JAVA: Lifecycle & States dari Thread di Java
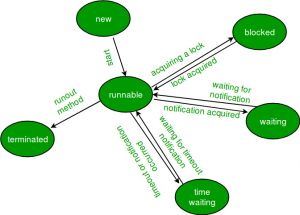
Sebuah thread di Java kapan saja ada di salah satu dari status berikut. Sebuah thread hanya terletak di salah satu status yang ditampilkan setiap saat:
- New
- Runnable
- Blocked
- Waiting
- Timed Waiting
- Terminated
Diagram yang ditunjukkan di bawah ini mewakili berbagai status thread setiap saat.
Life Cycle of a thread
- New Thread: When a new thread is created, it is in the new state. The thread has not yet started to run when the thread is in this state. When a thread lies in the new state, its code is yet to be run and hasn’t started to execute.
- Runnable State: A thread that is ready to run is moved to a runnable state. In this state, a thread might actually be running or it might be ready to run at any instant of time. It is the responsibility of the thread scheduler to give the thread, time to run. A multi-threaded program allocates a fixed amount of time to each individual thread. Each and every thread runs for a short while and then pauses and relinquishes the CPU to another thread so that other threads can get a chance to run. When this happens, all such threads that are ready to run, waiting for the CPU and the currently running thread lie in a runnable state.
- Blocked/Waiting state: When a thread is temporarily inactive, then it’s in one of the following states:
- Blocked
- Waiting
- Timed Waiting: A thread lies in a timed waiting state when it calls a method with a time-out parameter. A thread lies in this state until the timeout is completed or until a notification is received. For example, when a thread calls sleep or a conditional wait, it is moved to a timed waiting state.
- Terminated State: A thread terminates because of either of the following reasons:
- Because it exits normally. This happens when the code of the thread has been entirely executed by the program.
- Because there occurred some unusual erroneous event, like segmentation fault or an unhandled exception.
- New Thread: Saat thread baru dibuat, ia berada dalam status baru. Thread belum mulai berjalan saat thread dalam status ini. Saat thread berada di status baru, codenya belum dijalankan dan belum mulai dieksekusi.
- Runnable State: Sebuah thread yang siap dijalankan dipindahkan ke status runnable. Dalam keadaan ini, thread mungkin benar-benar berjalan atau mungkin siap untuk dijalankan kapan saja. Merupakan tanggung jawab penjadwal thread untuk memberikan thread, waktu untuk dijalankan. Program multi-thread mengalokasikan jumlah waktu yang tetap untuk setiap thread individu. Setiap thread berjalan untuk sementara waktu dan kemudian menjeda dan melepaskan CPU ke thread lain sehingga thread lain bisa mendapatkan kesempatan untuk berjalan. Ketika ini terjadi, semua thread yang siap dijalankan, menunggu CPU dan thread yang sedang berjalan berada dalam status dapat dijalankan.
- Blocked/Waiting state: Saat thread tidak aktif untuk sementara, maka thread tersebut berada di salah satu status berikut:
- Blocked
- Waiting
- Timed Waiting: Sebuah thread terletak pada status menunggu waktunya ketika memanggil method dengan parameter time-out. Sebuah thread terletak dalam status ini hingga batas waktu selesai atau hingga pemberitahuan diterima. Misalnya, ketika thread memanggil tidur atau menunggu bersyarat, itu dipindahkan ke status menunggu waktunya.
- Terminated State: Sebuah thread berakhir karena salah satu alasan berikut:
- Karena keluar secara normal. Ini terjadi ketika kode thread telah sepenuhnya dieksekusi oleh program.
- Karena terjadi beberapa kesalahan yang tidak biasa, seperti kesalahan segmentasi atau pengecualian yang tidak tertangani.
Implementing the Thread States in Java
Di Java, untuk mendapatkan status thread saat ini, gunakan method Thread.getState() untuk mendapatkan status thread saat ini. Java menyediakan Class java.lang.Thread.State yang mendefinisikan konstanta ENUM untuk status thread, sebagai ringkasannya diberikan di bawah ini:
1. New
Declaration: public static final Thread.State NEW
Deskripsi: Status Thread untuk Thread yang belum dimulai.
'2. Runnable
Declaration: public static final Thread.State RUNNABLE
Deskripsi: Status Thread untuk Thread yang dapat dijalankan. Sebuah Thread dalam keadaan runnable sedang dieksekusi di mesin virtual Java tetapi mungkin menunggu sumber daya lain dari sistem operasi seperti prosesor.
3. Blocked
Declaration: public static final Thread.State BLOCKED
Deskripsi: Status Thread untuk Thread yang diblokir menunggu kunci monitor. Sebuah Thread dalam status diblokir sedang menunggu kunci monitor untuk memasukkan block/method yang disinkronkan atau reenter ke block/method yang disinkronkan setelah memanggil Object.wait().
4. Waiting
Declaration: public static final Thread.State WAITING
Description: Thread state for a waiting thread. Thread state for a waiting thread. A thread is in the waiting state due to calling one of the following methods:
- Object.wait with no timeout
- Thread.join with no timeout
- LockSupport.park
5. Timed Waiting
Declaration: public static final Thread.State TIMED_WAITING
Description: Thread state for a waiting thread with a specified waiting time. A thread is in the timed waiting state due to calling one of the following methods with a specified positive waiting time:
- Thread.sleep
- Object.wait with timeout
- Thread.join with timeout
- LockSupport.parkNanos
- LockSupport.parkUntil
6. Terminated
Declaration: public static final Thread.State TERMINATED
Description: Thread state for a terminated thread. The thread has completed execution.
4. Waiting
Declaration: public static final Thread.State WAITING
Deskripsi: Status utas untuk utas menunggu. Status utas untuk utas menunggu. Sebuah utas dalam status menunggu karena memanggil salah satu metode berikut:
- Object.wait with no timeout
- Thread.join with no timeout
- LockSupport.park
5. Timed Waiting
Declaration: public static final Thread.State TIMED_WAITING
Deskripsi: Status utas untuk utas menunggu dengan waktu tunggu yang ditentukan. Sebuah thread berada dalam status menunggu waktunya karena memanggil salah satu metode berikut dengan waktu tunggu positif yang ditentukan:
- Thread.sleep
- Object.wait with timeout
- Thread.join with timeout
- LockSupport.parkNanos
- LockSupport.parkUntil
6. Terminated
Declaration: public static final Thread.State TERMINATED
Deskripsi: Status utas untuk utas yang dihentikan. Utas telah menyelesaikan eksekusi.
// Java program to demonstrate thread states
class thread implements Runnable {
public void run()
{
// moving thread2 to timed waiting state
try {
Thread.sleep(1500);
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(
"State of thread1 while it called join() method on thread2 -"
+ Test.thread1.getState());
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class Test implements Runnable {
public static Thread thread1;
public static Test obj;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
obj = new Test();
thread1 = new Thread(obj);
// thread1 created and is currently in the NEW
// state.
System.out.println(
"State of thread1 after creating it - "
+ thread1.getState());
thread1.start();
// thread1 moved to Runnable state
System.out.println(
"State of thread1 after calling .start() method on it - "
+ thread1.getState());
}
public void run()
{
thread myThread = new thread();
Thread thread2 = new Thread(myThread);
// thread1 created and is currently in the NEW
// state.
System.out.println(
"State of thread2 after creating it - "
+ thread2.getState());
thread2.start();
// thread2 moved to Runnable state
System.out.println(
"State of thread2 after calling .start() method on it - "
+ thread2.getState());
// moving thread1 to timed waiting state
try {
// moving thread1 to timed waiting state
Thread.sleep(200);
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(
"State of thread2 after calling .sleep() method on it - "
+ thread2.getState());
try {
// waiting for thread2 to die
thread2.join();
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(
"State of thread2 when it has finished it's execution - "
+ thread2.getState());
}
}
Output
State of thread1 after creating it - NEW State of thread1 after calling .start() method on it - RUNNABLE State of thread2 after creating it - NEW State of thread2 after calling .start() method on it - RUNNABLE State of thread2 after calling .sleep() method on it - TIMED_WAITING State of thread1 while it called join() method on thread2 -WAITING State of thread2 when it has finished it's execution - TERMINATED
Explanation: When a new thread is created, the thread is in the NEW state. When the start() method is called on a thread, the thread scheduler moves it to Runnable state. Whenever the join() method is called on a thread instance, the current thread executing that statement will wait for this thread to move to the Terminated state. So, before the final statement is printed on the console, the program calls join() on thread2 making the thread1 wait while thread2 completes its execution and is moved to the Terminated state. thread1 goes to Waiting state because it is waiting for thread2 to complete its execution as it has called join on thread2.
Penjelasan: Saat utas baru dibuat, utas tersebut dalam status BARU. Saat metode start() dipanggil pada sebuah utas, penjadwal utas memindahkannya ke status Runnable. Setiap kali metode join() dipanggil pada instance utas, utas saat ini yang mengeksekusi pernyataan itu akan menunggu utas ini pindah ke status Dihentikan. Jadi, sebelum pernyataan terakhir dicetak di konsol, program memanggil join() pada thread2 membuat thread1 menunggu sementara thread2 menyelesaikan eksekusinya dan dipindahkan ke status Dihentikan. thread1 masuk ke status Menunggu karena menunggu thread2 untuk menyelesaikan eksekusinya seperti yang disebut join di thread2.