Keamanan e-Mail dari Phishing
You may have come across the word phishing, but never really bothered to know about it. You have probably been phished without even knowing it yourself. Most people who have fallen victim of this unlawful act do not even know that their personal information has been stolen while on the internet. Simply put, phishing is a term used to describe an internet fraud carried out via email spoofing or some other forms of instant messaging in an attempt to acquire sensitive personal information, often for malicious reasons, by masquerading as a trustworthy entity. It is typically accomplished by contacting users with fake messages directing them to divulge their personal information such as credit card numbers, passwords, etc.
As millions of emails are sent every single day, there is a great likelihood of receiving a good number of these phishing emails and I do hope you did not fall into their trap!
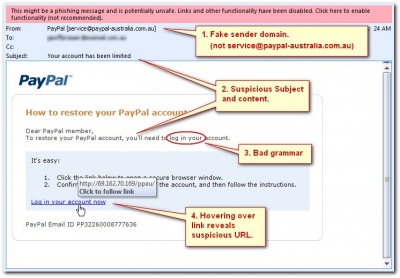
A good number of these phishing emails, mask themselves as top organizations as a good way of getting your attention. Some may even claim to be companies or sites, which you do not even hold an account with, which is why as an internet user, you should be observant. These phishers usually get their victims by sending them a link, often infected with malware, which they would click on, that, would take them to a site where their personal information is requested. Examples of Email Phishing
A common phishing practice usually employed is by spamming the recipients with messages under the name of a trusted organization. The main objective of these fake messages is to coerce the unsuspecting individuals to divulge all their private data. People who respond to these phishing emails put themselves and their organizations, in the case of employees, in great danger and pose a great risk on the computing devices that are in use. There are various forms of each, and new ones are being modified and sent out each day. The following is an example of a phishing fraud email that is floating around the internet:
phishing email signs
These types of phishing emails contain links, which will lead you to web pages with malicious codes and virus prowling in the background to affect your computers, stealing your personal data amongst other information. This is the reason why today, there is a need for the adequate understanding of identifying phish emails.
How to Identify Email Phishing?
Most of the time, it is not as easy as most people think, to spot an email phishing made to steal your personal information and identity. These phishers are experts in this field that the majority of people fall easily. Therefore, the only way out is to educate yourself and get knowledge of all sophisticated techniques they use in phishing emails. To make sure that you are not a victim of such phish mail, there are signs to check for it. They are-
The hyperlinks: This is perhaps the most comfortable way to spot phishers. When you take the cursor over the link in an email (in the FROM column), usually the complete and authentic URL would appear. E.g., an email from PayPal team should have its email address contains official domain name as “@paypal.com” and not something different. If this link does not match with what is written in an email, then it is certainly suspicious and it is suggested that you do not navigate further. Grammatical errors: If you have been looking for something to prove that the website or the email is not genuine, then you are likely to find it, as cyber criminals are associated with poor English grammar. The banks and the credit card organizations have their departments to assure that anything issued is grammatically correct, mostly to maintain the image of the enterprise. Although it is easy to find an illegitimate email, that is made to trick less informed users. If a user responds to fake email, it is a clear sign that attackers will try to infect the system in near future. The HTTPS: Most enterprises and banks carry out internet transactions with a safe connection in place. In an email, If you are being directed to the bank’s website and the URL bar is not showing “HTTPS” then, it is a sign that you should close the window. Also, look out for the padlock logo, which appears alongside the address bar. The SSL security certificate can be viewed by clicking on the bar. SSL generally secures ongoing information sent by the customer to the website server. Plain text / Absence of logos: Most legitimate messages are written in HTML including a mix of text and images. Many times, phishing e-mails have not images or company logo. If the written mail carries only text, looks suspicious, and pretends to be coming from the usual user, you should ignore such emails. Urgent / Too good to be true: Most of the time, these email phishers send you emails asking you to provide your personal information with a tone of urgency. They make you worry that something has bad happened and urge you to act quickly. The faster hackers get your information, the faster it is for them to move on to another victim. A typical example is a message saying, “click here” and entices users to deposit money into the bank account, which looks like a fraud and should be marked as “junk”. Listed at your email address: If you observe that your email address is in the category of the sender instead of the receiver, then it is a sign of a fake email message. Along the same line, if there is a large list of recipients on the ‘To’ section or ‘undisclosed recipients’, you should also be careful. Genuine emails will most possibly be sent directly only to you.
Email Safety Tips
Though the Email is a quick and secure medium for sending and receiving lots of information, it is, important that your personal information is kept secure and that you are not open to viruses or phishers. Below are a number of safety tips to help you stay secure when using the email.
Chose a secure password: It is a suggestion to ensure that when creating a password for your email account, that you make sure your password is minimum eight characters long. You also do this using a combination of uppercase and lowercase characters and minimum one number and/or symbol. Avoid using predictable passwords like ‘password’ or even your name, as these are often the first guesses for hackers/phishers. In addition, you should never try to use the same password across multiple accounts, i.e. using the same password for your email login and bank account login. Change your password regularly: As a recommendation, you should change your password every 60 daysto make sure your email account is secured and this is especially if you regularly log into your email account on publicly available computers. Be sure sign off & don’t save password: Ensure to log out from your account after going through your email. This is especially important whenever you use a public system like in a café. You should not click the ‘save your password’ tab when you are using a public computer to access your email. By clicking save, it saves your password and keep you logged in even after you have closed the system, thus, allowing other users to access to your account. Avoid spam emails: Do not open emails sent by someone you do not know or trust. Follow your instincts! Report the message as spam or drag to the junk section and move on. You should never reply to such emails or click on the links in them because by doing any of that or even delisting from such emails, you are simply informing the sender (phishers) that your email is active to receive more spam emails. Safe senders: By creating a safe senders list, you can be sure that only safe emails will enter your inbox. This will allow only the email address of people you know and trust to enter your inbox. Every other sender not on your list will automatically end up in your junk folder. Don’t share personal data: If you do receive any correspondence that claims to come from your bank, it is best you telephone your branch to confirm it and talk about the matter over the telephone instead. Never share confidential information such as passwords, bank details, and social security numbers via email. Always remember that whenever you send an email message, you have lost control over what is done with it or to whom it gets. Antivirus Software: Make sure that you have installed antivirus software and always keep it up to date. Norton is a good alternative that secures your PCs, Macs, Androids and iOS devices from virus, spyware, malware & phishing. Use dissimilar emails: Do not use the same email address for personal and public use. By this, I mean setting up a second email account for registering for public websites like online shopping sites, and signing up for a new service like newsletters. This will limit the amount of spam (as it is unavoidable) that your personal email account will receive. Update web browser timely: It is also advisable to update your web browser from time to time as security updates are often introduced to the latest web browsers hence, preventing malicious attacks on email accounts. Google Chrome is often thought of as one of the most secure web browsers available. Stay away from pop-up: You should never enter your personal information into a pop-up screen. Phishers sometimes direct unsuspecting individuals to a real organization’s website, but then an unapproved pop-up screen, which they created, will appear, with blanks asking you to provide your personal information. As a remedy to this, installing pop-up blocking software will help prevent this type of phishing attack. In addition, reporting such phishing emails to the companies that are being impersonated will also help to fight against the phishers.
Conclusion
Despite the advancements in IT, unfortunately, phishing continues to be a delinquent issue for individuals and companies worldwide as it creates a problem of mistrust between both the company and the user. More so, in the case of organizations, compromised accounts not only pose a threat to their IT or security department but also leads to a decline in trust and loyalty for the brand, hence, affecting their marketing/sales amongst others.
Even as people and businesses are becoming more attentive to their online security, the phishing professionals are changing techniques! Summarily, continuously arming ourselves with better knowledge of email phishing is the only chance we have against this menace, as it will help us stay ahead of the latest online threats to put an end to these sham.