE EPC to implement the Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS).[3] PFCP and the associated interfaces seek to formalize the interactions between different types of functional elements used in the Mobile Core Networks as deployed by most operators providing 4G, as well as 5G, services to mobile subscribers