Difference between revisions of "5G Daftar Istilah"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
! Istilah !! Istilah Panjang | ! Istilah !! Istilah Panjang | ||
! Penjelasan | ! Penjelasan | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 4G | ||
| + | | Fourth Generation | ||
| + | | 4G is the term given to the fourth generation of mobile communication systems, offering significantly advanced data rates across an all IP based bearer network. The main technology behind 4G is LTE (Long Term Evolution), although HSPA (High Speed Packet Access) networks and WiMAX based network may also be given the 4G label. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 5G | ||
| + | | Fifth Generation | ||
| + | | 5G is the term given to the fifth generation of mobile communication technology. Work began within the 3GPP on the first Release 15 specification for 5G, termed the NexGen (Next Generation) architecture in December 2016. The 5G NR (New Radio) standardization work is also in the development process, with the first phase of expected 5G deployments based on Release 15 due in 2020. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 5GC | | 5GC | ||
| Line 117: | Line 125: | ||
| Universal Mobile Telecommunications System | | Universal Mobile Telecommunications System | ||
| A 3G mobile communication system which supports improved data rates over GSM and subsequently provides an enhanced range of multimedia services. UMTS has increased convergence between telecommunications, IT (Information technology), media and content industries to deliver new services and create fresh revenue generating opportunities. UMTS delivers low cost, high capacity mobile communications, offering data rates as high as 2Mbps (under ideal conditions) with global roaming and other advanced capabilities. The specifications defining UMTS are formulated by the 3GPP. | | A 3G mobile communication system which supports improved data rates over GSM and subsequently provides an enhanced range of multimedia services. UMTS has increased convergence between telecommunications, IT (Information technology), media and content industries to deliver new services and create fresh revenue generating opportunities. UMTS delivers low cost, high capacity mobile communications, offering data rates as high as 2Mbps (under ideal conditions) with global roaming and other advanced capabilities. The specifications defining UMTS are formulated by the 3GPP. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | WiFi | ||
| + | | Wireless Fidelity | ||
| + | | WiFi is an interoperability standard developed by the WiFi Alliance and issued to those manufacturers whose IEEE 802.11 equipment has passed a suite of basic interoperability tests. Equipment passing these tests carries the WiFi logo. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| X2AP | | X2AP | ||
Revision as of 05:11, 29 December 2022
Berbagai istilah yang digunakan dalam 5G dilihat di
https://www.mpirical.com/glossary/
Berikut adalah beberapa yang digunakan disini yang di beri keterangan dalam bahasa Indonesia.
| Istilah | Istilah Panjang | Penjelasan |
|---|---|---|
| 4G | Fourth Generation | 4G is the term given to the fourth generation of mobile communication systems, offering significantly advanced data rates across an all IP based bearer network. The main technology behind 4G is LTE (Long Term Evolution), although HSPA (High Speed Packet Access) networks and WiMAX based network may also be given the 4G label. |
| 5G | Fifth Generation | 5G is the term given to the fifth generation of mobile communication technology. Work began within the 3GPP on the first Release 15 specification for 5G, termed the NexGen (Next Generation) architecture in December 2016. The 5G NR (New Radio) standardization work is also in the development process, with the first phase of expected 5G deployments based on Release 15 due in 2020. |
| 5GC | 5G Core Network | The 5G Core (3GPP) includes various functions: AUSF (Authentication Server Function), AMF (Core Access and Mobility Management Function), DN (Data Network), DSF (Data Storage Network Function), NRF (NF Repository Function), PCF (Policy Control Function), SMF (Session Management Function), UDM (Unified Data Management) and UPF (User Plane Function). |
| 5G NAS | 5G Non Access Stratum | The 5G NAS (Non-Access Stratum) includes procedures related to 5GMM (5GS Mobility Management) and 5GSM (5GS Session Management) on the 5GS (5G system). |
| 5G RAN | 5G Radio Access Network | The 5G Radio Access Network identifies a radio access network that connects to the 5GC (5G Core). Examples include the 5G New Radio and radio systems with New Radio extensions. |
| AMF | Authentication Management Field | AMF is a term used within the UMTS AKA (Authentication and Key Agreement) architecture. The AMF is a 16 bit value which is used to set the acceptable synchronization window in both the UE (User Equipment) and the network. |
| AUSF | Authentication Server Function | The Authentication Server Function is part of the 3GPP 5G Architecture. It is used to facilitate 5G security processes. |
| eNB | Evolved Node B | The eNB serves as the base station within the E-UTRAN, terminating the air interface on the network side. Consequently, the eNB is responsible for all radio resource management, as well as allocation of user traffic to the downlink/uplink, security and relaying of higher layer NAS (Non Access Stratum) signalling to the MME (Mobility Management Entity). The eNB is also capable of conducting an inter eNB handover procedure via the X2 interface. |
| EPC | Evolved Packet Core | Evolution of the core network started with Release 4. This provided the starting point for the introduction of IP into the CS domain of the core network as well as enhancements to enable real time and non real time services to be successfully integrated onto a common transport medium. In Release 8 of the 3GPP standards the functionality of the core network is made flatter with much of the intelligence required to support service delivery being placed within domains such as the IMS. Consequently the EPC comprises of the MME (Mobility Management Entity) that performs many of the mobility functions traditionally provided by the SGSN such as paging, security and Idle Mode procedures. EPC also includes the S-GW (Serving Gateway), which replaces the User Plane functionality of the SGSN, as well as the PDN-GW (Packet Data Network Gateway), which terminates the user plane within the EPC. |
| gNB | Next Generation Node B | The gNB is a 3GPP 5G Next Generation base station which supports the 5G New Radio. |
| GUMMEI | Globally Unique MME Identifier | The GUTI (Globally Unique Temporary Identity) has two main components, the GUMMEI (Globally Unique MME Identifier) that uniquely identifies the MME that allocated the GUTI and the M-TMSI (M-Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity) that provides for an unambiguous identity of the UE within this MME. |
| GUTI | Globally Unique Temporary ID | In LTE the GUTI is allocated to the UE by the MME and has two components. These are the GUMMEI (Globally Unique MME ID) and the M-TMSI (MME-TMSI). While the GUMMEI identifies the MME, the M-TMSI identifies the UE within the MME. |
| GTP-U | GPRS Tunnelling Protocol User | GPRS Tunnelling Protocol – User plane messages are exchanged between GSN (Gateway Support Node) pairs or GSN/ RNC (Radio Network Controller) pairs in a path. The user plane messages are used to carry user data packets, and signalling messages for path management and error indication. The GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTP) is a group of IP-based communications protocols used within GSM, UMTS, LTE and 5G NR radio networks. GTP-U is used to carry user data inside mobile networks. |
| IMSI | International Mobile Subscriber Identity | The International Mobile Subscriber Identity is a unique identifier allocated to each mobile subscriber in a GSM, UMTS, LTE and 5G network. It consists of a MCC (Mobile Country Code), a MNC (Mobile Network Code) and a MSIN (Mobile Subscriber Identification Number). |
| LAI | Location Area Identity | The Location Area Identity uniquely identifies a LA (Location Area) within any PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network). It is comprised of the MCC (Mobile Country Code), MNC (Mobile Network Code) and the LAC (Location Area Code). |
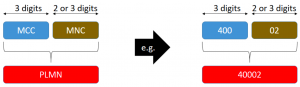
| MCC | Mobile Country Code | The Mobile Country Code is a three digit number uniquely identifying a given country. It is utilized within numerous identities across 3GPP mobile networks, including the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity), LAI (Location Area Identity) and GUTI (Globally Unique Temporary ID).
Mobile Country Code is used in wireless telephone networks such as GSM, CDMA, WCDMA or LTE in order to identify mobile user belongs to which country. MCC consists of 3 decimal digits. |
| MME | Mobility Management Entity | The MME is responsible for mobility and session management procedures in the EPC. As such, the MME communicates with the mobile via NAS (Non Access Stratum) signalling and communicates with the HSS through Diameter. Key responsibilities include ECM (EPS Connection Management), EMM (EPS Mobility Management), gateway selection, NAS security and handover assistance. |
| MNC | Mobile Network Code | The Mobile Network Code is either a two or three digit number used to uniquely identify a given network from within a specified country ( MCC (Mobile Country Code)). The MNC is used as part of the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) and LAI (Location Area Identity) etc. |
| NAS | Non Access Stratum | The Non Access Stratum is a functional layer running between the UE (User Equipment) and the CN (Core Network). The layer supports traffic and signalling messages between the CN and UE (User Equipment). |
| PFCP | Packet Forwarding Control Protocol (PFCP) | Packet Forwarding Control Protocol (PFCP) is a 3GPP protocol used on the Sx/N4 interface between the control plane and the user plane function, specified in TS 29.244.[1] It is one of the main protocols introduced in the 5G Next Generation Mobile Core Network (aka 5GC[2]), but also used in the 4G/LTE EPC to implement the Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS).[3] PFCP and the associated interfaces seek to formalize the interactions between different types of functional elements used in the Mobile Core Networks as deployed by most operators providing 4G, as well as 5G, services to mobile subscribers |
| PLMN | Public Land Mobile Network | A Public Land Mobile Network is a generic name for all mobile wireless networks that use land based radio transmitters or base stations. Public Land Mobile Network Identifier or with abbreviated version PLMN is a combination of MCC and MNC. It is unique value and globally used to identify the mobile network that a user subscribed. |
| S1AP | S1 Application Protocol | S1AP is used between the eNB and the MME in order to support operations such as E-RAB (E-UTRAN Radio Access Bearer) Management, transfer of UE Context information, NAS Signalling transport, Paging and EPC based mobility. |
| SGW-U | Serving Gateway User plane function | The SGW-U is the user data plane ingress and egress point of the E-UTRAN side of the EPC when control and user plane separation is in place. As such, when the subscriber moves around the E-UTRAN, their point of attachment to the EPC remains fixed at the SGW-U (unless the network decides that a SGW-U relocation is required). A single subscriber may be supported by multiple SGW-U if connectivity to multiple PDNs are in place. Additional responsibilities include lawful interception of subscriber traffic, inter-operator accounting, as well as downlink data buffering whilst the subscriber is paged. |
| TAC | Tracking Area Code | An element of the TAI which serves to uniquely identify the Tracking Area. Tracking Area is a logical concept of an area where a user can move around without updating the MME. The network allocates a list with one or more TAs to the user. In certain operation modes, the UE may move freely in all TAs of the list without updating the MME. You can think of 'Tracking Area' as 'Routing Area' in UMTS. |
| TAI | Timing Advance Index | The MS (Mobile Station) performing uplink or downlink packet transfer, will receive a packet uplink or downlink assignment message. This message will contain the MS assigned TAI and the PTCCH (Packet Timing Control Channel). The TAI specifies which PTCCH subchannel is to be used by the MS. |
| TMSI | Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity | In order to ensure subscriber identity confidentiality the VLR (Visitor Location Register) and SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node) may allocate TMSI (Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identities) to visiting mobile subscribers. The VLR and SGSN must be capable of correlating an allocated TMSI with the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) of the MS (Mobile Station) to which it is allocated. A MS may be allocated two TMSI, one for services provided through the VLR, and the other known as the P-TMSI (Packet TMSI) for services provided through the SGSN. |
| UE | User Equipment | The UMTS Subscriber or UE (User Equipment) is a combination of ME (Mobile Equipment) and SIM / USIM (Subscriber Identity Module / UMTS Subscriber Identity Module). |
| UMTS | Universal Mobile Telecommunications System | A 3G mobile communication system which supports improved data rates over GSM and subsequently provides an enhanced range of multimedia services. UMTS has increased convergence between telecommunications, IT (Information technology), media and content industries to deliver new services and create fresh revenue generating opportunities. UMTS delivers low cost, high capacity mobile communications, offering data rates as high as 2Mbps (under ideal conditions) with global roaming and other advanced capabilities. The specifications defining UMTS are formulated by the 3GPP. |
| WiFi | Wireless Fidelity | WiFi is an interoperability standard developed by the WiFi Alliance and issued to those manufacturers whose IEEE 802.11 equipment has passed a suite of basic interoperability tests. Equipment passing these tests carries the WiFi logo. |
| X2AP | X2 Application Protocol | X2AP is a control protocol found between eNBs on the X2 control plane. Main functions of X2AP include X2 based mobility, as well as X2 “Global Procedures”. The former is largely associated with eNB (Evolved Node B) controlled handover procedures whereas the latter deals with the establishment and management of the X2 connection. |