Difference between revisions of "Android Studio: Hello World"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
Activity adalah salah satu fitur yang membedakan dari framework Android. Activity memberikan pengguna dengan akses ke aplikasi anda, dan mungkin ada banyak Activity. Sebuah aplikasi biasanya akan memiliki Activity utama ketika pengguna meluncurkan aplikasi, Activity lain untuk saat memilih beberapa konten untuk melihat, misalnya, dan kegiatan lainnya ketika ia melakukan tugas-tugas lain dalam aplikasi. Lihat Kegiatan untuk informasi lebih lanjut. | Activity adalah salah satu fitur yang membedakan dari framework Android. Activity memberikan pengguna dengan akses ke aplikasi anda, dan mungkin ada banyak Activity. Sebuah aplikasi biasanya akan memiliki Activity utama ketika pengguna meluncurkan aplikasi, Activity lain untuk saat memilih beberapa konten untuk melihat, misalnya, dan kegiatan lainnya ketika ia melakukan tugas-tugas lain dalam aplikasi. Lihat Kegiatan untuk informasi lebih lanjut. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==File Source== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Your Android project is now a basic "Hello World" app that contains some default files. Take a moment to review the most important of these: | ||
| + | |||
| + | app/src/main/res/layout/activity_my.xml | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is the XML layout file for the activity you added when you created the project with Android Studio. Following the New Project workflow, Android Studio presents this file with both a text view and a preview of the screen UI. The file includes some default settings and a TextView element that displays the message, "Hello world!" | ||
| + | |||
| + | app/src/main/java/com.mycompany.myfirstapp/MyActivity.java | ||
| + | |||
| + | A tab for this file appears in Android Studio when the New Project workflow finishes. When you select the file you see the class definition for the activity you created. When you build and run the app, the Activity class starts the activity and loads the layout file that says "Hello World!" | ||
| + | app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml | ||
| + | |||
| + | The manifest file describes the fundamental characteristics of the app and defines each of its components. You'll revisit this file as you follow these lessons and add more components to your app. | ||
| + | |||
| + | app/build.gradle | ||
| + | |||
| + | Android Studio uses Gradle to compile and build your app. There is a build.gradle file for each module of your project, as well as a build.gradle file for the entire project. Usually, you're only interested in the build.gradle file for the module, in this case the app or application module. This is where your app's build dependencies are set, including the defaultConfig settings: | ||
| + | |||
| + | compiledSdkVersion is the platform version against which you will compile your app. By default, this is set to the latest version of Android available in your SDK. (It should be Android 4.1 or greater; if you don't have such a version available, you must install one using the SDK Manager.) You can still build your app to support older versions, but setting this to the latest version allows you to enable new features and optimize your app for a great user experience on the latest devices. | ||
| + | applicationId is the fully qualified package name for your application that you specified during the New Project workflow. | ||
| + | minSdkVersion is the Minimum SDK version you specified during the New Project workflow. This is the earliest version of the Android SDK that your app supports. | ||
| + | targetSdkVersion indicates the highest version of Android with which you have tested your application. As new versions of Android become available, you should test your app on the new version and update this value to match the latest API level and thereby take advantage of new platform features. For more information, read Supporting Different Platform Versions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | See Building Your Project with Gradle for more information about Gradle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note also the /res subdirectories that contain the resources for your application: | ||
| + | |||
| + | drawable<density>/ | ||
| + | Directories for drawable objects (such as bitmaps) that are designed for various densities, such as medium-density (mdpi) and high-density (hdpi) screens. Other drawable directories contain assets designed for other screen densities. Here you'll find the ic_launcher.png that appears when you run the default app. | ||
| + | |||
| + | layout/ | ||
| + | Directory for files that define your app's user interface like activity_my.xml, discussed above, which describes a basic layout for the MyActivity class. | ||
| + | |||
| + | menu/ | ||
| + | Directory for files that define your app's menu items. | ||
| + | |||
| + | values/ | ||
| + | Directory for other XML files that contain a collection of resources, such as string and color definitions. The strings.xml file defines the "Hello world!" string that displays when you run the default app. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To run the app, continue to the next lesson. | ||
==Referensi== | ==Referensi== | ||
Revision as of 05:26, 4 May 2015
Bagian ini mengajarkan Anda bagaimana membangun aplikasi Android pertama Anda. Anda akan belajar cara membuat sebuah proyek Android dan menjalankan versi debuggable dari app. Anda juga akan belajar beberapa dasar-dasar desain aplikasi Android, termasuk bagaimana membangun antarmuka pengguna yang sederhana dan menangani input pengguna.
Set Up Environment Anda
Sebelum kita mulai latihan, pastikan development environment telah di set dengan baik. Kita perlu:
- Download Android Studio.
- Download SDK tools terakhir dan platform menggunakan SDK Manager.
Catatan: Meskipun sebagian besar kelas latihan ini mengharapkan bahwa Anda menggunakan Android Studio, beberapa prosedur termasuk petunjuk alternatif untuk menggunakan SDK tool dari command line sebagai gantinya.
Bagian ini menggunakan format tutorial untuk membuat aplikasi Android kecil yang mengajarkan Anda beberapa konsep mendasar tentang perkembangan Android, jadi penting bahwa Anda mengikuti setiap langkah.
Membuat sebuah Android Project
Sebuah proyek Android berisi semua file yang terdiri dari kode sumber untuk aplikasi Android Anda.
Pelajaran ini menunjukkan bagaimana untuk membuat proyek baru baik menggunakan Android Studio atau menggunakan SDK tool dari command line.
Catatan: Anda harus sudah memiliki SDK Android diinstal, dan jika Anda menggunakan Android Studio, Anda juga harus memiliki Android Studio diinstal. Jika Anda tidak memiliki ini, ikuti panduan untuk Instalasi SDK Android sebelum Anda mulai pelajaran ini.
Buat Project dengan Android Studio
- Di Android Studio, membuat sebuah project baru:
- Jika tidak ada project yang dibuka, di Welcome screen, klik New Project.
- Jika ada project yang dibuka, dari File menum pilih New Project.
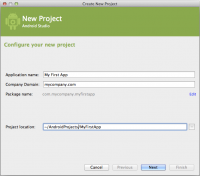
- Di bawah Configure your new project, isi kolom seperti pada gambar 1 dan klik Next. Mungkin akan lebih mudah untuk mengikuti pelajaran ini jika Anda menggunakan nilai yang sama seperti yang ditunjukkan.
- Application Name adalah nama app yang akan muncul ke user. Untuk project ini, digunakan "My First App."
- Company domain memberikan qualifier yang akan di tambahkan ke package name; Android Studio akan mengingat qualifier ini untuk semua new project yang kita buat.
- Package name adalah fully qualified name untuk project (mengikuti aturan yang sama dengan cara penamaan packages di bahasa pemrogramman Java). Nama package harus unik untuk semua packages yang di instalasi di sistem Android. Kita dapat mengedit nilai ini secara independen dari nama aplikasi atau company domain.
- Project location adalah directory di system anda yang akan digunakan untuk menyimpan file project.
- Di bawah pilih form factors dari aplikasi kita akan di run, cek box untuk Phone dan Tablet.
- Untuk Minimum SDK, pilih API 8: Android 2.2 (Froyo).
Minimum Required SDK adalah versi terawal Android yang akan didukung oleh aplikasi anda, ditunjukkan dengan menggunakan tingkat API. Untuk mendukung perangkat sebanyak mungkin, anda harus mengatur ini ke versi terendah yang tersedia yang memungkinkan aplikasi anda untuk memberikan yang fitur core set. Jika setiap fitur dari aplikasi anda hanya mungkin pada versi yang lebih baru dari Android dan itu tidak penting untuk fitur core set app, anda dapat mengaktifkan fitur hanya ketika berjalan pada versi yang mendukungnya (seperti yang dibahas dalam Mendukung Versi platform yang berbeda).
- Biarkan semua opsi lainnya (TV, Wear, dan Glass) tidak di cek dan klik Next.
- Di bawah Add an activity to <template>, pilih Blank Activity dan klik Next.
- Di bawah Choose options untuk new file anda, ubah Activity Name menjadi MyActivity. Nama Layout berubah ke activity_my, dan Title ke MyActivity. Nama Menu Resource menjadi menu_my.
- Klik tombol Finish untuk membuat project.
Catatan: Activity
Activity adalah salah satu fitur yang membedakan dari framework Android. Activity memberikan pengguna dengan akses ke aplikasi anda, dan mungkin ada banyak Activity. Sebuah aplikasi biasanya akan memiliki Activity utama ketika pengguna meluncurkan aplikasi, Activity lain untuk saat memilih beberapa konten untuk melihat, misalnya, dan kegiatan lainnya ketika ia melakukan tugas-tugas lain dalam aplikasi. Lihat Kegiatan untuk informasi lebih lanjut.
File Source
Your Android project is now a basic "Hello World" app that contains some default files. Take a moment to review the most important of these:
app/src/main/res/layout/activity_my.xml
This is the XML layout file for the activity you added when you created the project with Android Studio. Following the New Project workflow, Android Studio presents this file with both a text view and a preview of the screen UI. The file includes some default settings and a TextView element that displays the message, "Hello world!"
app/src/main/java/com.mycompany.myfirstapp/MyActivity.java
A tab for this file appears in Android Studio when the New Project workflow finishes. When you select the file you see the class definition for the activity you created. When you build and run the app, the Activity class starts the activity and loads the layout file that says "Hello World!" app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml
The manifest file describes the fundamental characteristics of the app and defines each of its components. You'll revisit this file as you follow these lessons and add more components to your app.
app/build.gradle
Android Studio uses Gradle to compile and build your app. There is a build.gradle file for each module of your project, as well as a build.gradle file for the entire project. Usually, you're only interested in the build.gradle file for the module, in this case the app or application module. This is where your app's build dependencies are set, including the defaultConfig settings:
compiledSdkVersion is the platform version against which you will compile your app. By default, this is set to the latest version of Android available in your SDK. (It should be Android 4.1 or greater; if you don't have such a version available, you must install one using the SDK Manager.) You can still build your app to support older versions, but setting this to the latest version allows you to enable new features and optimize your app for a great user experience on the latest devices.
applicationId is the fully qualified package name for your application that you specified during the New Project workflow.
minSdkVersion is the Minimum SDK version you specified during the New Project workflow. This is the earliest version of the Android SDK that your app supports.
targetSdkVersion indicates the highest version of Android with which you have tested your application. As new versions of Android become available, you should test your app on the new version and update this value to match the latest API level and thereby take advantage of new platform features. For more information, read Supporting Different Platform Versions.
See Building Your Project with Gradle for more information about Gradle.
Note also the /res subdirectories that contain the resources for your application:
drawable<density>/ Directories for drawable objects (such as bitmaps) that are designed for various densities, such as medium-density (mdpi) and high-density (hdpi) screens. Other drawable directories contain assets designed for other screen densities. Here you'll find the ic_launcher.png that appears when you run the default app.
layout/ Directory for files that define your app's user interface like activity_my.xml, discussed above, which describes a basic layout for the MyActivity class.
menu/ Directory for files that define your app's menu items.
values/ Directory for other XML files that contain a collection of resources, such as string and color definitions. The strings.xml file defines the "Hello world!" string that displays when you run the default app.
To run the app, continue to the next lesson.