JAVA: Main thread di Java
Java menyediakan dukungan bawaan untuk pemrograman multithread. Program multithread berisi dua atau lebih bagian yang dapat berjalan secara bersamaan. Setiap bagian dari program semacam itu disebut thread, dan setiap thread menentukan jalur eksekusi yang terpisah.
Ketika program Java dijalankan, satu thread segera mulai berjalan. Ini biasanya disebut main thread dari program kita karena ini adalah thread yang dieksekusi ketika program kita dimulai.
Ada properti tertentu yang terkait dengan main thread, yaitu sebagai berikut:
- Ini adalah thread dari mana thread "child" lainnya akan muncul.
- Seringkali, itu harus menjadi thread terakhir untuk menyelesaikan eksekusi karena melakukan berbagai tindakan shutdown
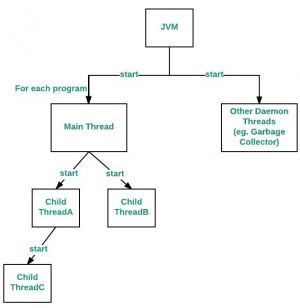
Flow Diagram adalah sebagai berikut:
Cara Mengontrol Main thread
Main thread dibuat secara otomatis ketika program kita dimulai. Untuk mengontrolnya kita harus mendapatkan referensi untuk itu. Ini dapat dilakukan dengan memanggil metode currentThread() yang ada di Thread Class. Method ini mengembalikan referensi ke thread yang dipanggil. Prioritas default dari main thread adalah 5 dan untuk semua prioritas user thread yang tersisa akan diwarisi dari parent ke child.
Contoh
// Java program to control the Main Thread
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Class 1
// Main class extending thread class
public class Test extends Thread {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Getting reference to Main thread
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// Getting name of Main thread
System.out.println("Current thread: "
+ t.getName());
// Changing the name of Main thread
t.setName("Geeks");
System.out.println("After name change: "
+ t.getName());
// Getting priority of Main thread
System.out.println("Main thread priority: "
+ t.getPriority());
// Setting priority of Main thread to MAX(10)
t.setPriority(MAX_PRIORITY);
// Print and display the main thread priority
System.out.println("Main thread new priority: "
+ t.getPriority());
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("Main thread");
}
// Main thread creating a child thread
Thread ct = new Thread() {
// run() method of a thread
public void run()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("Child thread");
}
}
};
// Getting priority of child thread
// which will be inherited from Main thread
// as it is created by Main thread
System.out.println("Child thread priority: "
+ ct.getPriority());
// Setting priority of Main thread to MIN(1)
ct.setPriority(MIN_PRIORITY);
System.out.println("Child thread new priority: "
+ ct.getPriority());
// Starting child thread
ct.start();
}
}
// Class 2
// Helper class extending Thread class
// Child Thread class
class ChildThread extends Thread {
@Override public void run()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// Print statement whenever child thread is
// called
System.out.println("Child thread");
}
}
}
Output
Current thread: main After name change: Geeks Main thread priority: 5 Main thread new priority: 10 Main thread Main thread Main thread Main thread Main thread Child thread priority: 10 Child thread new priority: 1 Child thread Child thread Child thread Child thread Child thread
Hubungan antara metghod main() dan main thread di Java adalah sebagai berikut. Untuk setiap program, main thread dibuat oleh JVM (Java Virtual Machine). Thread "Main" pertama-tama memverifikasi keberadaan metode main(), dan kemudian menginisialisasi Class. Perhatikan bahwa dari JDK 6, metode main() adalah wajib dalam aplikasi java mandiri.
Deadlocking with use of Main Thread(only single thread)
We can create a deadlock by just using the Main thread, i.e. by just using a single thread.
Kita dapat membuat kebuntuan hanya dengan menggunakan utas Utama, yaitu dengan hanya menggunakan satu utas.
Contoh
// Java program to demonstrate deadlock
// using Main thread
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Print statement
System.out.println("Entering into Deadlock");
// Joining the current thread
Thread.currentThread().join();
// This statement will never execute
System.out.println("This statement will never execute");
}
// Catch block to handle the exceptions
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Display the exception along with line number
// using printStackTrace() method
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Output:
Output explanation:
The statement “Thread.currentThread().join()”, will tell Main thread to wait for this thread(i.e. wait for itself) to die. Thus Main thread wait for itself to die, which is nothing but a deadlock.
Pernyataan "Thread.currentThread().join()", akan memberi tahu utas Utama untuk menunggu utas ini (yaitu menunggu dirinya sendiri) mati. Jadi utas Utama menunggu dirinya sendiri untuk mati, yang tidak lain adalah jalan buntu.