JAVA: Perintah Continue di Java
Misalkan seseorang ingin code di jalankan untuk nilai-nilai variabel sesuai code yang dirancang untuk di jalankan tetapi dengan paksa pengguna yang sama ingin melewatkan eksekusi kode yang seharusnya dieksekusi seperti yang dirancang tetapi tidak akan sesuai permintaan pengguna. Dengan kata lain, ini adalah masalah pengambilan keputusan sesuai permintaan pengguna.
Contoh Real-Life:
Bayangkan seorang pria memanjat untuk pergi ke rumahnya melalui 11 anak tangga. Karena terburu-buru untuk memanjat, dia langsung menaiki 3 anak tangga dan kemudian 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 dan melompat ke tangga terakhir. Selama ini dia melewatkan tangga 1, 2 dan 10 dan dia menyelesaikan tujuannya untuk mencapai rumahnya. Dia melanjutkan perjalanannya melewati tangga yang dia pilih.
Di komputer, ini menafsirkan tangga yang/seharusnya dilewati sebagai 'continue'. Tindakan untuk melewatkan eksekusi yang seharusnya dieksekusi, ditafsirkan sebagai pernyataan continue di bahasa pemrograman mana pun.
Pernyataan continue sering digunakan di dalam bahasa pemrograman di dalam struktur kontrol loop. Di dalam loop, ketika pernyataan continue ditemukan, kontrol langsung melompat ke awal loop untuk iterasi berikutnya daripada menjalankan pernyataan dari iterasi saat tersebut. Pernyataan continue digunakan ketika kita ingin melewati kondisi tertentu dan melanjutkan eksekusi lainnya. Pernyataan continue Java digunakan untuk semua jenis perulangan tetapi umumnya digunakan dalam perulangan for, while, dan do-while.
- Dalam kasus for loop, kata kunci continue memaksa kontrol untuk langsung melompat ke perintah update.
- Sedangkan dalam kasus while loop atau perulangan do-while, kontrol langsung melompat ke ekspresi Boolean.
Sintaks: continue kata kunci bersama dengan titik koma
continue;
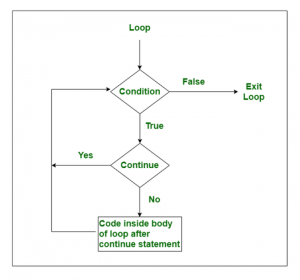
Flow Chart dari Pernyataan Continue
Diagram alur di atas paling penting untuk memahami keyword ini. Selalu ingat kondisi selalu ditempatkan di dalam kotak ketupat dan pernyataan dalam kotak persegi panjang. Dilanjutkan melompat ke bagian implementasi
Case 1: Continue statement inside for loop
In this program, illustration for how to use the continue statement within For loop. When the value of ‘i’ becomes 10 or 12, the continue statement plays its role and skip their execution but for other values of’ ‘i’ the loop will run smoothly.
// Java Program to illustrate the use of continue statement
// Importing Classes/Files
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// For loop for iteration
for (int i = 0; i <= 15; i++) {
// Check condition for continue
if (i == 10 || i == 12) {
// Using continue statement to skip the
// execution of loop when i==10 or i==12
continue;
}
// Printing elements to show continue statement
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
}
Output :
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 13 14 15
Case 2: Continue statement inside while loop
In the above program, we give example, how to use the continue statement within the While loop. When the value of count becomes 7 or 15, the continue statement plays its role and skip their execution but for other values of the count, the loop will run smoothly.
// Java Program to illustrate the use of continue statement
// inside the While loop
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initializing a variable say it count to a value
// greater than the value greater among the loop
// values
int count = 20;
// While loop for iteration
while (count >= 0) {
if (count == 7 || count == 15) {
count--;
// Decrementing variable initialized above
// Showing continue execution inside loop
// skipping when count==7 or count==15
continue;
}
// Printing values after continue statement
System.out.print(count + " ");
// Decrementing the count variable
count--;
}
}
}
Output:
20 19 18 17 16 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Case 3: Continue statement inside do while loop
In the above program, we give example, how to use the continue statement within the do-While loop. When the value of i becomes 4 or 18, the continue statement plays its role and skip their execution but for other values of i, the loop will run smoothly.
// Java Program to illustrate the use of continue statement
// inside the Do-While loop
// Importing generic Classes/Files
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating and Initializing a variable
int i = 0;
// Do-While loop for iteration
do {
if (i == 4 || i == 18) {
// Incrementing loop variable by 2
i += 2;
// Illustrating continue statement skipping
// the execution when i==7 or i==15
continue;
}
// Printing to showcase continue affect
System.out.println(i);
// Incrementing variable by 2
i += 2;
// Condition check
} while (i <= 35);
}
}
Output:
0 2 6 8 10 12 14 16 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34
Case 4: Continue statement inside Inner loop(Nested Loop)
In the above program, we give example, how to use the continue statement within Nested loops. When the value of i becomes 3 and j become 2, the continue statement plays its role and skip their execution but for other values of i and j, the loop will run smoothly.
Dalam program di atas, kami memberikan contoh, bagaimana menggunakan pernyataan continue dalam loop bersarang. Ketika nilai i menjadi 3 dan j menjadi 2, pernyataan continue memainkan perannya dan melewatkan eksekusinya tetapi untuk nilai i dan j lainnya, loop akan berjalan dengan lancar.
// Java Program to illustrate the use of continue statement
// inside an inner loop or simply nested loops
// Importing generic Classes/Files
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
// Main drive method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Outer loop for iteration
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
// Inner loop for iteration
for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
if (i == 3 && j == 2) {
// Continue statement in inner loop to
// skip the execution when i==3 and j==2
continue;
}
// Print elements to showcase keyword affect
System.out.println(i + " * " + j);
}
}
}
}
Output:
1 * 1 1 * 2 1 * 3 2 * 1 2 * 2 2 * 3 3 * 1 3 * 3 4 * 1 4 * 2 4 * 3