Difference between revisions of "JAVA: Pengambilan Keputusan di Java"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) (Created page with "Decision Making in programming is similar to decision-making in real life. In programming also face some situations where we want a certain block of code to be executed when s...") |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | Proses pengambilan keputusan dalam pemrograman mirip dengan pengambilan keputusan dalam kehidupan nyata. Dalam pemrograman juga menghadapi beberapa situasi di mana kita ingin blok code tertentu dieksekusi ketika beberapa kondisi terpenuhi. | |
| − | + | Sebuah bahasa pemrograman menggunakan pernyataan kontrol untuk mengontrol aliran eksekusi program berdasarkan kondisi tertentu. Ini digunakan untuk menyebabkan aliran eksekusi berjalan / maju dan bercabang berdasarkan perubahan status program. | |
| − | + | Perintah untuk melakukan pemilihan di Java: | |
| − | if | + | * if |
| − | if-else | + | * if-else |
| − | nested-if | + | * nested-if |
| − | if-else-if | + | * if-else-if |
| − | switch-case | + | * switch-case |
| − | jump – break, continue, return | + | * jump – break, continue, return |
| − | 1. if: if | + | |
| + | ==1. if:== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pernyataan if adalah pernyataan pengambilan keputusan yang paling sederhana. Ini digunakan untuk memutuskan apakah pernyataan atau blok pernyataan tertentu akan dieksekusi atau tidak, yaitu jika kondisi tertentu benar maka blok pernyataan akan dieksekusi jika tidak. | ||
Syntax: | Syntax: | ||
| − | if(condition) | + | if(condition) |
| − | { | + | { |
| − | + | // Statements to execute if | |
| − | + | // condition is true | |
| − | } | + | } |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Di sini, kondisi setelah di evaluasi akan benar atau salah. jika pernyataan menerima nilai boolean - jika nilainya benar maka akan mengeksekusi blok perintah di bawahnya. | |
| − | if(condition) | + | Jika kita tidak memberikan kurung kurawal '{' dan '}' setelah if( condition ) maka secara default pernyataan if akan menganggap pernyataan langsung berada di dalam bloknya. Sebagai contoh, |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | // Here if the condition is true, if block | + | if(condition) |
| − | // will consider only statement1 to be inside | + | statement1; |
| − | // its block. | + | statement2; |
| − | + | ||
| + | // Here if the condition is true, if block | ||
| + | // will consider only statement1 to be inside | ||
| + | // its block. | ||
| − | + | [[File:If.png|center|200px|thumb]] | |
| + | Contoh: | ||
| − | // Java program to illustrate If statement | + | // Java program to illustrate If statement |
| − | class IfDemo { | + | class IfDemo { |
| − | + | public static void main(String args[]) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | int i = 10; | |
| − | + | if (i > 15) | |
| − | + | System.out.println("10 is less than 15"); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | // This statement will be executed | |
| − | + | // as if considers one statement by default | |
| − | + | System.out.println("I am Not in if"); | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | } | + | } |
| + | |||
Output | Output | ||
| − | I am Not in if | + | I am Not in if |
| − | 2. if-else: | + | |
| + | ==2. if-else:== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pernyataan if sendiri memberi tahu kita bahwa jika suatu kondisi benar, itu akan mengeksekusi blok perintah dan jika kondisinya salah, blok tersebut tidak akan dilakukan. Tetapi bagaimana jika kita ingin melakukan sesuatu yang lain jika kondisinya salah. Di sinilah pernyataan lain. Kita dapat menggunakan pernyataan else dengan pernyataan if untuk mengeksekusi blok code ketika kondisinya salah. | ||
Syntax: | Syntax: | ||
| − | if (condition) | + | if (condition) |
| − | { | + | { |
| − | + | // Executes this block if | |
| − | + | // condition is true | |
| − | } | + | } |
| − | else | + | else |
| − | { | + | { |
| − | + | // Executes this block if | |
| − | + | // condition is false | |
| − | } | + | } |
| − | + | ||
| + | [[File:If-else.png|center|200px|thumb]] | ||
| − | + | Contoh: | |
| + | // Java program to illustrate if-else statement | ||
| + | class IfElseDemo { | ||
| + | public static void main(String args[]) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | int i = 10; | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (i < 15) | ||
| + | System.out.println("i is smaller than 15"); | ||
| + | else | ||
| + | System.out.println("i is greater than 15"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Output | Output | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | i is smaller than 15 | |
| + | |||
| − | 3. nested-if: | + | ==3. nested-if:== |
| + | |||
| + | Sebuah nested if adalah pernyataan if yang merupakan target dari if atau else lainnya. Pernyataan nested if berarti pernyataan if di dalam pernyataan if. Ya, java memungkinkan kita untuk membuat pernyataan if di dalam pernyataan if. yaitu, kita dapat menempatkan pernyataan if di dalam pernyataan if yang lain. | ||
Syntax: | Syntax: | ||
| − | if (condition1) | + | if (condition1) |
| − | { | + | { |
| − | + | // Executes when condition1 is true | |
| − | + | if (condition2) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | // Executes when condition2 is true | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | } | + | } |
| − | + | ||
| + | [[File:Nested-if-modified-1.png|center|400px|thumb]] | ||
| − | + | Contoh: | |
| + | // Java program to illustrate nested-if statement | ||
| + | |||
| + | class NestedIfDemo { | ||
| + | public static void main(String args[]) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | int i = 10; | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (i == 10) { | ||
| + | // First if statement | ||
| + | if (i < 15) | ||
| + | System.out.println("i is smaller than 15"); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Nested - if statement | ||
| + | // Will only be executed if statement above | ||
| + | // it is true | ||
| + | if (i < 12) | ||
| + | System.out.println( | ||
| + | "i is smaller than 12 too"); | ||
| + | else | ||
| + | System.out.println("i is greater than 15"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Output | Output | ||
| − | i is smaller than 15 | + | i is smaller than 15 |
| − | i is smaller than 12 too | + | i is smaller than 12 too |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==4. if-else-if ladder:== | |
| − | + | Di sini, pengguna dapat memutuskan di antara beberapa opsi. Pernyataan if dieksekusi dari atas ke bawah. Segera setelah salah satu kondisi yang mengendalikan if benar, pernyataan yang terkait dengan itu jika dieksekusi, dan sisa perintah-perintah di bawahnya akan dilewati. Jika tidak ada kondisi yang benar, maka pernyataan else terakhir akan dieksekusi. | |
| − | if (condition) | + | if (condition) |
| − | + | statement; | |
| − | else if (condition) | + | else if (condition) |
| − | + | statement; | |
| − | . | + | . |
| − | . | + | . |
| − | else | + | else |
| − | + | statement; | |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:If-elseif.png|center|300px|thumb]] | |
| + | Contoh: | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Java program to illustrate if-else-if ladder | ||
| + | |||
| + | class ifelseifDemo { | ||
| + | public static void main(String args[]) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | int i = 20; | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (i == 10) | ||
| + | System.out.println("i is 10"); | ||
| + | else if (i == 15) | ||
| + | System.out.println("i is 15"); | ||
| + | else if (i == 20) | ||
| + | System.out.println("i is 20"); | ||
| + | else | ||
| + | System.out.println("i is not present"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Output | Output | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | i is 20 | |
| + | |||
| + | ==5. switch-case:== | ||
| − | + | Pernyataan switch adalah pernyataan multiway branch. Ini menyediakan cara mudah untuk mengirimkan eksekusi ke berbagai bagian kode berdasarkan nilai ekspresi. | |
Syntax: | Syntax: | ||
| − | switch (expression) | + | switch (expression) |
| − | { | + | { |
| − | + | case value1: | |
| − | + | statement1; | |
| − | + | break; | |
| − | + | case value2: | |
| − | + | statement2; | |
| − | + | break; | |
| − | + | . | |
| − | + | . | |
| − | + | case valueN: | |
| − | + | statementN; | |
| − | + | break; | |
| − | + | default: | |
| − | + | statementDefault; | |
| − | } | + | } |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * Ekspresi dapat bertipe byte, short, int char, atau enumeration. Dimulai dengan JDK7, ekspresi juga bisa bertipe String. | |
| − | + | * Nilai kasus duplikat tidak diperbolehkan. | |
| − | + | * Pernyataan default adalah opsional. | |
| − | + | * Pernyataan break digunakan di dalam switch untuk mengakhiri urutan pernyataan. | |
| − | + | * Pernyataan break adalah opsional. Jika dihilangkan, eksekusi akan berlanjut ke kasus berikutnya. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==6. jump:== | |
| + | Java mendukung tiga pernyatan lompat: '''break''', '''continue''' and '''return'''. Ketiga pernyataan ini mentransfer kendali ke bagian lain dari program. | ||
| − | + | * '''Break:''' Di Java, break sebagian besar digunakan untuk: | |
| − | + | ** Hentikan urutan dalam pernyataan switch. | |
| − | + | ** Untuk keluar dari loop. | |
| − | + | ** Digunakan sebagai bentuk goto yang "beradab". | |
| − | + | * '''Continue:''' Terkadang berguna untuk memaksakan iterasi awal dari sebuah loop. Artinya,kita mungkin ingin terus menjalankan loop tetapi berhenti memproses sisa kode di tubuhnya untuk iterasi khusus ini. Ini, pada dasarnya, sebuah goto yang melewati badan loop, ke ujung loop. Pernyataan lanjutkan melakukan tindakan seperti itu. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:Continue-1.png|center|300px|thumb]] | |
| − | + | Contoh: | |
| − | |||
| + | // Java program to illustrate using | ||
| + | // continue in an if statement | ||
| + | class ContinueDemo { | ||
| + | public static void main(String args[]) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { | ||
| + | // If the number is even | ||
| + | // skip and continue | ||
| + | if (i % 2 == 0) | ||
| + | continue; | ||
| + | |||
| + | // If number is odd, print it | ||
| + | System.out.print(i + " "); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Output | Output | ||
| − | + | 1 3 5 7 9 | |
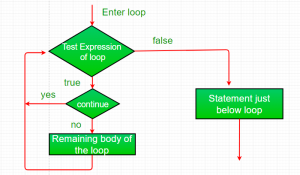
| + | * '''Return:''' Pernyataan return digunakan untuk secara eksplisit kembali dari suatu method. Artinya, ini menyebabkan kontrol program untuk mentransfer kembali ke pemanggil method. | ||
| + | Contoh: | ||
| + | // Java program to illustrate using return | ||
| + | class Return { | ||
| + | public static void main(String args[]) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | boolean t = true; | ||
| + | System.out.println("Before the return."); | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (t) | ||
| + | return; | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Compiler will bypass every statement | ||
| + | // after return | ||
| + | System.out.println("This won't execute."); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | Output | ||
| + | Before the return. | ||
==Referensi== | ==Referensi== | ||
* https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/decision-making-javaif-else-switch-break-continue-jump/ | * https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/decision-making-javaif-else-switch-break-continue-jump/ | ||
Latest revision as of 07:40, 4 May 2022
Proses pengambilan keputusan dalam pemrograman mirip dengan pengambilan keputusan dalam kehidupan nyata. Dalam pemrograman juga menghadapi beberapa situasi di mana kita ingin blok code tertentu dieksekusi ketika beberapa kondisi terpenuhi.
Sebuah bahasa pemrograman menggunakan pernyataan kontrol untuk mengontrol aliran eksekusi program berdasarkan kondisi tertentu. Ini digunakan untuk menyebabkan aliran eksekusi berjalan / maju dan bercabang berdasarkan perubahan status program.
Perintah untuk melakukan pemilihan di Java:
- if
- if-else
- nested-if
- if-else-if
- switch-case
- jump – break, continue, return
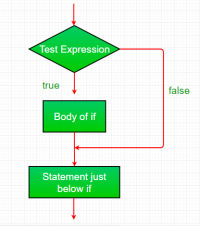
1. if:
Pernyataan if adalah pernyataan pengambilan keputusan yang paling sederhana. Ini digunakan untuk memutuskan apakah pernyataan atau blok pernyataan tertentu akan dieksekusi atau tidak, yaitu jika kondisi tertentu benar maka blok pernyataan akan dieksekusi jika tidak.
Syntax:
if(condition)
{
// Statements to execute if
// condition is true
}
Di sini, kondisi setelah di evaluasi akan benar atau salah. jika pernyataan menerima nilai boolean - jika nilainya benar maka akan mengeksekusi blok perintah di bawahnya.
Jika kita tidak memberikan kurung kurawal '{' dan '}' setelah if( condition ) maka secara default pernyataan if akan menganggap pernyataan langsung berada di dalam bloknya. Sebagai contoh,
if(condition) statement1; statement2; // Here if the condition is true, if block // will consider only statement1 to be inside // its block.
Contoh:
// Java program to illustrate If statement
class IfDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i = 10;
if (i > 15)
System.out.println("10 is less than 15");
// This statement will be executed
// as if considers one statement by default
System.out.println("I am Not in if");
}
}
Output
I am Not in if
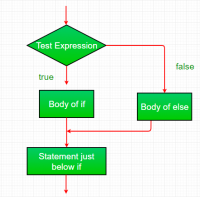
2. if-else:
Pernyataan if sendiri memberi tahu kita bahwa jika suatu kondisi benar, itu akan mengeksekusi blok perintah dan jika kondisinya salah, blok tersebut tidak akan dilakukan. Tetapi bagaimana jika kita ingin melakukan sesuatu yang lain jika kondisinya salah. Di sinilah pernyataan lain. Kita dapat menggunakan pernyataan else dengan pernyataan if untuk mengeksekusi blok code ketika kondisinya salah.
Syntax:
if (condition)
{
// Executes this block if
// condition is true
}
else
{
// Executes this block if
// condition is false
}
Contoh:
// Java program to illustrate if-else statement
class IfElseDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i = 10;
if (i < 15)
System.out.println("i is smaller than 15");
else
System.out.println("i is greater than 15");
}
}
Output
i is smaller than 15
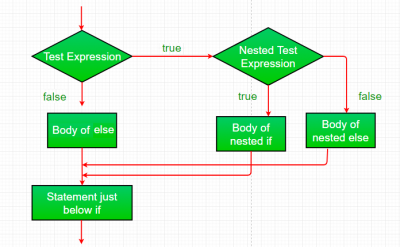
3. nested-if:
Sebuah nested if adalah pernyataan if yang merupakan target dari if atau else lainnya. Pernyataan nested if berarti pernyataan if di dalam pernyataan if. Ya, java memungkinkan kita untuk membuat pernyataan if di dalam pernyataan if. yaitu, kita dapat menempatkan pernyataan if di dalam pernyataan if yang lain.
Syntax:
if (condition1)
{
// Executes when condition1 is true
if (condition2)
{
// Executes when condition2 is true
}
}
Contoh:
// Java program to illustrate nested-if statement
class NestedIfDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i = 10;
if (i == 10) {
// First if statement
if (i < 15)
System.out.println("i is smaller than 15");
// Nested - if statement
// Will only be executed if statement above
// it is true
if (i < 12)
System.out.println(
"i is smaller than 12 too");
else
System.out.println("i is greater than 15");
}
}
}
Output
i is smaller than 15 i is smaller than 12 too
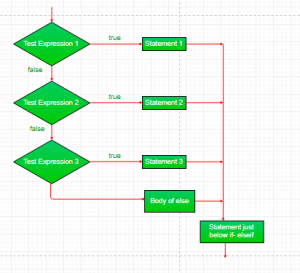
4. if-else-if ladder:
Di sini, pengguna dapat memutuskan di antara beberapa opsi. Pernyataan if dieksekusi dari atas ke bawah. Segera setelah salah satu kondisi yang mengendalikan if benar, pernyataan yang terkait dengan itu jika dieksekusi, dan sisa perintah-perintah di bawahnya akan dilewati. Jika tidak ada kondisi yang benar, maka pernyataan else terakhir akan dieksekusi.
if (condition)
statement;
else if (condition)
statement;
.
.
else
statement;
Contoh:
// Java program to illustrate if-else-if ladder
class ifelseifDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i = 20;
if (i == 10)
System.out.println("i is 10");
else if (i == 15)
System.out.println("i is 15");
else if (i == 20)
System.out.println("i is 20");
else
System.out.println("i is not present");
}
}
Output
i is 20
5. switch-case:
Pernyataan switch adalah pernyataan multiway branch. Ini menyediakan cara mudah untuk mengirimkan eksekusi ke berbagai bagian kode berdasarkan nilai ekspresi.
Syntax:
switch (expression)
{
case value1:
statement1;
break;
case value2:
statement2;
break;
.
.
case valueN:
statementN;
break;
default:
statementDefault;
}
- Ekspresi dapat bertipe byte, short, int char, atau enumeration. Dimulai dengan JDK7, ekspresi juga bisa bertipe String.
- Nilai kasus duplikat tidak diperbolehkan.
- Pernyataan default adalah opsional.
- Pernyataan break digunakan di dalam switch untuk mengakhiri urutan pernyataan.
- Pernyataan break adalah opsional. Jika dihilangkan, eksekusi akan berlanjut ke kasus berikutnya.
6. jump:
Java mendukung tiga pernyatan lompat: break, continue and return. Ketiga pernyataan ini mentransfer kendali ke bagian lain dari program.
- Break: Di Java, break sebagian besar digunakan untuk:
- Hentikan urutan dalam pernyataan switch.
- Untuk keluar dari loop.
- Digunakan sebagai bentuk goto yang "beradab".
- Continue: Terkadang berguna untuk memaksakan iterasi awal dari sebuah loop. Artinya,kita mungkin ingin terus menjalankan loop tetapi berhenti memproses sisa kode di tubuhnya untuk iterasi khusus ini. Ini, pada dasarnya, sebuah goto yang melewati badan loop, ke ujung loop. Pernyataan lanjutkan melakukan tindakan seperti itu.
Contoh:
// Java program to illustrate using
// continue in an if statement
class ContinueDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// If the number is even
// skip and continue
if (i % 2 == 0)
continue;
// If number is odd, print it
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
}
Output
1 3 5 7 9
- Return: Pernyataan return digunakan untuk secara eksplisit kembali dari suatu method. Artinya, ini menyebabkan kontrol program untuk mentransfer kembali ke pemanggil method.
Contoh:
// Java program to illustrate using return
class Return {
public static void main(String args[])
{
boolean t = true;
System.out.println("Before the return.");
if (t)
return;
// Compiler will bypass every statement
// after return
System.out.println("This won't execute.");
}
}
Output
Before the return.