Difference between revisions of "JAVA: Method di Java"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) (Created page with "A method in Java or Java Method is a collection of statements that perform some specific task and return the result to the caller. A Java method can perform some specific task...") |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | Method di Java atau Java Method adalah kumpulan perintah yang melakukan beberapa tugas tertentu dan mengembalikan hasilnya ke pemanggil. Method Java dapat melakukan beberapa tugas tertentu tanpa perlu memberikan return apa pun. Metdod di Java memungkinkan kita untuk menggunakan kembali code tanpa mengetik ulang code. Di Java, setiap method harus menjadi bagian dari Class yang berbeda dengan bahasa seperti C, C++, dan Python. | |
| − | + | Catatan: Method adalah penghemat waktu dan penolong kita yang memungkinkan kita menggunakan ulang code tanpa menulis ulang code. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Method Declaration== | |
| − | + | Secara umum, deklarasi method ada enam (6) komponen: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * '''Modifier:''' Ini mendefinisikan jenis akses dari method yaitu dari mana method tersebut dapat diakses di aplikasi kita. Di Java, ada 4 jenis akses. | |
| + | public: Itu dapat diakses di semua Class dalam aplikasi yang kita buat. | ||
| + | protected: Itu dapat diakses di dalam Class di mana dia didefinisikan dan di subclass-nya. | ||
| + | private: Itu hanya dapat diakses di dalam Class di mana ia didefinisikan. | ||
| + | default: Itu dideklarasikan/didefinisikan tanpa menggunakan modifier apa pun. Itu dapat diakses di dalam class dan package yang sama di mana class didefinisikan. | ||
| + | * '''Return type:''' Tipe data dari nilai yang dikembalikan oleh method atau batal jika tidak mengembalikan (return) sebuah nilai. | ||
| + | * '''Method Name:''' aturan untuk nama field berlaku untuk nama method juga, tetapi konvensinya sedikit berbeda. | ||
| + | * '''Parameter list:''' Comma-separated list di definisikan, didahului dengan tipe datanya, di dalam kurung tertutup. Jika tidak ada parameter, kita harus menggunakan tanda kurung kosong (). | ||
| + | * '''Exception list:''' exception yang kita harapkan dapat di throw oleh method, kita dapat menentukan exception ini. | ||
| + | * '''Method body:''' di tutup antara dua kurung kurawal. Berisi code yang harus di jalankan untuk operasi yang kita inginkan.. | ||
| − | + | [[File:Methods-in-java.png|center|400px|thumb]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Type Method di Java== | |
| − | + | Ada dua (2) type dari Method di Java: | |
| − | + | # '''Predefined Method:''' Di Java, predefined method adalah metode yang sudah didefinisikan di library Class Java yang dikenal sebagai metdod yang telah ditentukan sebelumnya. Ini juga dikenal sebagai method library standar atau method build-in. Kita dapat langsung menggunakan method ini hanya dengan memanggilnya dalam program kapan saja. | |
| − | + | # '''User-defined Method:''' Method yang ditulis oleh pengguna atau pemrogram dikenal sebagai user-defined method. Method ini dimodifikasi sesuai dengan kebutuhan. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Ciri Method== | |
| − | + | Ini terdiri dari nama method dan daftar parameter (jumlah parameter, type parameter, dan urutan parameter). Type return dan exception bukan bagian dari ciri method. | |
| − | |||
| − | Method | + | Contoh Ciri Method dari sebuah fungsi: |
| − | max(int x, int y) | + | max(int x, int y) |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Jumlah parameter adalah 2, type parameter adalah int. | |
| − | + | ==Bagaimana Menamakan Method?== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Nama method biasanya satu kata harus kata kerja dengan huruf kecil atau multi-kata, yang dimulai dengan kata kerja dalam huruf kecil diikuti oleh kata sifat, kata benda….. Setelah kata pertama, huruf pertama dari setiap kata harus dikapitalisasi . | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ===Rules to Name a Method=== | ||
| − | + | * Saat mendefinisikan method, ingatlah bahwa nama method harus berupa kata kerja dan dimulai dengan huruf kecil. | |
| − | + | * Jika nama method memiliki lebih dari dua kata, nama depan harus berupa kata kerja diikuti oleh kata sifat atau kata benda. | |
| − | + | * Dalam nama method dengan multi-kata, huruf pertama setiap kata harus dalam huruf besar kecuali kata pertama. Misalnya, findSum, computeMax, setX dan getX. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Umumnya, sebuah method memiliki nama unik di dalam Class di mana ia didefinisikan, tetapi terkadang sebuah method mungkin memiliki nama yang sama dengan nama method lain dalam Class yang sama karena kelebihan method diperbolehkan di Java. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ===Method Calling=== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Method perlu dipanggil untuk menggunakan fungsinya. Ada tiga (3) situasi ketika suatu method dipanggil: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Sebuah method kembali ke code yang memanggilnya ketika: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * Dia menyelesaikan semua statement dalam method | |
| + | * Dia mencapai statement return | ||
| + | * Throw sebuah exception | ||
| − | + | ==Contoh 1:== | |
| − | // Java Program to Illustrate | + | // Java Program to Illustrate Methods |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | // Importing required classes | |
| − | + | import java.io.*; | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | // Class 1 | ||
| + | // Helper class | ||
| + | class Addition { | ||
| + | // Initially taking sum as 0 | ||
| + | // as we have not started computation | ||
| + | int sum = 0; | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Method | ||
| + | // To add two numbers | ||
| + | public int addTwoInt(int a, int b) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Adding two integer value | ||
| + | sum = a + b; | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Returning summation of two values | ||
| + | return sum; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Class 2 | ||
| + | // Helper class | ||
| + | class GFG { | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Main driver method | ||
| + | public static void main(String[] args) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Creating object of class 1 inside main() method | ||
| + | Addition add = new Addition(); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Calling method of above class | ||
| + | // to add two integer | ||
| + | // using instance created | ||
| + | int s = add.addTwoInt(1, 2); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Printing the sum of two numbers | ||
| + | System.out.println("Sum of two integer values :" | ||
| + | + s); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
Output | Output | ||
| − | + | * Jumlah dari dua nilai integer :3 | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Contoh 2:== | |
| − | + | // Java Program to Illustrate Method Calling | |
| − | + | // Via Different Ways of Calling a Method | |
| − | + | ||
| + | // Importing required classes | ||
| + | import java.io.*; | ||
| + | // Class 1 | ||
| + | // Helper class | ||
| + | class Test { | ||
| + | |||
| + | public static int i = 0; | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Constructor of class | ||
| + | Test() | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Counts the number of the objects of the class | ||
| + | i++; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Method 1 | ||
| + | // To access static members of the class and | ||
| + | // and for getting total no of objects | ||
| + | // of the same class created so far | ||
| + | public static int get() | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | |||
| + | // statements to be executed.... | ||
| + | return i; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Method 2 | ||
| + | // Instance method calling object directly | ||
| + | // that is created inside another class 'GFG'. | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Can also be called by object directly created in the | ||
| + | // same class and from another method defined in the | ||
| + | // same class and return integer value as return type is | ||
| + | // int. | ||
| + | public int m1() | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Display message only | ||
| + | System.out.println( | ||
| + | "Inside the method m1 by object of GFG class"); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Calling m2() method within the same class. | ||
| + | this.m2(); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Statements to be executed if any | ||
| + | return 1; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Method 3 | ||
| + | // Returns nothing | ||
| + | public void m2() | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Print statement | ||
| + | System.out.println( | ||
| + | "In method m2 came from method m1"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Class 2 | ||
| + | // Main class | ||
| + | class GFG { | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Main driver method | ||
| + | public static void main(String[] args) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Creating object of above class inside the class | ||
| + | Test obj = new Test(); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Calling method 2 inside main() method | ||
| + | int i = obj.m1(); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Display message only | ||
| + | System.out.println( | ||
| + | "Control returned after method m1 :" + i); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Call m2() method | ||
| + | // obj.m2(); | ||
| + | int no_of_objects = Test.get(); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Print statement | ||
| + | System.out.print( | ||
| + | "No of instances created till now : "); | ||
| + | |||
| + | System.out.println(no_of_objects); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | Output | |
| + | * Dalam method m1 sebagai object dari Class GFG | ||
| + | * Dalam method m2 kembali dari method m1 | ||
| + | * Control dikembalikan dari method m1 :1 | ||
| + | * Jumlah instance yang dibuat sampai sekarang : 1 | ||
| + | Flow control dari program di atas adalah sebagai berikut: | ||
| − | Methods | + | [[File:Methods-in-java2.png|center|400px|thumb]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==Alokasi Memory untuk Call Method== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Method call diimplementasikan melalui sebuah stack. Setiap kali suatu method dipanggil, frame stack dibuat di dalam area stack dan setelah itu, argumen yang diteruskan ke dan variabel lokal serta nilai yang akan dikembalikan oleh metode yang dipanggil ini disimpan dalam frame stack ini dan ketika eksekusi method yang dipanggil selesai , frame stack yang dialokasikan akan dihapus. Ada register penunjuk stack yang melacak bagian atas stack yang disesuaikan. | ||
==Referensi== | ==Referensi== | ||
* https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/methods-in-java/ | * https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/methods-in-java/ | ||
Latest revision as of 10:02, 3 May 2022
Method di Java atau Java Method adalah kumpulan perintah yang melakukan beberapa tugas tertentu dan mengembalikan hasilnya ke pemanggil. Method Java dapat melakukan beberapa tugas tertentu tanpa perlu memberikan return apa pun. Metdod di Java memungkinkan kita untuk menggunakan kembali code tanpa mengetik ulang code. Di Java, setiap method harus menjadi bagian dari Class yang berbeda dengan bahasa seperti C, C++, dan Python.
Catatan: Method adalah penghemat waktu dan penolong kita yang memungkinkan kita menggunakan ulang code tanpa menulis ulang code.
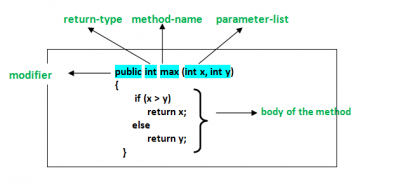
Method Declaration
Secara umum, deklarasi method ada enam (6) komponen:
- Modifier: Ini mendefinisikan jenis akses dari method yaitu dari mana method tersebut dapat diakses di aplikasi kita. Di Java, ada 4 jenis akses.
public: Itu dapat diakses di semua Class dalam aplikasi yang kita buat. protected: Itu dapat diakses di dalam Class di mana dia didefinisikan dan di subclass-nya. private: Itu hanya dapat diakses di dalam Class di mana ia didefinisikan. default: Itu dideklarasikan/didefinisikan tanpa menggunakan modifier apa pun. Itu dapat diakses di dalam class dan package yang sama di mana class didefinisikan.
- Return type: Tipe data dari nilai yang dikembalikan oleh method atau batal jika tidak mengembalikan (return) sebuah nilai.
- Method Name: aturan untuk nama field berlaku untuk nama method juga, tetapi konvensinya sedikit berbeda.
- Parameter list: Comma-separated list di definisikan, didahului dengan tipe datanya, di dalam kurung tertutup. Jika tidak ada parameter, kita harus menggunakan tanda kurung kosong ().
- Exception list: exception yang kita harapkan dapat di throw oleh method, kita dapat menentukan exception ini.
- Method body: di tutup antara dua kurung kurawal. Berisi code yang harus di jalankan untuk operasi yang kita inginkan..
Type Method di Java
Ada dua (2) type dari Method di Java:
- Predefined Method: Di Java, predefined method adalah metode yang sudah didefinisikan di library Class Java yang dikenal sebagai metdod yang telah ditentukan sebelumnya. Ini juga dikenal sebagai method library standar atau method build-in. Kita dapat langsung menggunakan method ini hanya dengan memanggilnya dalam program kapan saja.
- User-defined Method: Method yang ditulis oleh pengguna atau pemrogram dikenal sebagai user-defined method. Method ini dimodifikasi sesuai dengan kebutuhan.
Ciri Method
Ini terdiri dari nama method dan daftar parameter (jumlah parameter, type parameter, dan urutan parameter). Type return dan exception bukan bagian dari ciri method.
Contoh Ciri Method dari sebuah fungsi:
max(int x, int y)
Jumlah parameter adalah 2, type parameter adalah int.
Bagaimana Menamakan Method?
Nama method biasanya satu kata harus kata kerja dengan huruf kecil atau multi-kata, yang dimulai dengan kata kerja dalam huruf kecil diikuti oleh kata sifat, kata benda….. Setelah kata pertama, huruf pertama dari setiap kata harus dikapitalisasi .
Rules to Name a Method
- Saat mendefinisikan method, ingatlah bahwa nama method harus berupa kata kerja dan dimulai dengan huruf kecil.
- Jika nama method memiliki lebih dari dua kata, nama depan harus berupa kata kerja diikuti oleh kata sifat atau kata benda.
- Dalam nama method dengan multi-kata, huruf pertama setiap kata harus dalam huruf besar kecuali kata pertama. Misalnya, findSum, computeMax, setX dan getX.
Umumnya, sebuah method memiliki nama unik di dalam Class di mana ia didefinisikan, tetapi terkadang sebuah method mungkin memiliki nama yang sama dengan nama method lain dalam Class yang sama karena kelebihan method diperbolehkan di Java.
Method Calling
Method perlu dipanggil untuk menggunakan fungsinya. Ada tiga (3) situasi ketika suatu method dipanggil:
Sebuah method kembali ke code yang memanggilnya ketika:
- Dia menyelesaikan semua statement dalam method
- Dia mencapai statement return
- Throw sebuah exception
Contoh 1:
// Java Program to Illustrate Methods
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Addition {
// Initially taking sum as 0
// as we have not started computation
int sum = 0;
// Method
// To add two numbers
public int addTwoInt(int a, int b)
{
// Adding two integer value
sum = a + b;
// Returning summation of two values
return sum;
}
}
// Class 2
// Helper class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of class 1 inside main() method
Addition add = new Addition();
// Calling method of above class
// to add two integer
// using instance created
int s = add.addTwoInt(1, 2);
// Printing the sum of two numbers
System.out.println("Sum of two integer values :"
+ s);
}
}
Output
- Jumlah dari dua nilai integer :3
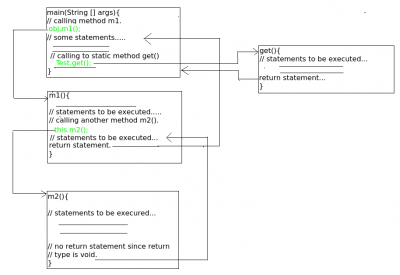
Contoh 2:
// Java Program to Illustrate Method Calling
// Via Different Ways of Calling a Method
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Test {
public static int i = 0;
// Constructor of class
Test()
{
// Counts the number of the objects of the class
i++;
}
// Method 1
// To access static members of the class and
// and for getting total no of objects
// of the same class created so far
public static int get()
{
// statements to be executed....
return i;
}
// Method 2
// Instance method calling object directly
// that is created inside another class 'GFG'.
// Can also be called by object directly created in the
// same class and from another method defined in the
// same class and return integer value as return type is
// int.
public int m1()
{
// Display message only
System.out.println(
"Inside the method m1 by object of GFG class");
// Calling m2() method within the same class.
this.m2();
// Statements to be executed if any
return 1;
}
// Method 3
// Returns nothing
public void m2()
{
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"In method m2 came from method m1");
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of above class inside the class
Test obj = new Test();
// Calling method 2 inside main() method
int i = obj.m1();
// Display message only
System.out.println(
"Control returned after method m1 :" + i);
// Call m2() method
// obj.m2();
int no_of_objects = Test.get();
// Print statement
System.out.print(
"No of instances created till now : ");
System.out.println(no_of_objects);
}
}
Output
- Dalam method m1 sebagai object dari Class GFG
- Dalam method m2 kembali dari method m1
- Control dikembalikan dari method m1 :1
- Jumlah instance yang dibuat sampai sekarang : 1
Flow control dari program di atas adalah sebagai berikut:
Alokasi Memory untuk Call Method
Method call diimplementasikan melalui sebuah stack. Setiap kali suatu method dipanggil, frame stack dibuat di dalam area stack dan setelah itu, argumen yang diteruskan ke dan variabel lokal serta nilai yang akan dikembalikan oleh metode yang dipanggil ini disimpan dalam frame stack ini dan ketika eksekusi method yang dipanggil selesai , frame stack yang dialokasikan akan dihapus. Ada register penunjuk stack yang melacak bagian atas stack yang disesuaikan.