Orange: Distances
Sumber: https://docs.biolab.si//3/visual-programming/widgets/unsupervised/distances.html
Menghitung distance antara baris/kolom di dataset.
Input
Data: input dataset
Output
Distances: distance matrix
Widget Distances menghitung jarak antara baris atau kolom dalam dataset. Secara default, data akan dinormalisasi untuk memastikan perlakuan yang sama atas individual feature. Normalisasi selalu dilakukan column-wise (menggunakan kolom sebagai referensi).
Sparse data hanya bisa digunakan dengan Euclidean, Manhattan dan Cosine metric.
Matrix distance yang dihasilkan dapat diumpankan lebih lanjut ke Hierarchical Clustering untuk mengungkap group dalam data, ke Distance Map atau Distance Matrix untuk memvisualisasikan jarak (Distance Matrix bisa sangat lambat untuk dataset yang besar), ke MDS untuk memetakan contoh data menggunakan matrix distance dan akhirnya, disimpan dengan Save Distance Matrix. Distance File dapat di load dengan Distance File.
Distances juga bekerja dengan baik dengan add-on Orange. Distance Matrix dapat diumpankan ke Network from Distances (Network add-on) untuk mengubah matrix menjadi graph dan ke Duplicate Detection (Text add-on) untuk menemukan duplikasi dokumen dalam corpus.
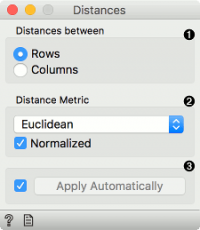
- Choose whether to measure distances between rows or columns.
- Choose the Distance Metric:
- Euclidean (“straight line”, distance between two points)
- Manhattan (the sum of absolute differences for all attributes)
- Cosine (the cosine of the angle between two vectors of an inner product space)
- Jaccard (the size of the intersection divided by the size of the union of the sample sets)
- Spearman(linear correlation between the rank of the values, remapped as a distance in a [0, 1] interval)
- Spearman absolute(linear correlation between the rank of the absolute values, remapped as a distance in a [0, 1] interval)
- Pearson (linear correlation between the values, remapped as a distance in a [0, 1] interval)
- Pearson absolute (linear correlation between the absolute values, remapped as a distance in a [0, 1] interval)
- Hamming (the number of features at which the corresponding values are different)
- Bhattacharyya distance (Similarity between two probability distributions, not a real distance as it doesn’t obey triangle inequality.)
- Normalize the features. Normalization is always done column-wise. Values are zero centered and scaled. In case of missing values, the widget automatically imputes the average value of the row or the column. The widget works for both numeric and categorical data. In case of categorical data, the distance is 0 if the two values are the same (‘green’ and ‘green’) and 1 if they are not (‘green’ and ‘blue’).
- ick Apply Automatically to automatically commit changes to other widgets. Alternatively, press ‘Apply’.
Contoh
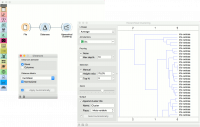
The first example shows a typical use of the Distances widget. We are using the iris.tab data from the File widget. We compute distances between data instances (rows) and pass the result to the Hierarchical Clustering. This is a simple workflow to find groups of data instances.
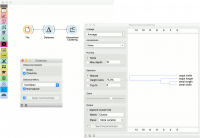
Alternatively, we can compute distance between columns and find how similar our features are.
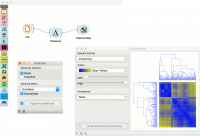
The second example shows how to visualize the resulting distance matrix. A nice way to observe data similarity is in a Distance Map or in MDS.