Difference between revisions of "JAVA: Operator Aritmatik dengan Contoh"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
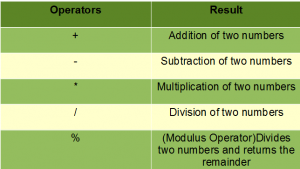
These operators involve the mathematical operators that can be used to perform various simple or advanced arithmetic operations on the primitive data types referred to as the operands. These operators consist of various unary and binary operators that can be applied on a single or two operands. Let’s look at the various operators that Java has to provide under the arithmetic operators. | These operators involve the mathematical operators that can be used to perform various simple or advanced arithmetic operations on the primitive data types referred to as the operands. These operators consist of various unary and binary operators that can be applied on a single or two operands. Let’s look at the various operators that Java has to provide under the arithmetic operators. | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [[File:Arithmeticoperators.png|center|300px|thumb]] | ||
Now let’s look at each one of the arithmetic operators in Java: | Now let’s look at each one of the arithmetic operators in Java: | ||
Revision as of 05:43, 6 May 2022
Operators constitute the basic building block to any programming language. Java too provides many types of operators which can be used according to the need to perform various calculations and functions, be it logical, arithmetic, relational, etc. They are classified based on the functionality they provide. Here are a few types:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Unary Operators
- Assignment Operator
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Ternary Operator
- Bitwise Operators
- Shift Operators
This article explains all that one needs to know regarding Arithmetic Operators.
Arithmetic Operators
These operators involve the mathematical operators that can be used to perform various simple or advanced arithmetic operations on the primitive data types referred to as the operands. These operators consist of various unary and binary operators that can be applied on a single or two operands. Let’s look at the various operators that Java has to provide under the arithmetic operators.
Now let’s look at each one of the arithmetic operators in Java:
1. Addition(+):
This operator is a binary operator and is used to add two operands.
Syntax:
num1 + num2
Example:
num1 = 10, num2 = 20 sum = num1 + num2 = 30
// Java code to illustrate Addition operator
import java.io.*;
class Addition {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// initializing variables
int num1 = 10, num2 = 20, sum = 0;
// Displaying num1 and num2
System.out.println("num1 = " + num1);
System.out.println("num2 = " + num2);
// adding num1 and num2
sum = num1 + num2;
System.out.println("The sum = " + sum);
}
}
Output
num1 = 10 num2 = 20 The sum = 30
2. Subtraction(-):
This operator is a binary operator and is used to subtract two operands.
Syntax:
num1 - num2
Example:
num1 = 20, num2 = 10 sub = num1 - num2 = 10
// Java code to illustrate Subtraction operator
import java.io.*;
class Subtraction {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// initializing variables
int num1 = 20, num2 = 10, sub = 0;
// Displaying num1 and num2
System.out.println("num1 = " + num1);
System.out.println("num2 = " + num2);
// subtracting num1 and num2
sub = num1 - num2;
System.out.println("Subtraction = " + sub);
}
}
Output
num1 = 20 num2 = 10 Subtraction = 10
3. Multiplication(*):
This operator is a binary operator and is used to multiply two operands.
Syntax:
num1 * num2
Example:
num1 = 20, num2 = 10 mult = num1 * num2 = 200
// Java code to illustrate Multiplication operator
import java.io.*;
class Multiplication {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// initializing variables
int num1 = 20, num2 = 10, mult = 0;
// Displaying num1 and num2
System.out.println("num1 = " + num1);
System.out.println("num2 = " + num2);
// Multiplying num1 and num2
mult = num1 * num2;
System.out.println("Multiplication = " + mult);
}
}
Output
num1 = 20 num2 = 10 Multiplication = 200
4. Division(/):
This is a binary operator that is used to divide the first operand(dividend) by the second operand(divisor) and give the quotient as a result.
Syntax:
num1 / num2
Example:
num1 = 20, num2 = 10 div = num1 / num2 = 2
// Java code to illustrate Division operator
import java.io.*;
class Division {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// initializing variables
int num1 = 20, num2 = 10, div = 0;
// Displaying num1 and num2
System.out.println("num1 = " + num1);
System.out.println("num2 = " + num2);
// Dividing num1 and num2
div = num1 / num2;
System.out.println("Division = " + div);
}
}
Output
num1 = 20 num2 = 10 Division = 2
5. Modulus(%):
This is a binary operator that is used to return the remainder when the first operand(dividend) is divided by the second operand(divisor).
Syntax:
num1 % num2
Example:
num1 = 5, num2 = 2 mod = num1 % num2 = 1
// Java code to illustrate Modulus operator
import java.io.*;
class Modulus {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// initializing variables
int num1 = 5, num2 = 2, mod = 0;
// Displaying num1 and num2
System.out.println("num1 = " + num1);
System.out.println("num2 = " + num2);
// Remaindering num1 and num2
mod = num1 % num2;
System.out.println("Remainder = " + mod);
}
}
Output
num1 = 5 num2 = 2 Remainder = 1