Difference between revisions of "JAVA: Pernyataan if-else dengan Contoh"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
==Cara kerja pernyataan if-else== | ==Cara kerja pernyataan if-else== | ||
| − | + | 1. Control falls into the if block. | |
| − | + | 2. The flow jumps to Condition. | |
| − | + | 3. Condition is tested. | |
** If Condition yields true, go to Step 4. | ** If Condition yields true, go to Step 4. | ||
** If Condition yields false, go to Step 5. | ** If Condition yields false, go to Step 5. | ||
| − | + | 4. The if-block or the body inside the if is executed. | |
| − | + | 5. The else block or the body inside the else is executed. | |
| − | + | 6. Flow exits the if-else block. | |
Flowchart if-else: | Flowchart if-else: | ||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
Welcome to GeeksforGeeks | Welcome to GeeksforGeeks | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Referensi== | ==Referensi== | ||
* https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/java-if-else-statement-with-examples/ | * https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/java-if-else-statement-with-examples/ | ||
Revision as of 07:52, 4 May 2022
Pengambilan Keputusan di Java membantu menulis pernyataan berbasis keputusan dan mengeksekusi serangkaian code tertentu berdasarkan kondisi tertentu.
Pernyataan if memberi tahu kita bahwa jika suatu kondisi benar, itu akan mengeksekusi blok pernyataan dan jika kondisinya salah, blok pernyataan tersebut tidak akan dilakukan. Tetapi bagaimana jika kita ingin melakukan sesuatu yang lain jika kondisinya salah. Di sinilah pernyataan lain. Kita dapat menggunakan pernyataan else dengan pernyataan if untuk mengeksekusi blok code ketika kondisinya salah.
Syntax:
if (condition)
{
// Executes this block if
// condition is true
}
else
{
// Executes this block if
// condition is false
}
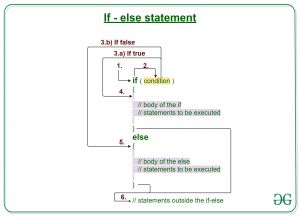
Cara kerja pernyataan if-else
1. Control falls into the if block. 2. The flow jumps to Condition. 3. Condition is tested.
- If Condition yields true, go to Step 4.
- If Condition yields false, go to Step 5.
4. The if-block or the body inside the if is executed. 5. The else block or the body inside the else is executed. 6. Flow exits the if-else block.
Flowchart if-else:
Flowchart of if-else in Java
Contoh 1:
// Java program to illustrate if-else statement
class IfElseDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i = 20;
if (i < 15)
System.out.println("i is smaller than 15");
else
System.out.println("i is greater than 15");
System.out.println("Outside if-else block");
}
}
Output
i is greater than 15 Outside if-else block
Dry-Running Example 1:
1. Program starts. 2. i is initialized to 20. 3. if-condition is checked. 20<15, yields false. 4. flow enters the else block.
4.a) "i is greater than 15" is printed
5. "Outside if-else block" is printed.
Contoh 2:
// Java program to illustrate if-else statement
class IfElseDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String str = "geeksforgeeks";
if (str == "geeks")
System.out.println("Hello geek");
else
System.out.println("Welcome to GeeksforGeeks");
}
}
Output
Welcome to GeeksforGeeks