JAVA: Exception
Exception Handling di Java adalah salah satu cara yang efektif untuk menangani kesalahan runtime sehingga aliran reguler aplikasi dapat dipertahankan. Java Exception Handling adalah mekanisme untuk menangani kesalahan runtime seperti ClassNotFoundException, IOException, SQLException, RemoteException, dll.
Exception adalah peristiwa yang tidak diinginkan atau tidak terduga, yang terjadi selama eksekusi program yaitu pada saat dijalankan, yang mengganggu aliran normal instruksi program. Exception dapat ditangkap dan ditangani oleh program. Ketika exception terjadi dalam suatu method, ini akan menciptakan sebuah object. Object ini disebut exception object. Ini berisi informasi tentang exception seperti nama dan deskripsi exception dan status program saat exception terjadi.
Penyebab utama mengapa sebuah exception terjadi
- Input user yang salah/invalid
- Kegagalan Device
- Loss dari sambungan network
- Keterbatasan fisik (out of disk memory)
- Error code
- Membuka file yang tidak ada
Errors mewakili kondisi yang tidak dapat dipulihkan seperti Java virtual machine (JVM) kehabisan memori, memory leaks, stack overflow errors, library incompatibility, infinite recursion, dll. Kesalahan biasanya di luar kendali programmer dan kita sebaiknya tidak mencoba menangani error.
Mari kita bahas bagian terpenting yang merupakan perbedaan antara Error dan Exception yaitu sebagai berikut:
- Error: Kesalahan menunjukkan masalah serius yang sebaiknya tidak ditangkap oleh aplikasi yang baik.
- Exception: menunjukkan kondisi yang mungkin dapat / dicoba ditangkap oleh aplikasi yang wajar.
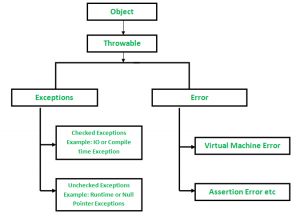
Hirarki Exception
Semua jenis exception dan error adalah subclass dari class Throwable, yang merupakan base class dari sebuah hirarki. Satu cabang adalah Exception. Class ini digunakan untuk kondisi luar biasa yang harus ditangkap oleh program. NullPointerException adalah contoh pengecualian semacam itu. Cabang lain, Error digunakan oleh Java run-time system (JVM) untuk menunjukkan error yang berkaitan dengan run-time environment itu sendiri (JRE). StackOverflowError adalah contoh error tersebut.
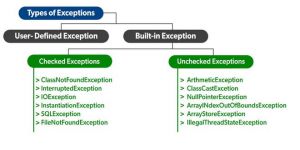
Tipe Exception
Java mendefinisikan beberapa jenis exception yang berhubungan dengan berbagai class library. Java juga memungkinkan pengguna untuk menentukan exception mereka sendiri.
Exception dapat di kategorikan dalam dua hal:
- Built-in Exception
- Checked Exception
- Unchecked Exception
- User-Defined Exception
Mari kita bahas pengecualian terdaftar yang ditentukan di atas yaitu sebagai berikut:
Built-in Exception:
Built-in exception adalah exception yang tersedia di Java Library. Exception ini cocok untuk menjelaskan situasi error tertentu.
- Checked Exception: Exception yang diperiksa disebut compile-time exception karena exception ini diperiksa pada waktu kompilasi oleh kompiler.
- Unchecked Exception: Unchecked exception berlawanan dengan Checked exception. Kompiler tidak akan memeriksa exception ini pada waktu kompilasi. Dengan kata sederhana, jika sebuah program mengeluarkan unchecked exception, dan bahkan jika kita tidak menangani atau mendeklarasikannya, program tersebut tidak akan memberikan error kompilasi.
User-Defined Exception:
Terkadang, built-in exception di Java tidak dapat menggambarkan situasi tertentu. Dalam kasus seperti itu, pengguna juga dapat membuat exception yang disebut 'user-defined Exception'.
Kelebihan Exception Handling di Java adalah sebagai berikut:
- Ketentuan untuk Menyelesaikan Eksekusi Program
- Identifikasi Kode Program dan Kode Penanganan Error yang Mudah
- Penyebaran Kesalahan
- Pelaporan Kesalahan yang Berarti
- Mengidentifikasi Jenis Kesalahan
Bagaimana JVM menangani Exception?
Default Exception Handling: Whenever inside a method, if an exception has occurred, the method creates an Object known as an Exception Object and hands it off to the run-time system(JVM). The exception object contains the name and description of the exception and the current state of the program where the exception has occurred. Creating the Exception Object and handling it in the run-time system is called throwing an Exception. There might be a list of the methods that had been called to get to the method where an exception occurred. This ordered list of the methods is called Call Stack. Now the following procedure will happen.
Penanganan Pengecualian Default: Kapan pun di dalam suatu metode, jika pengecualian telah terjadi, metode tersebut membuat Objek yang dikenal sebagai Objek Pengecualian dan menyerahkannya ke sistem run-time (JVM). Objek pengecualian berisi nama dan deskripsi pengecualian dan status program saat ini di mana pengecualian telah terjadi. Membuat Objek Pengecualian dan menanganinya dalam sistem run-time disebut melempar Pengecualian. Mungkin ada daftar metode yang dipanggil untuk sampai ke metode di mana pengecualian terjadi. Daftar metode yang diurutkan ini disebut Call Stack. Sekarang prosedur berikut akan terjadi.
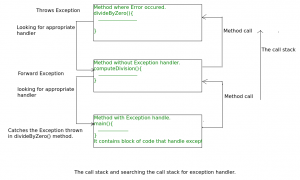
- The run-time system searches the call stack to find the method that contains a block of code that can handle the occurred exception. The block of the code is called an Exception handler.
- The run-time system starts searching from the method in which the exception occurred, and proceeds through the call stack in the reverse order in which methods were called.
- If it finds an appropriate handler then it passes the occurred exception to it. An appropriate handler means the type of the exception object thrown matches the type of the exception object it can handle.
- If the run-time system searches all the methods on the call stack and couldn’t have found the appropriate handler then the run-time system handover the Exception Object to the default exception handler, which is part of the run-time system. This handler prints the exception information in the following format and terminates the program abnormally.
- Sistem run-time mencari tumpukan panggilan untuk menemukan metode yang berisi blok kode yang dapat menangani pengecualian yang terjadi. Blok kode tersebut disebut Exception handler.
- Sistem run-time mulai mencari dari metode di mana pengecualian terjadi, dan melanjutkan melalui tumpukan panggilan dalam urutan terbalik di mana metode dipanggil.
- Jika menemukan penangan yang sesuai maka melewati pengecualian yang terjadi padanya. Handler yang sesuai berarti jenis objek pengecualian yang dilempar cocok dengan jenis objek pengecualian yang dapat ditanganinya.
- Jika sistem run-time mencari semua metode pada tumpukan panggilan dan tidak dapat menemukan handler yang sesuai, maka sistem run-time akan menyerahkan Objek Pengecualian ke handler eksepsi default, yang merupakan bagian dari sistem run-time. Handler ini mencetak informasi pengecualian dalam format berikut dan menghentikan program secara tidak normal.
Exception in thread "xxx" Name of Exception : Description ... ...... .. // Call Stack
Look at the below diagram to understand the flow of the call stack.
Illustration:
// Java Program to Demonstrate How Exception Is Thrown
// Class
// ThrowsExecp
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Taking an empty string
String str = null;
// Getting length of a string
System.out.println(str.length());
}
}
Output:
Let us see an example that illustrates how a run-time system searches for appropriate exception handling code on the call stack.
Contoh:
// Java Program to Demonstrate Exception is Thrown
// How the runTime System Searches Call-Stack
// to Find Appropriate Exception Handler
// Class
// ExceptionThrown
class GFG {
// Method 1
// It throws the Exception(ArithmeticException).
// Appropriate Exception handler is not found
// within this method.
static int divideByZero(int a, int b)
{
// this statement will cause ArithmeticException
// (/by zero)
int i = a / b;
return i;
}
// The runTime System searches the appropriate
// Exception handler in method also but couldn't have
// found. So looking forward on the call stack
static int computeDivision(int a, int b)
{
int res = 0;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
res = divideByZero(a, b);
}
// Catch block to handle NumberFormatException
// exception Doesn't matches with
// ArithmeticException
catch (NumberFormatException ex) {
// Display message when exception occurs
System.out.println(
"NumberFormatException is occurred");
}
return res;
}
// Method 2
// Found appropriate Exception handler.
// i.e. matching catch block.
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a = 1;
int b = 0;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
int i = computeDivision(a, b);
}
// Catch block to handle ArithmeticException
// exceptions
catch (ArithmeticException ex) {
// getMessage() will print description
// of exception(here / by zero)
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
Output
/ by zero