Difference between revisions of "Orange: kNN"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
sumber: https://docs.orange.biolab.si/3/visual-programming/widgets/model/knn.html | sumber: https://docs.orange.biolab.si/3/visual-programming/widgets/model/knn.html | ||
| − | + | Prediksi berdasarkan instance training terdekat. | |
==Input== | ==Input== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
Model: trained model | Model: trained model | ||
| − | + | Widget kNN menggunakan algoritma kNN yang akan mencari k contoh training terdekat di ruang feature dan menggunakan rata-rata feature terdekat tersebut untuk mem-prediksi. | |
[[File:KNN-stamped.png|center|200px|thumb]] | [[File:KNN-stamped.png|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
==Contoh== | ==Contoh== | ||
| − | + | Contoh pertama adalah tugas klasifikasi pada dataset iris. Kita bandingkan hasil dari k-Nearest neighbors dengan default model Constant, yang akan memprediksi class majoritas. | |
[[File:Constant-classification.png|center|200px|thumb]] | [[File:Constant-classification.png|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
Revision as of 17:58, 2 March 2020
sumber: https://docs.orange.biolab.si/3/visual-programming/widgets/model/knn.html
Prediksi berdasarkan instance training terdekat.
Input
Data: input dataset Preprocessor: preprocessing method(s)
Output
Learner: kNN learning algorithm Model: trained model
Widget kNN menggunakan algoritma kNN yang akan mencari k contoh training terdekat di ruang feature dan menggunakan rata-rata feature terdekat tersebut untuk mem-prediksi.
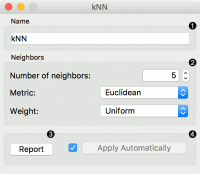
- A name under which it will appear in other widgets. The default name is “kNN”.
- Set the number of nearest neighbors, the distance parameter (metric) and weights as model criteria.
- Metric can be:
- Euclidean (“straight line”, distance between two points)
- Manhattan (sum of absolute differences of all attributes)
- Maximal (greatest of absolute differences between attributes)
- Mahalanobis (distance between point and distribution).
- Metric can be:
- The Weights you can use are:
- Uniform: all points in each neighborhood are weighted equally.
- Distance: closer neighbors of a query point have a greater influence than the neighbors further away.
- The Weights you can use are:
- Produce a report.
- When you change one or more settings, you need to click Apply, which will put a new learner on the output and, if the training examples are given, construct a new model and output it as well. Changes can also be applied automatically by clicking the box on the left side of the Apply button.
Contoh
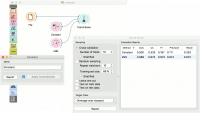
Contoh pertama adalah tugas klasifikasi pada dataset iris. Kita bandingkan hasil dari k-Nearest neighbors dengan default model Constant, yang akan memprediksi class majoritas.
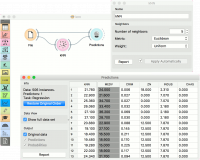
The second example is a regression task. This workflow shows how to use the Learner output. For the purpose of this example, we used the housing dataset. We input the kNN prediction model into Predictions and observe the predicted values.
Referensi