Difference between revisions of "OpenVPN: Instalasi di Ubuntu 16.04"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| (51 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
paket easy-rsa dibutuhkan untuk membantu kita dalam men-setup internal CA (certificate authority) | paket easy-rsa dibutuhkan untuk membantu kita dalam men-setup internal CA (certificate authority) | ||
| − | |||
==Step 2: Set Up CA Directory== | ==Step 2: Set Up CA Directory== | ||
| Line 195: | Line 194: | ||
==Step 6: Generate Client Certificate & Key Pair== | ==Step 6: Generate Client Certificate & Key Pair== | ||
| − | + | Selanjutnya, kita dapat men-generate sertifikat client dan pasangan kunci. Meskipun ini dapat dilakukan pada mesin klien dan kemudian ditandatangani oleh server / CA untuk tujuan keamanan, untuk panduan ini kita akan men-generate kunci yang ditandatangani langsung di server supaya lebih sederhana saja. Pada prakteknya, sebetulnya proses ini sebaiknya dilakukan di client. | |
| + | |||
| + | Kita akan membuat satu (sebuah) kunci / sertifikat klien untuk panduan ini, tetapi jika anda memiliki lebih dari satu client, anda dapat mengulangi proses ini sebanyak yang anda mau. Berikan nilai unik pada skrip untuk setiap client. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Karena anda dapat kembali ke langkah ini di lain waktu, kami akan men-source ulang file vars. Kita akan menggunakan client1 sebagai nilai untuk sertifikat / pasangan kunci pertama kita untuk panduan ini. | ||
| − | + | Untuk menghasilkan kredensial '''tanpa password''', untuk membantu dalam koneksi otomatis, gunakan perintah build-key seperti ini: | |
| − | + | cd ~/openvpn-ca | |
| + | source vars | ||
| + | ./build-key client1 | ||
| − | + | Jika sebaliknya, anda ingin membuat kredensial yang dilindungi password, gunakan perintah build-key-pass: | |
| − | + | cd ~/openvpn-ca | |
| − | + | source vars | |
| − | + | ./build-key-pass client1 | |
| − | + | Sekali lagi, default seharusnya sudah terisi, jadi anda cukup menekan ENTER untuk melanjutkan. Tinggalkan pasword kosong dan pastikan untuk memasukkan y untuk petunjuk yang menanyakan apakah akan menandatangani dan komit sertifikat. | |
| − | + | Jika ada masalah, maka database key ada di folder ~/openvpn-ca/keys | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Step 7: Konfigurasi OpenVPN Service== | |
| − | + | Selanjutnya, kita dapat mulai mengkonfigurasi layanan OpenVPN menggunakan kredensial dan file yang telah kita buat. | |
| − | + | ===Copy File ke Direktori OpenVPN=== | |
| − | Copy | ||
| − | + | Untuk memulai, kita perlu mengcopy file yang kita butuhkan ke direktori konfigurasi /etc/openvpn. | |
| − | + | Kita bisa mulai dengan semua file yang baru kita buat. File tersebut ditempatkan di dalam direktori ~/openvpn-ca/keys saat dibuat. Kita perlu memindahkan sertifikat CA, sertifikat dan key server, tanda tangan digital HMAC, dan file Diffie-Hellman: | |
| − | + | cd ~/openvpn-ca/keys | |
| − | + | sudo cp ca.crt server.crt server.key ta.key dh2048.pem /etc/openvpn | |
| − | + | Selanjutnya, kita perlu mengcopy dan unzip file konfigurasi OpenVPN contoh ke dalam direktori konfigurasi sehingga kita dapat menggunakannya sebagai dasar untuk setup: | |
| − | + | gunzip -c /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/sample-config-files/server.conf.gz | sudo tee /etc/openvpn/server.conf | |
| − | + | ===Atur Konfigurasi OpenVPN=== | |
| − | + | Setelah file kita di tempat yang benar, kiita dapat memodifikasi file konfigurasi server: | |
sudo nano /etc/openvpn/server.conf | sudo nano /etc/openvpn/server.conf | ||
| − | Basic Configuration | + | ===Basic Configuration=== |
| − | + | Pertama, temukan bagian HMAC dengan mencari petunjuk tls-auth. Hapus ";" untuk menghapus tanda komentar pada baris tls-auth. Di bawah ini, tambahkan parameter key-direction dan set "0": | |
/etc/openvpn/server.conf | /etc/openvpn/server.conf | ||
| − | tls-auth ta.key 0 # This file is secret | + | tls-auth ta.key 0 # This file is secret |
| − | key-direction 0 | + | key-direction 0 |
| − | + | Selanjutnya, temukan bagian pada cipher cryptographic dengan mencari baris cipher yang dikomentari. Cipher AES-128-CBC menawarkan tingkat enkripsi yang baik dan didukung dengan baik. Hapus ";" untuk menghapus tanda komentar pada cipher AES-128-CBC line: | |
/etc/openvpn/server.conf | /etc/openvpn/server.conf | ||
| − | cipher AES-128-CBC | + | cipher AES-128-CBC |
| − | + | Di bawah ini, tambahkan baris auth untuk memilih algoritma message digest HMAC. Untuk ini, SHA256 adalah pilihan yang baik: | |
/etc/openvpn/server.conf | /etc/openvpn/server.conf | ||
| − | auth SHA256 | + | auth SHA256 |
| − | + | Akhirnya, temukan pengaturan user dan grup dan hapus ";" pada awal untuk menghapus tanda komentar baris-baris itu: | |
/etc/openvpn/server.conf | /etc/openvpn/server.conf | ||
| − | user nobody | + | user nobody |
| − | group nogroup | + | group nogroup |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===IP LAN Local=== | ||
| − | + | IP LAN local bisa di set di directive | |
| − | + | server 10.8.0.0 255.255.255.0 | |
| − | + | ||
| + | Jika ada jaringan lain selain 10.8.x.x, bisa menggunakan perintah push untuk memberitahukan ke client misalnya | ||
| + | |||
| + | push "route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0" | ||
| + | push "route 192.168.20.0 255.255.255.0" | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jika push dilakukan, maka semua komputer di jaringan 192.168.10.x dan 192.168.20.x juga harus di set agar mengetahui adanya jaringan 10.8.0.0/24 yang bisa dihubungi melalui gateway openvpn. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===(Optional) Paksa perubahan DNS untuk Redirect semua Traffic melalui VPN=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pengaturan di atas akan membuat koneksi VPN antara dua mesin, tetapi tidak akan memaksa koneksi apa pun untuk menggunakan tunnel. Jika anda ingin menggunakan VPN untuk mengarahkan semua lalu lintas anda, anda mungkin ingin memaksa pengaturan DNS ke komputer klien. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Anda dapat melakukan ini, menghilangkan komentar beberapa arahan yang akan mengkonfigurasi mesin klien untuk mengalihkan semua lalu lintas web melalui VPN. Temukan bagian redirect-gateway dan hapus titik koma ";" dari awal kalimat redirect-gateway: | ||
/etc/openvpn/server.conf | /etc/openvpn/server.conf | ||
| − | push "redirect-gateway def1 bypass-dhcp" | + | push "redirect-gateway def1 bypass-dhcp" |
| − | + | Tepat di bawah ini, temukan bagian dhcp-option. Sekali lagi, hapus ";" dari depan kedua baris untuk menghilangkan komentar: | |
/etc/openvpn/server.conf | /etc/openvpn/server.conf | ||
| − | push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.222.222" | + | push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.222.222" |
| − | push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.220.220" | + | push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.220.220" |
| − | + | Ini harus membantu klien dalam konfigurasi ulang pengaturan DNS mereka untuk menggunakan tunnel VPN sebagai gateway default. Pastikan IP address DNS adalah IP address yang dilalukan oleh melalui VPN. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ===(Optional) Atur Port dan Protocol=== | |
| + | |||
| + | Secara default, server OpenVPN menggunakan port 1194 dan protokol UDP untuk menerima koneksi klien. Jika Anda perlu menggunakan port yang berbeda karena lingkungan jaringan yang terbatas di mana klien Anda mungkin berada, Anda dapat mengubah opsi port. Jika anda tidak menghosting konten web server OpenVPN anda, port 443 adalah pilihan populer karena ini biasanya diizinkan melalui aturan firewall. | ||
/etc/openvpn/server.conf | /etc/openvpn/server.conf | ||
| Line 285: | Line 303: | ||
port 443 | port 443 | ||
| − | + | Seringkali protokol yang menggunakan port tersebut di batasi juga. Jika demikian, ubah proto dari UDP ke TCP: | |
/etc/openvpn/server.conf | /etc/openvpn/server.conf | ||
| Line 291: | Line 309: | ||
proto tcp | proto tcp | ||
| − | + | Jika anda tidak perlu menggunakan port yang berbeda, sebaiknya biarkan kedua pengaturan ini sebagai default. | |
| − | (Optional) | + | |
| + | ===(Optional) Penggunaan Kredensial Non-Default=== | ||
| − | + | Jika anda memilih nama yang berbeda selama ./build-key-server command sebelumnya, ubah cert dan key lines yang anda lihat untuk menunjuk ke file .crt dan .key yang sesuai. Jika anda menggunakan server default, ini harus sudah diatur dengan benar: | |
/etc/openvpn/server.conf | /etc/openvpn/server.conf | ||
| − | cert server.crt | + | cert server.crt |
| − | key server.key | + | key server.key |
| + | |||
| + | Setelah selesai, simpan dan tutup file. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Step 8: Mengatur Konfigurasi Network Server== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Selanjutnya, kita perlu menyesuaikan beberapa aspek dari jaringan server sehingga OpenVPN dapat mengarahkan lalu lintas dengan benar. Untuk keperluan latiham kita dapat menggunakan topologi pada gambar berikut, | ||
| − | + | [[File:Belajar-vpn.jpeg|center|300px|thumb]] | |
| − | + | Untuk operasi yang sebenarnya, kita perlu mengatur agar konfigurasi yang di berikan sesuai dengan topologi jaringan yang ada. | |
| − | + | ===Ijinkan IP Forwarding=== | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Pertama, kita perlu mengizinkan server mem-forward lalu lintas. Ini cukup penting untuk fungsionalitas yang kami inginkan untuk disediakan server VPN kita. | |
| − | + | Kita dapat mengaturnya dengan memodifikasi /etc/sysctl.conf | |
| − | + | sudo nano /etc/sysctl.conf | |
| − | + | Di dalam, cari baris yang mengatur net.ipv4.ip_forward. Hapus karakter "#" dari awal baris untuk membuka pengaturan: | |
/etc/sysctl.conf | /etc/sysctl.conf | ||
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 | net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 | ||
| − | + | Simpan dan tutup file saat anda selesai. | |
| − | + | Untuk membaca file dan atur nilai untuk sesi saat ini, ketik: | |
| − | + | sudo sysctl -p | |
| − | + | ===Atur UFW Rules untuk Masquerade Client Connection=== | |
| − | + | Jika anda mengikuti panduan pengaturan server awal Ubuntu 16.04 di prasyarat, anda seharusnya memiliki firewall UFW pada tempatnya. Terlepas dari apakah anda menggunakan firewall untuk memblokir lalu lintas yang tidak diinginkan (yang hampir selalu harus anda lakukan), kita memerlukan firewall dalam panduan ini untuk memanipulasi beberapa lalu lintas yang masuk ke server. Kita perlu memodifikasi file aturan untuk mengatur masquerading, sebuah konsep iptables yang menyediakan NAT dinamis on-the-fly agar rute koneksi klien menjadi benar. | |
| − | + | Sebelum kita membuka file konfigurasi firewall untuk menambahkan masquerading, kita perlu mencari antarmuka jaringan publik dari mesin kami. Untuk melakukan ini, ketik: | |
| − | + | ip route | grep default | |
| − | + | Antarmuka publik anda harus mengikuti kata "dev". Sebagai contoh, hasil ini menunjukkan antarmuka bernama ens18, yang terlihat di bawah ini: | |
| − | + | default via 192.168.0.223 dev ens18 onlink | |
| − | default via | ||
| − | + | Ketika anda memiliki antarmuka yang terkait dengan rute default anda, buka file /etc/ufw/before.rules untuk menambahkan konfigurasi yang relevan: | |
| − | + | sudo nano /etc/ufw/before.rules | |
| − | + | File ini menangani konfigurasi yang harus diletakkan sebelum aturan UFW konvensional dimuat. Pada bagian atas file, tambahkan baris yang di perlihatkan di bawah ini. Ini akan menetapkan kebijakan default untuk rantai POSTROUTING di tabel nat dan me-masquerade lalu lintas apa pun yang berasal dari VPN: | |
| − | + | Catatan: Pastikan untuk mengganti ens18 di baris A-POSTROUTING di bawah ini dengan antarmuka yang anda temukan dalam perintah di atas. | |
/etc/ufw/before.rules | /etc/ufw/before.rules | ||
| Line 355: | Line 378: | ||
# ufw-before-forward | # ufw-before-forward | ||
# | # | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
# START OPENVPN RULES | # START OPENVPN RULES | ||
# NAT table rules | # NAT table rules | ||
*nat | *nat | ||
:POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] | :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] | ||
| − | # Allow traffic from OpenVPN client to | + | # Allow traffic from OpenVPN client to ens18 (change to the interface you discovered!) |
| − | -A POSTROUTING -s 10.8.0.0/8 -o | + | -A POSTROUTING -s 10.8.0.0/8 -o ens18 -j MASQUERADE |
COMMIT | COMMIT | ||
# END OPENVPN RULES | # END OPENVPN RULES | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
# Don't delete these required lines, otherwise there will be errors | # Don't delete these required lines, otherwise there will be errors | ||
*filter | *filter | ||
. . . | . . . | ||
| − | + | Simpan dan tutup file setelah anda selesai. | |
| − | + | Kita perlu memberi tahu UFW untuk mengizinkan paket yang diforward secara default. Untuk melakukan ini, kita akan membuka file /etc/default/ufw: | |
sudo nano /etc/default/ufw | sudo nano /etc/default/ufw | ||
| − | + | Di dalamnya, temukan direktif DEFAULT_FORWARD_POLICY. Kita akan mengubah nilai dari DROP ke ACCEPT: | |
/etc/default/ufw | /etc/default/ufw | ||
| − | DEFAULT_FORWARD_POLICY="ACCEPT" | + | DEFAULT_FORWARD_POLICY="ACCEPT" |
| + | |||
| + | Simpan dan tutup file setelah anda selesai. | ||
| − | + | ===Buka OpenVPN Port=== | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Selanjutnya, kita akan mengatur firewall itu sendiri untuk memungkinkan lalu lintas paket data ke OpenVPN. | |
| − | + | Jika anda tidak mengubah port dan protokol di file /etc/openvpn/server.conf, anda tetap harus membuka lalu lintas UDP ke port 1194. Jika anda memodifikasi port dan / atau protokol, masukan nilai yang anda pilih di sini. | |
| − | + | Kita juga akan menambahkan port SSH jika anda lupa menambahkannya ketika mengikuti tutorial prasyarat: | |
| − | + | sudo ufw allow 1194/udp | |
| − | + | sudo ufw allow OpenSSH | |
| − | + | ===Aktifkan Perubahan=== | |
| − | + | Sekarang, kita dapat menonaktifkan dan mengaktifkan kembali UFW untuk memuat perubahan dari semua file yang telah kita modifikasi: | |
| − | |||
| − | + | sudo ufw disable | |
| − | + | sudo ufw enable | |
| − | + | Server kita sekarang sudah di konfigurasi untuk benar menangani lalu lintas OpenVPN. | |
| − | + | ==Step 9: Start dan Enable OpenVPN Service== | |
| − | + | Kita akhirnya siap untuk memulai layanan OpenVPN di server. Kita dapat melakukan ini menggunakan systemd. | |
| − | + | Kita perlu men-start server OpenVPN dengan memberitahukan nama file konfigurasi yang kita gunakan sebagai variabel setelah nama file unit systemd file. File konfigurasi untuk server yang kita gunakan adalah /etc/openvpn/server.conf, jadi kita akan menambahkan @server ke akhir file unit kami ketika memanggilnya: | |
| − | + | sudo systemctl start openvpn@server | |
| − | + | Periksa kembali apakah layanan telah berhasil dijalankan dengan mengetik: | |
| + | |||
| + | sudo systemctl status openvpn@server | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jika semuanya berjalan lancar, output anda akan terlihat seperti ini: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ● openvpn@server.service - OpenVPN connection to server | ||
| + | Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/openvpn@.service; disabled; vendor preset | ||
| + | Active: active (running) since Mon 2018-06-25 07:26:46 WIB; 9s ago | ||
| + | Docs: man:openvpn(8) | ||
| + | https://community.openvpn.net/openvpn/wiki/Openvpn23ManPage | ||
| + | https://community.openvpn.net/openvpn/wiki/HOWTO | ||
| + | Process: 25449 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/openvpn --daemon ovpn-%i --status /run/open | ||
| + | Main PID: 25453 (openvpn) | ||
| + | CGroup: /system.slice/system-openvpn.slice/openvpn@server.service | ||
| + | └─25453 /usr/sbin/openvpn --daemon ovpn-server --status /run/openvpn/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: /sbin/ip addr add dev tun0 local 1 | ||
| + | Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: /sbin/ip route add 10.8.0.0/24 via | ||
| + | Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: GID set to nogroup | ||
| + | Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: UID set to nobody | ||
| + | Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: UDPv4 link local (bound): [undef] | ||
| + | Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: UDPv4 link remote: [undef] | ||
| + | Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: MULTI: multi_init called, r=256 v= | ||
| + | Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: IFCONFIG POOL: base=10.8.0.4 size= | ||
| + | Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: IFCONFIG POOL LIST | ||
| + | Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: Initialization Sequence Completed | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Anda juga dapat memeriksa apakah antarmuka tun0 OpenVPN tersedia dengan mengetik: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ip addr show tun0 | |
| − | + | Anda akan melihat antarmuka yang dikonfigurasi: | |
| − | + | 3: tun0: <POINTOPOINT,MULTICAST,NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 100 | |
| + | link/none | ||
| + | inet 10.8.0.1 peer 10.8.0.2/32 scope global tun0 | ||
| + | valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever | ||
| − | + | Jika semuanya berjalan dengan baik, aktifkan layanan sehingga dimulai secara otomatis saat boot: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | sudo systemctl enable openvpn@server | |
| − | + | ==Step 10: Membuat Konfigurasi Infrastruktur Client== | |
| − | + | Selanjutnya, kita perlu menyiapkan sistem yang akan memungkinkan kita untuk membuat file konfigurasi klien dengan mudah. | |
| − | + | ===Buat Struktur Config Directory Client=== | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Buat struktur direktori di direktori home anda untuk menyimpan file: | |
| − | + | mkdir -p ~/client-configs/files | |
| − | + | Karena file konfigurasi client akan memiliki key client , kita harus mengunci izin di dalam direktori: | |
| − | + | chmod 700 ~/client-configs/files | |
| − | + | ===Buat Konfigurasi Dasar=== | |
| − | + | Selanjutnya, copy contoh konfigurasi client ke direktori untuk digunakan sebagai konfigurasi dasar kita: | |
| − | + | cp /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/sample-config-files/client.conf ~/client-configs/base.conf | |
| − | + | Buka file baru ini di editor text anda: | |
| − | + | nano ~/client-configs/base.conf | |
| − | + | Di dalam, kita perlu membuat beberapa penyesuaian. | |
| − | + | Pertama, temukan remote directive. Ini mengarahkan client ke alamat server OpenVPN kita. Ini harus menjadi alamat IP publik dari server OpenVPN anda. Jika anda mengubah port yang sedang didengarkan oleh server OpenVPN, ubah 1194 ke port yang anda pilih: | |
~/client-configs/base.conf | ~/client-configs/base.conf | ||
| − | . . . | + | . . . |
| − | # The hostname/IP and port of the server. | + | # The hostname/IP and port of the server. |
| − | # You can have multiple remote entries | + | # You can have multiple remote entries |
| − | # to load balance between the servers. | + | # to load balance between the servers. |
| − | remote server_IP_address 1194 | + | remote server_IP_address 1194 |
| − | . . . | + | . . . |
| + | |||
| + | Misalnya, | ||
| + | |||
| + | remote 202.18.126.200 1194 # kalau ada di IP public | ||
| + | remote 192.168.0.200 1194 # kalau sedang belajar :) .. | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | ||
| + | Pastikan protokol sesuai dengan nilai yang anda gunakan dalam konfigurasi server: | ||
~/client-configs/base.conf | ~/client-configs/base.conf | ||
| − | proto udp | + | proto udp |
| − | + | Selanjutnya, hapus tanda komentar pada directive user dan grup dengan menghapus ";": | |
~/client-configs/base.conf | ~/client-configs/base.conf | ||
| − | # Downgrade privileges after initialization (non-Windows only) | + | # Downgrade privileges after initialization (non-Windows only) |
| − | user nobody | + | user nobody |
| − | group nogroup | + | group nogroup |
| − | + | Temukan directive yang mengatur ca, cert, dan key. Buka comment pada directive tersebut karena kita akan menambahkan sertifikat dan key dalam file itu tersebut: | |
~/client-configs/base.conf | ~/client-configs/base.conf | ||
| − | # SSL/TLS parms. | + | # SSL/TLS parms. |
| − | # See the server config file for more | + | # See the server config file for more |
| − | # description. It's best to use | + | # description. It's best to use |
| − | # a separate .crt/.key file pair | + | # a separate .crt/.key file pair |
| − | # for each client. A single ca | + | # for each client. A single ca |
| − | # file can be used for all clients. | + | # file can be used for all clients. |
| − | #ca ca.crt | + | #ca ca.crt |
| − | #cert client.crt | + | #cert client.crt |
| − | #key client.key | + | #key client.key |
| − | Mirror | + | Mirror pengaturan cipher dan auth yang kita atur di file /etc/openvpn/server.conf: |
~/client-configs/base.conf | ~/client-configs/base.conf | ||
| − | cipher AES-128-CBC | + | cipher AES-128-CBC |
| − | auth SHA256 | + | auth SHA256 |
| − | + | Selanjutnya, tambahkan directive key-direction di dalam file. Ini harus di set ke "1" agar berfungsi dengan server: | |
~/client-configs/base.conf | ~/client-configs/base.conf | ||
| − | key-direction 1 | + | key-direction 1 |
| − | + | Akhirnya, tambahkan beberapa baris yang di commented. Kita ingin memasukkan ini dengan setiap konfigurasi, tetapi seharusnya hanya di enable untuk client Linux yang dikirimkan dengan file /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf. Script ini menggunakan utilitas resolvconf untuk memperbarui informasi DNS untuk client Linux. | |
~/client-configs/base.conf | ~/client-configs/base.conf | ||
| − | # script-security 2 | + | # script-security 2 |
| − | # up /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf | + | # up /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf |
| − | # down /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf | + | # down /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf |
| − | + | Jika client anda menjalankan Linux dan memiliki file /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf, anda harus menghapus tanda comment pada baris tersebut dari file konfigurasi client OpenVPN yang dihasilkan. | |
| − | + | Simpan file ketika Anda selesai. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Buat Script untuk Membuat Konfigurasi=== | |
| − | + | Selanjutnya, kita akan membuat skrip sederhana untuk mengkompilasi konfigurasi dasar kami dengan file sertifikat, key, dan enkripsi yang relevan. Ini akan menempatkan konfigurasi yang dihasilkan di direktori ~/client-configs/files . | |
| − | + | Buat dan buka file beri nama make_config.sh dalam direktori ~/client-configs: | |
| − | + | nano ~/client-configs/make_config.sh | |
| + | |||
| + | Di dalam, paste script berikut: | ||
~/client-configs/make_config.sh | ~/client-configs/make_config.sh | ||
| − | #!/bin/bash | + | #!/bin/bash |
| + | |||
| + | # First argument: Client identifier | ||
| + | |||
| + | KEY_DIR=~/openvpn-ca/keys | ||
| + | OUTPUT_DIR=~/client-configs/files | ||
| + | BASE_CONFIG=~/client-configs/base.conf | ||
| + | |||
| + | cat ${BASE_CONFIG} \ | ||
| + | <(echo -e '<ca>') \ | ||
| + | ${KEY_DIR}/ca.crt \ | ||
| + | <(echo -e '</ca>\n<cert>') \ | ||
| + | ${KEY_DIR}/${1}.crt \ | ||
| + | <(echo -e '</cert>\n<key>') \ | ||
| + | ${KEY_DIR}/${1}.key \ | ||
| + | <(echo -e '</key>\n<tls-auth>') \ | ||
| + | ${KEY_DIR}/ta.key \ | ||
| + | <(echo -e '</tls-auth>') \ | ||
| + | > ${OUTPUT_DIR}/${1}.ovpn | ||
| − | + | Simpan dan tutup file jika anda sudah selesai. | |
| − | + | Ijinkan file untuk bisa di execute ketik: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | chmod 700 ~/client-configs/make_config.sh | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Step 11: Generate Konfigurasi Client== | |
| − | + | Sekarang, kita dapat dengan mudah men-generate file konfigurasi client. | |
| − | + | Jika anda mengikuti panduan ini, anda membuat sertifikat dan key client yang disebut client1.crt dan client1.key masing-masing dengan menjalankan perintah ./build-key client1 pada step 6. Kita dapat membuat konfigurasi untuk kredensial ini dengan pindah ke direktori ~/client-configs dan menggunakan skrip yang kita buat: | |
| − | + | cd ~/client-configs | |
| + | ./make_config.sh client1 | ||
| − | + | Jika semua berjalan dengan lancar, kita akan memperoleh file client1.ovpn di directory ~/client-configs/files | |
| + | |||
| + | ls ~/client-configs/files | ||
| + | |||
| + | Output | ||
| − | + | client1.ovpn | |
| − | + | ===Transfer file konfigurasi ke device Client=== | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Kita perlu mentransfer file konfigurasi client ke perangkat yang relevan. Misalnya, ini bisa berupa komputer atau perangkat seluler anda. | |
| − | + | Sementara aplikasi yang tepat digunakan untuk melakukan transfer ini akan tergantung pada pilihan anda dan sistem operasi perangkat, anda perlu menggunakan SFTP (SSH file transfer protocol) atau SCP (Secure Copy) pada backend. Ini akan mentransfer file autentikasi VPN klien anda melalui koneksi terenkripsi. | |
| − | + | Berikut ini contoh perintah SFTP menggunakan contoh client1.ovpn. Perintah ini dapat dijalankan dari komputer anda (OS X atau Linux). Ini menempatkan file .ovpn di direktori home anda: | |
| − | client1.ovpn | ||
| − | + | sftp sammy@openvpn_server_ip:client-configs/files/client1.ovpn ~/ | |
| − | + | Atau jika anda menggunakan linux, dapat juga menggunakan perintah scp berikut | |
| − | + | scp sammy@openvpn_server_ip:client-configs/files/client1.ovpn ~/ | |
| − | + | ==Step 12: Instalasi Konfigurasi Client== | |
| − | + | Sekarang, kita akan membahas cara menginstal profil VPN client Windows, OS X, iOS, dan Android. Tidak satu pun dari instruksi client ini bergantung satu sama lain, jadi silakan lewati ke mana pun yang berlaku untuk anda. | |
| − | + | Koneksi OpenVPN akan dibuka saat kita membuka file .ovpn. Dalam contoh ini, koneksi akan disebut client1.ovpn untuk file client pertama yang kami hasilkan. | |
| − | + | ===Windows=== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Instalasi''' | |
| − | + | Aplikasi client OpenVPN di Windows bisa di ambil situs openvpn | |
| − | + | * https://openvpn.net/ | |
| − | + | * http://swupdate.openvpn.org/privatetunnel/client/privatetunnel-win-2.8.exe | |
| − | + | OpenVPN membutuhkan ijin administrator untuk bisa di instalasi. | |
| + | Setelah menginstalasi OpenVPN, copy file .ovpn ke: | ||
| − | + | C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\config | |
| − | + | Saat menjalankan OpenVPN, dia akan secara automatis melihat profile dan langsung membuka sambungan. | |
| − | OpenVPN | ||
| − | + | OpenVPN harus dijalankan sebagai administrator setiap kali digunakan, bahkan oleh akun administratif. Untuk melakukan ini tanpa harus mengklik kanan dan memilih Run as administrator setiap kali anda menggunakan VPN, anda dapat mengatur ini, tetapi ini harus dilakukan dari akun administratif. Ini juga berarti bahwa pengguna standar harus memasukkan password administrator untuk menggunakan OpenVPN. Di sisi lain, pengguna standar tidak dapat terhubung dengan benar ke server kecuali aplikasi OpenVPN pada klien memiliki hak admin, oleh karenanya hak istimewa yang ditinggikan diperlukan. | |
| − | + | Untuk mengatur aplikasi OpenVPN agar selalu berjalan sebagai administrator, klik kanan pada ikon shortcut-nya dan buka Properties. Di bagian bawah tab "Compatibility", klik tombol untuk "Change Settings for all users". Di jendela baru, cek "Run this program as an administrator". | |
| − | + | '''Connecting''' | |
| − | OpenVPN | + | Setiap kali anda membuka GUI OpenVPN, Windows akan menanyakan apakah anda mengijinkan program untuk melakukan perubahan pada komputer anda. Klik "Yes". Meluncurkan aplikasi klien OpenVPN hanya menempatkan applet di system tray sehingga VPN dapat terhubung dan terputus sesuai kebutuhan; applet tersebut tidak benar-benar membuat koneksi VPN. |
| − | + | Setelah OpenVPN dimulai, jalankan koneksi dengan masuk ke system tray applet dan klik kanan pada ikon applet OpenVPN. Ini membuka menu context. Pilih client1 di bagian atas menu (itu profil client1.ovpn) dan pilih Connect. | |
| − | + | Jendela status akan terbuka yang menunjukkan keluaran log saat koneksi dibuat, dan sebuah pesan akan muncul setelah klien terhubung. | |
| − | + | Disconnect sambungan dari VPN dengan cara yang sama: Buka system tray applet, klik kanan ikon applet OpenVPN, pilih profil client dan klik Disconnect. | |
| − | + | ===OS X=== | |
| − | + | '''Installing''' | |
| − | + | Tunnelblick adalah client OpenVPN yang free dan open source untuk Mac OS X. Anda dapat mendownload disk image versi terakhir dari Tunnelblick Downloads page. Double-click file .dmg dan ikuti prompt untuk menginstalasi. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Di akhir proses instalasi, Tunnelblick akan bertanya apakah anda memiliki file konfigurasi. Akan lebih mudah untuk menjawab "np" dan membiarkan Tunnelblick selesai. Buka Finder window dan double-click client1.ovpn. Tunnelblick akan menginstalasi client profile. Administrative privilege dibutuhkan untuk itu. | |
| − | + | '''Connecting''' | |
| − | + | Jalankan Tunnelblick dengan double-clicking Tunnelblick di Application folder. Setelah Tunnelblick di jalankan, akan ada icon Tunnelblick di menu bar di sebelah kanan atas layar untuk mengatur sambungan. Klik icon, dan kemudian Connect menu item untuk memulai sambungan VPN. Pilih client1. | |
| − | + | ===Linux=== | |
| − | + | '''Instalasi''' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Jika anda menggunakan Linux, ada banyak tools yang dapat di gunakan tergantung dari distribusi linux yang digunakan. Desktop atau windows manager mungkin menyediakan utilitas untuk connection. | |
| − | + | Cara yang paling umum untuk connecting, adalah dengan menggunakan software OpenVPN. | |
| − | + | Di Ubuntu atau Debian, proses instalasi tidak berbeda jauh dengan di server dengan menulis: | |
| − | + | sudo apt-get update | |
| − | + | sudo apt-get install openvpn | |
| − | + | Di CentOS kita dapat mengenable EPEL repository dan menginstalasi-nya dengan menulis: | |
| − | + | sudo yum install epel-release | |
| − | + | sudo yum install openvpn | |
| − | Configuring | + | '''Configuring''' |
| − | + | Cek apakah distribusi anda memasukan script /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf: | |
| − | + | ls /etc/openvpn | |
Output | Output | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | update-resolve-conf | |
| + | |||
| + | Selanjutnya, edit file konfigurasi client OpenVPN: | ||
| − | + | nano client1.ovpn | |
| − | Uncomment | + | Uncomment tiga kalimat yang kita letakan untuk mengatur setting DNS jika anda dapat memperoleh file update-resolv-conf: |
client1.ovpn | client1.ovpn | ||
| − | script-security 2 | + | script-security 2 |
| − | up /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf | + | up /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf |
| − | down /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf | + | down /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf |
| − | + | Jika anda menggunakan CentOS, ubah group dari nogroup ke nobody agar cocok dengan group yang tersedia di distribusi: | |
client1.ovpn | client1.ovpn | ||
| − | group nobody | + | group nobody |
| + | |||
| + | Sava dan close file tersebut. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Connection''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sekarang, anda dapat connect ke VPN (untuk client1.ovpn) melalui perintah: | ||
| + | |||
| + | sudo openvpn --config client1.ovpn | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | Jika tersambung akan muncul interface baru tun0 | |
| + | |||
| + | ifconfig | ||
| + | |||
| + | Output, kira-kira | ||
| + | |||
| + | tun0 Link encap:UNSPEC HWaddr 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00 | ||
| + | inet addr:10.8.0.6 P-t-P:10.8.0.5 Mask:255.255.255.255 | ||
| + | UP POINTOPOINT RUNNING NOARP MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 | ||
| + | RX packets:32 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 | ||
| + | TX packets:42 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 | ||
| + | collisions:0 txqueuelen:100 | ||
| + | RX bytes:5080 (5.0 KB) TX bytes:5457 (5.4 KB) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jika ada routing ke arah openvpn 10.8.0.x | ||
| + | |||
| + | netstat -nr | ||
| + | |||
| + | Output | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kernel IP routing table | ||
| + | Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface | ||
| + | 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.223 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 enp3s0 | ||
| + | 10.8.0.1 10.8.0.5 255.255.255.255 UGH 0 0 0 tun0 | ||
| + | 10.8.0.5 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 tun0 | ||
| + | 50.235.87.130 192.168.0.223 255.255.255.255 UGH 0 0 0 enp3s0 | ||
| + | 169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 enp3s0 | ||
| + | 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 enp3s0 | ||
| + | 192.168.10.0 10.8.0.5 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 tun0 | ||
| + | 222.124.18.79 192.168.0.223 255.255.255.255 UGH 0 0 0 enp3s0 | ||
| − | + | Jika di perlukan untuk membuat routing tambahan ke LAN (misalnya 192.168.10.0/24) di balik server openvpn (gateway 10.8.0.5), dapat menggunakan perintah | |
| − | + | sudo route add -net 192.168.10.0/24 gw 10.8.0.5 | |
==Referensi== | ==Referensi== | ||
* https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-set-up-an-openvpn-server-on-ubuntu-16-04 | * https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-set-up-an-openvpn-server-on-ubuntu-16-04 | ||
Latest revision as of 11:28, 30 March 2020
Sumber: https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-set-up-an-openvpn-server-on-ubuntu-16-04
Ingin mengakses Internet dengan aman dari smartphone atau laptop anda ketika terhubung ke jaringan tidak bisa dipercaya seperti WiFi dari hotel atau cafe? Virtual Private Network (VPN) memungkinkan Anda untuk melintasi jaringan yang tidak bisa dipercaya secara private dan aman seolah-olah Anda berada di jaringan private. Lalu lintas muncul dari server VPN dan melanjutkan perjalanannya ke tujuan.
Ketika dikombinasikan dengan sambungan HTTPS, pengaturan ini memungkinkan anda untuk mengamankan login dan transaksi wireless anda. Anda dapat menghindari pembatasan geografis dan penyensoran, dan melindungi lokasi anda dan lalu lintas HTTP yang tidak terenkripsi dari jaringan yang tidak dipercaya.
OpenVPN adalah solusi VPN Secure Socket Layer (SSL) open source dengan fitur lengkap yang mengakomodasi berbagai konfigurasi. Dalam tutorial ini, kami akan menyiapkan server OpenVPN pada Droplet dan kemudian mengonfigurasi aksesnya dari Windows, OS X, iOS dan Android. Tutorial ini berusaha agar proses instalasi dan langkah-langkah konfigurasi dijaga sesederhana mungkin.
Persyaratan
Untuk bisa menyelesaikan tutorial ini, anda membutuhkan
- Ubuntu 16.04 server
- bisa akses root (sudo) dari non-root user
Step 1: Install OpenVPN
Instalasi aplikasi yang dibutuhkan
sudo su apt update apt -y install openvpn easy-rsa
paket easy-rsa dibutuhkan untuk membantu kita dalam men-setup internal CA (certificate authority)
Step 2: Set Up CA Directory
OpenVPN adalah VPN TLS / SSL. Ini berarti bahwa ia menggunakan sertifikat untuk mengenkripsi lalu lintas antara server dan klien. Untuk mengeluarkan sertifikat tepercaya, kita perlu menyiapkan otoritas sertifikat / certificate authority (CA) sendiri yang sederhana.
Untuk itu, kita copy template directory easy-rsa ke home directory dengan perintah make-cadir
make-cadir ~/openvpn-ca
Pindah ke directory CA tersebut untuk memulai konfigurasi CA
cd ~/openvpn-ca
Step 3: Konfigurasi variabel CA
Untuk mengkonfigurasi nilai CA, kita perlu mengedit file
cd ~/openvpn-ca nano vars
Minimal yang perlu di edit adalah variabel yang berada di bagian agak bawah file tersebut, sebagai berikut,
. . . export KEY_COUNTRY="US" export KEY_PROVINCE="CA" export KEY_CITY="SanFrancisco" export KEY_ORG="Fort-Funston" export KEY_EMAIL="me@myhost.mydomain" export KEY_OU="MyOrganizationalUnit" . . .
Edit sesuai dengan nilai yang anda sukai, jangan di kosongkan, misalnya,
. . . export KEY_COUNTRY="ID" export KEY_PROVINCE="DKI" export KEY_CITY="Jakarta" export KEY_ORG="CobaSaja" export KEY_EMAIL="admin@cobasaja.com" export KEY_OU="Riset" . . .
Di bagian bawah parameter di atas, kita juga dapat mengedit nilai KEY_NAME, yang akan mengisi field subject. Untuk membuat sederhana, kita dapat saja menyebutnya "server".
export KEY_NAME="server"
Jika kita selesai, save dan tutup file.
Step 4: Build Certificate Authority
Sekarang, kita dapat menggunakan variabel yang telah kita tetapkan dan utilitas easy-rsa untuk membangun Certificate Authority (CA). Pastikan anda berada di directory CA, dan coba melihat isi file vars yang sudah kita edit,
cd ~/openvpn-ca source ./vars
Sampai keluar kata2
NOTE: If you run ./clean-all, I will be doing a rm -rf on /root/openvpn-ca/keys
Jalankan
cd ~/openvpn-ca ./clean-all
Setelah lingkungan bersih, kita dapat membuat root CA dengan menulis
cd ~/openvpn-ca ./build-ca
Pada dasarnya kita cukup meng-ENTER semua varibel, sebagai berikut,
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key .............................+++ .....................................................................+++ writing new private key to 'ca.key' ----- You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [ID]: State or Province Name (full name) [DKI]: Locality Name (eg, city) [Jakarta]: Organization Name (eg, company) [CobaSaja]: Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) [Riset]: Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) [CobaSaja CA]: Name [server]: Email Address [admin@cobasaja.com]:
CA sekarang sudah dibuat. Selanjutnya kita perlu membuat berbagai file lainnya yang dibutuhkan.
Step 5: Membuat Server Certificate, Key, dan Encryption File
Selanjutnya, kita perlu membuat certificate server dan pasangan key, maupun berbagai file yang digunakan saat proses enkripsi.
Jika anda menggunakan nama server lain, selain "server". Maka kita perlu memodifikasi /etc/openvpn/server.conf . Juga arah ke file .crt dan .key. Jika kita menggunakan nama "server, maka dapat menggunakan perintah berikut,
cd ~/openvpn-ca/ ./build-key-server server
Hasilnya kira-kira,
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key ........................+++ ......+++ writing new private key to 'server.key' ----- You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [ID]: State or Province Name (full name) [DKI]: Locality Name (eg, city) [Jakarta]: Organization Name (eg, company) [CobaSaja]: Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) [Riset]: Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) [server]: Name [server]: Email Address [admin@cobasaja.com]: Please enter the following 'extra' attributes to be sent with your certificate request A challenge password []:123456 An optional company name []:CobaSaja.com
Masukan password & company name yang anda suka / inginkan, output akan berlanjut sebagai berikut,
Using configuration from /root/openvpn-ca/openssl-1.0.0.cnf Check that the request matches the signature Signature ok The Subject's Distinguished Name is as follows countryName :PRINTABLE:'ID' stateOrProvinceName :PRINTABLE:'DKI' localityName :PRINTABLE:'Jakarta' organizationName :PRINTABLE:'CobaSaja' organizationalUnitName:PRINTABLE:'Riset' commonName :PRINTABLE:'server' name :PRINTABLE:'server' emailAddress :IA5STRING:'admin@cobasaja.com' Certificate is to be certified until Jun 21 02:42:33 2028 GMT (3650 days) Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y 1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y
Tekan "y" untuk menanda tangani sertifikat, hasilnya adalah
Write out database with 1 new entries Data Base Updated
Selanjutnya, kita akan membuat beberapa file lainnya. Kita akan men-generate key Diffie-Hellman yang kuat untuk digunakan saat exchange key dengan menuliskan perintah,
./build-dh
Ini akan membutuhkan beberapa waktu untuk selesai. Selanjutnya, kita men-generate HMAC signature untuk menguatkan kemampuan server dalam TLS integrity verification, melalui perintah:
openvpn --genkey --secret keys/ta.key
Step 6: Generate Client Certificate & Key Pair
Selanjutnya, kita dapat men-generate sertifikat client dan pasangan kunci. Meskipun ini dapat dilakukan pada mesin klien dan kemudian ditandatangani oleh server / CA untuk tujuan keamanan, untuk panduan ini kita akan men-generate kunci yang ditandatangani langsung di server supaya lebih sederhana saja. Pada prakteknya, sebetulnya proses ini sebaiknya dilakukan di client.
Kita akan membuat satu (sebuah) kunci / sertifikat klien untuk panduan ini, tetapi jika anda memiliki lebih dari satu client, anda dapat mengulangi proses ini sebanyak yang anda mau. Berikan nilai unik pada skrip untuk setiap client.
Karena anda dapat kembali ke langkah ini di lain waktu, kami akan men-source ulang file vars. Kita akan menggunakan client1 sebagai nilai untuk sertifikat / pasangan kunci pertama kita untuk panduan ini.
Untuk menghasilkan kredensial tanpa password, untuk membantu dalam koneksi otomatis, gunakan perintah build-key seperti ini:
cd ~/openvpn-ca source vars ./build-key client1
Jika sebaliknya, anda ingin membuat kredensial yang dilindungi password, gunakan perintah build-key-pass:
cd ~/openvpn-ca source vars ./build-key-pass client1
Sekali lagi, default seharusnya sudah terisi, jadi anda cukup menekan ENTER untuk melanjutkan. Tinggalkan pasword kosong dan pastikan untuk memasukkan y untuk petunjuk yang menanyakan apakah akan menandatangani dan komit sertifikat.
Jika ada masalah, maka database key ada di folder ~/openvpn-ca/keys
Step 7: Konfigurasi OpenVPN Service
Selanjutnya, kita dapat mulai mengkonfigurasi layanan OpenVPN menggunakan kredensial dan file yang telah kita buat.
Copy File ke Direktori OpenVPN
Untuk memulai, kita perlu mengcopy file yang kita butuhkan ke direktori konfigurasi /etc/openvpn.
Kita bisa mulai dengan semua file yang baru kita buat. File tersebut ditempatkan di dalam direktori ~/openvpn-ca/keys saat dibuat. Kita perlu memindahkan sertifikat CA, sertifikat dan key server, tanda tangan digital HMAC, dan file Diffie-Hellman:
cd ~/openvpn-ca/keys sudo cp ca.crt server.crt server.key ta.key dh2048.pem /etc/openvpn
Selanjutnya, kita perlu mengcopy dan unzip file konfigurasi OpenVPN contoh ke dalam direktori konfigurasi sehingga kita dapat menggunakannya sebagai dasar untuk setup:
gunzip -c /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/sample-config-files/server.conf.gz | sudo tee /etc/openvpn/server.conf
Atur Konfigurasi OpenVPN
Setelah file kita di tempat yang benar, kiita dapat memodifikasi file konfigurasi server:
sudo nano /etc/openvpn/server.conf
Basic Configuration
Pertama, temukan bagian HMAC dengan mencari petunjuk tls-auth. Hapus ";" untuk menghapus tanda komentar pada baris tls-auth. Di bawah ini, tambahkan parameter key-direction dan set "0": /etc/openvpn/server.conf
tls-auth ta.key 0 # This file is secret key-direction 0
Selanjutnya, temukan bagian pada cipher cryptographic dengan mencari baris cipher yang dikomentari. Cipher AES-128-CBC menawarkan tingkat enkripsi yang baik dan didukung dengan baik. Hapus ";" untuk menghapus tanda komentar pada cipher AES-128-CBC line: /etc/openvpn/server.conf
cipher AES-128-CBC
Di bawah ini, tambahkan baris auth untuk memilih algoritma message digest HMAC. Untuk ini, SHA256 adalah pilihan yang baik: /etc/openvpn/server.conf
auth SHA256
Akhirnya, temukan pengaturan user dan grup dan hapus ";" pada awal untuk menghapus tanda komentar baris-baris itu: /etc/openvpn/server.conf
user nobody group nogroup
IP LAN Local
IP LAN local bisa di set di directive
server 10.8.0.0 255.255.255.0
Jika ada jaringan lain selain 10.8.x.x, bisa menggunakan perintah push untuk memberitahukan ke client misalnya
push "route 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0" push "route 192.168.20.0 255.255.255.0"
Jika push dilakukan, maka semua komputer di jaringan 192.168.10.x dan 192.168.20.x juga harus di set agar mengetahui adanya jaringan 10.8.0.0/24 yang bisa dihubungi melalui gateway openvpn.
(Optional) Paksa perubahan DNS untuk Redirect semua Traffic melalui VPN
Pengaturan di atas akan membuat koneksi VPN antara dua mesin, tetapi tidak akan memaksa koneksi apa pun untuk menggunakan tunnel. Jika anda ingin menggunakan VPN untuk mengarahkan semua lalu lintas anda, anda mungkin ingin memaksa pengaturan DNS ke komputer klien.
Anda dapat melakukan ini, menghilangkan komentar beberapa arahan yang akan mengkonfigurasi mesin klien untuk mengalihkan semua lalu lintas web melalui VPN. Temukan bagian redirect-gateway dan hapus titik koma ";" dari awal kalimat redirect-gateway: /etc/openvpn/server.conf
push "redirect-gateway def1 bypass-dhcp"
Tepat di bawah ini, temukan bagian dhcp-option. Sekali lagi, hapus ";" dari depan kedua baris untuk menghilangkan komentar: /etc/openvpn/server.conf
push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.222.222" push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.220.220"
Ini harus membantu klien dalam konfigurasi ulang pengaturan DNS mereka untuk menggunakan tunnel VPN sebagai gateway default. Pastikan IP address DNS adalah IP address yang dilalukan oleh melalui VPN.
(Optional) Atur Port dan Protocol
Secara default, server OpenVPN menggunakan port 1194 dan protokol UDP untuk menerima koneksi klien. Jika Anda perlu menggunakan port yang berbeda karena lingkungan jaringan yang terbatas di mana klien Anda mungkin berada, Anda dapat mengubah opsi port. Jika anda tidak menghosting konten web server OpenVPN anda, port 443 adalah pilihan populer karena ini biasanya diizinkan melalui aturan firewall. /etc/openvpn/server.conf
# Optional! port 443
Seringkali protokol yang menggunakan port tersebut di batasi juga. Jika demikian, ubah proto dari UDP ke TCP: /etc/openvpn/server.conf
# Optional! proto tcp
Jika anda tidak perlu menggunakan port yang berbeda, sebaiknya biarkan kedua pengaturan ini sebagai default.
(Optional) Penggunaan Kredensial Non-Default
Jika anda memilih nama yang berbeda selama ./build-key-server command sebelumnya, ubah cert dan key lines yang anda lihat untuk menunjuk ke file .crt dan .key yang sesuai. Jika anda menggunakan server default, ini harus sudah diatur dengan benar: /etc/openvpn/server.conf
cert server.crt key server.key
Setelah selesai, simpan dan tutup file.
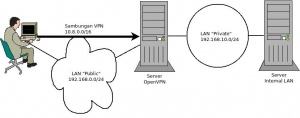
Step 8: Mengatur Konfigurasi Network Server
Selanjutnya, kita perlu menyesuaikan beberapa aspek dari jaringan server sehingga OpenVPN dapat mengarahkan lalu lintas dengan benar. Untuk keperluan latiham kita dapat menggunakan topologi pada gambar berikut,
Untuk operasi yang sebenarnya, kita perlu mengatur agar konfigurasi yang di berikan sesuai dengan topologi jaringan yang ada.
Ijinkan IP Forwarding
Pertama, kita perlu mengizinkan server mem-forward lalu lintas. Ini cukup penting untuk fungsionalitas yang kami inginkan untuk disediakan server VPN kita.
Kita dapat mengaturnya dengan memodifikasi /etc/sysctl.conf
sudo nano /etc/sysctl.conf
Di dalam, cari baris yang mengatur net.ipv4.ip_forward. Hapus karakter "#" dari awal baris untuk membuka pengaturan: /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
Simpan dan tutup file saat anda selesai.
Untuk membaca file dan atur nilai untuk sesi saat ini, ketik:
sudo sysctl -p
Atur UFW Rules untuk Masquerade Client Connection
Jika anda mengikuti panduan pengaturan server awal Ubuntu 16.04 di prasyarat, anda seharusnya memiliki firewall UFW pada tempatnya. Terlepas dari apakah anda menggunakan firewall untuk memblokir lalu lintas yang tidak diinginkan (yang hampir selalu harus anda lakukan), kita memerlukan firewall dalam panduan ini untuk memanipulasi beberapa lalu lintas yang masuk ke server. Kita perlu memodifikasi file aturan untuk mengatur masquerading, sebuah konsep iptables yang menyediakan NAT dinamis on-the-fly agar rute koneksi klien menjadi benar.
Sebelum kita membuka file konfigurasi firewall untuk menambahkan masquerading, kita perlu mencari antarmuka jaringan publik dari mesin kami. Untuk melakukan ini, ketik:
ip route | grep default
Antarmuka publik anda harus mengikuti kata "dev". Sebagai contoh, hasil ini menunjukkan antarmuka bernama ens18, yang terlihat di bawah ini:
default via 192.168.0.223 dev ens18 onlink
Ketika anda memiliki antarmuka yang terkait dengan rute default anda, buka file /etc/ufw/before.rules untuk menambahkan konfigurasi yang relevan:
sudo nano /etc/ufw/before.rules
File ini menangani konfigurasi yang harus diletakkan sebelum aturan UFW konvensional dimuat. Pada bagian atas file, tambahkan baris yang di perlihatkan di bawah ini. Ini akan menetapkan kebijakan default untuk rantai POSTROUTING di tabel nat dan me-masquerade lalu lintas apa pun yang berasal dari VPN:
Catatan: Pastikan untuk mengganti ens18 di baris A-POSTROUTING di bawah ini dengan antarmuka yang anda temukan dalam perintah di atas. /etc/ufw/before.rules
# # rules.before # # Rules that should be run before the ufw command line added rules. Custom # rules should be added to one of these chains: # ufw-before-input # ufw-before-output # ufw-before-forward #
# START OPENVPN RULES # NAT table rules *nat :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] # Allow traffic from OpenVPN client to ens18 (change to the interface you discovered!) -A POSTROUTING -s 10.8.0.0/8 -o ens18 -j MASQUERADE COMMIT # END OPENVPN RULES
# Don't delete these required lines, otherwise there will be errors *filter . . .
Simpan dan tutup file setelah anda selesai.
Kita perlu memberi tahu UFW untuk mengizinkan paket yang diforward secara default. Untuk melakukan ini, kita akan membuka file /etc/default/ufw:
sudo nano /etc/default/ufw
Di dalamnya, temukan direktif DEFAULT_FORWARD_POLICY. Kita akan mengubah nilai dari DROP ke ACCEPT: /etc/default/ufw
DEFAULT_FORWARD_POLICY="ACCEPT"
Simpan dan tutup file setelah anda selesai.
Buka OpenVPN Port
Selanjutnya, kita akan mengatur firewall itu sendiri untuk memungkinkan lalu lintas paket data ke OpenVPN.
Jika anda tidak mengubah port dan protokol di file /etc/openvpn/server.conf, anda tetap harus membuka lalu lintas UDP ke port 1194. Jika anda memodifikasi port dan / atau protokol, masukan nilai yang anda pilih di sini.
Kita juga akan menambahkan port SSH jika anda lupa menambahkannya ketika mengikuti tutorial prasyarat:
sudo ufw allow 1194/udp sudo ufw allow OpenSSH
Aktifkan Perubahan
Sekarang, kita dapat menonaktifkan dan mengaktifkan kembali UFW untuk memuat perubahan dari semua file yang telah kita modifikasi:
sudo ufw disable sudo ufw enable
Server kita sekarang sudah di konfigurasi untuk benar menangani lalu lintas OpenVPN.
Step 9: Start dan Enable OpenVPN Service
Kita akhirnya siap untuk memulai layanan OpenVPN di server. Kita dapat melakukan ini menggunakan systemd.
Kita perlu men-start server OpenVPN dengan memberitahukan nama file konfigurasi yang kita gunakan sebagai variabel setelah nama file unit systemd file. File konfigurasi untuk server yang kita gunakan adalah /etc/openvpn/server.conf, jadi kita akan menambahkan @server ke akhir file unit kami ketika memanggilnya:
sudo systemctl start openvpn@server
Periksa kembali apakah layanan telah berhasil dijalankan dengan mengetik:
sudo systemctl status openvpn@server
Jika semuanya berjalan lancar, output anda akan terlihat seperti ini:
● openvpn@server.service - OpenVPN connection to server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/openvpn@.service; disabled; vendor preset
Active: active (running) since Mon 2018-06-25 07:26:46 WIB; 9s ago
Docs: man:openvpn(8)
https://community.openvpn.net/openvpn/wiki/Openvpn23ManPage
https://community.openvpn.net/openvpn/wiki/HOWTO
Process: 25449 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/openvpn --daemon ovpn-%i --status /run/open
Main PID: 25453 (openvpn)
CGroup: /system.slice/system-openvpn.slice/openvpn@server.service
└─25453 /usr/sbin/openvpn --daemon ovpn-server --status /run/openvpn/
Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: /sbin/ip addr add dev tun0 local 1
Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: /sbin/ip route add 10.8.0.0/24 via
Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: GID set to nogroup
Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: UID set to nobody
Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: UDPv4 link local (bound): [undef]
Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: UDPv4 link remote: [undef]
Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: MULTI: multi_init called, r=256 v=
Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: IFCONFIG POOL: base=10.8.0.4 size=
Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: IFCONFIG POOL LIST
Jun 25 07:26:46 refserver ovpn-server[25453]: Initialization Sequence Completed
Anda juga dapat memeriksa apakah antarmuka tun0 OpenVPN tersedia dengan mengetik:
ip addr show tun0
Anda akan melihat antarmuka yang dikonfigurasi:
3: tun0: <POINTOPOINT,MULTICAST,NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 100
link/none
inet 10.8.0.1 peer 10.8.0.2/32 scope global tun0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Jika semuanya berjalan dengan baik, aktifkan layanan sehingga dimulai secara otomatis saat boot:
sudo systemctl enable openvpn@server
Step 10: Membuat Konfigurasi Infrastruktur Client
Selanjutnya, kita perlu menyiapkan sistem yang akan memungkinkan kita untuk membuat file konfigurasi klien dengan mudah.
Buat Struktur Config Directory Client
Buat struktur direktori di direktori home anda untuk menyimpan file:
mkdir -p ~/client-configs/files
Karena file konfigurasi client akan memiliki key client , kita harus mengunci izin di dalam direktori:
chmod 700 ~/client-configs/files
Buat Konfigurasi Dasar
Selanjutnya, copy contoh konfigurasi client ke direktori untuk digunakan sebagai konfigurasi dasar kita:
cp /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/sample-config-files/client.conf ~/client-configs/base.conf
Buka file baru ini di editor text anda:
nano ~/client-configs/base.conf
Di dalam, kita perlu membuat beberapa penyesuaian.
Pertama, temukan remote directive. Ini mengarahkan client ke alamat server OpenVPN kita. Ini harus menjadi alamat IP publik dari server OpenVPN anda. Jika anda mengubah port yang sedang didengarkan oleh server OpenVPN, ubah 1194 ke port yang anda pilih: ~/client-configs/base.conf
. . . # The hostname/IP and port of the server. # You can have multiple remote entries # to load balance between the servers. remote server_IP_address 1194 . . .
Misalnya,
remote 202.18.126.200 1194 # kalau ada di IP public remote 192.168.0.200 1194 # kalau sedang belajar :) ..
Pastikan protokol sesuai dengan nilai yang anda gunakan dalam konfigurasi server: ~/client-configs/base.conf
proto udp
Selanjutnya, hapus tanda komentar pada directive user dan grup dengan menghapus ";": ~/client-configs/base.conf
# Downgrade privileges after initialization (non-Windows only) user nobody group nogroup
Temukan directive yang mengatur ca, cert, dan key. Buka comment pada directive tersebut karena kita akan menambahkan sertifikat dan key dalam file itu tersebut: ~/client-configs/base.conf
# SSL/TLS parms. # See the server config file for more # description. It's best to use # a separate .crt/.key file pair # for each client. A single ca # file can be used for all clients. #ca ca.crt #cert client.crt #key client.key
Mirror pengaturan cipher dan auth yang kita atur di file /etc/openvpn/server.conf: ~/client-configs/base.conf
cipher AES-128-CBC auth SHA256
Selanjutnya, tambahkan directive key-direction di dalam file. Ini harus di set ke "1" agar berfungsi dengan server: ~/client-configs/base.conf
key-direction 1
Akhirnya, tambahkan beberapa baris yang di commented. Kita ingin memasukkan ini dengan setiap konfigurasi, tetapi seharusnya hanya di enable untuk client Linux yang dikirimkan dengan file /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf. Script ini menggunakan utilitas resolvconf untuk memperbarui informasi DNS untuk client Linux. ~/client-configs/base.conf
# script-security 2 # up /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf # down /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf
Jika client anda menjalankan Linux dan memiliki file /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf, anda harus menghapus tanda comment pada baris tersebut dari file konfigurasi client OpenVPN yang dihasilkan.
Simpan file ketika Anda selesai.
Buat Script untuk Membuat Konfigurasi
Selanjutnya, kita akan membuat skrip sederhana untuk mengkompilasi konfigurasi dasar kami dengan file sertifikat, key, dan enkripsi yang relevan. Ini akan menempatkan konfigurasi yang dihasilkan di direktori ~/client-configs/files .
Buat dan buka file beri nama make_config.sh dalam direktori ~/client-configs:
nano ~/client-configs/make_config.sh
Di dalam, paste script berikut: ~/client-configs/make_config.sh
#!/bin/bash
# First argument: Client identifier
KEY_DIR=~/openvpn-ca/keys
OUTPUT_DIR=~/client-configs/files
BASE_CONFIG=~/client-configs/base.conf
cat ${BASE_CONFIG} \
<(echo -e '<ca>') \
${KEY_DIR}/ca.crt \
<(echo -e '</ca>\n<cert>') \
${KEY_DIR}/${1}.crt \
<(echo -e '</cert>\n<key>') \
${KEY_DIR}/${1}.key \
<(echo -e '</key>\n<tls-auth>') \
${KEY_DIR}/ta.key \
<(echo -e '</tls-auth>') \
> ${OUTPUT_DIR}/${1}.ovpn
Simpan dan tutup file jika anda sudah selesai.
Ijinkan file untuk bisa di execute ketik:
chmod 700 ~/client-configs/make_config.sh
Step 11: Generate Konfigurasi Client
Sekarang, kita dapat dengan mudah men-generate file konfigurasi client.
Jika anda mengikuti panduan ini, anda membuat sertifikat dan key client yang disebut client1.crt dan client1.key masing-masing dengan menjalankan perintah ./build-key client1 pada step 6. Kita dapat membuat konfigurasi untuk kredensial ini dengan pindah ke direktori ~/client-configs dan menggunakan skrip yang kita buat:
cd ~/client-configs ./make_config.sh client1
Jika semua berjalan dengan lancar, kita akan memperoleh file client1.ovpn di directory ~/client-configs/files
ls ~/client-configs/files
Output
client1.ovpn
Transfer file konfigurasi ke device Client
Kita perlu mentransfer file konfigurasi client ke perangkat yang relevan. Misalnya, ini bisa berupa komputer atau perangkat seluler anda.
Sementara aplikasi yang tepat digunakan untuk melakukan transfer ini akan tergantung pada pilihan anda dan sistem operasi perangkat, anda perlu menggunakan SFTP (SSH file transfer protocol) atau SCP (Secure Copy) pada backend. Ini akan mentransfer file autentikasi VPN klien anda melalui koneksi terenkripsi.
Berikut ini contoh perintah SFTP menggunakan contoh client1.ovpn. Perintah ini dapat dijalankan dari komputer anda (OS X atau Linux). Ini menempatkan file .ovpn di direktori home anda:
sftp sammy@openvpn_server_ip:client-configs/files/client1.ovpn ~/
Atau jika anda menggunakan linux, dapat juga menggunakan perintah scp berikut
scp sammy@openvpn_server_ip:client-configs/files/client1.ovpn ~/
Step 12: Instalasi Konfigurasi Client
Sekarang, kita akan membahas cara menginstal profil VPN client Windows, OS X, iOS, dan Android. Tidak satu pun dari instruksi client ini bergantung satu sama lain, jadi silakan lewati ke mana pun yang berlaku untuk anda.
Koneksi OpenVPN akan dibuka saat kita membuka file .ovpn. Dalam contoh ini, koneksi akan disebut client1.ovpn untuk file client pertama yang kami hasilkan.
Windows
Instalasi
Aplikasi client OpenVPN di Windows bisa di ambil situs openvpn
OpenVPN membutuhkan ijin administrator untuk bisa di instalasi. Setelah menginstalasi OpenVPN, copy file .ovpn ke:
C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\config
Saat menjalankan OpenVPN, dia akan secara automatis melihat profile dan langsung membuka sambungan.
OpenVPN harus dijalankan sebagai administrator setiap kali digunakan, bahkan oleh akun administratif. Untuk melakukan ini tanpa harus mengklik kanan dan memilih Run as administrator setiap kali anda menggunakan VPN, anda dapat mengatur ini, tetapi ini harus dilakukan dari akun administratif. Ini juga berarti bahwa pengguna standar harus memasukkan password administrator untuk menggunakan OpenVPN. Di sisi lain, pengguna standar tidak dapat terhubung dengan benar ke server kecuali aplikasi OpenVPN pada klien memiliki hak admin, oleh karenanya hak istimewa yang ditinggikan diperlukan.
Untuk mengatur aplikasi OpenVPN agar selalu berjalan sebagai administrator, klik kanan pada ikon shortcut-nya dan buka Properties. Di bagian bawah tab "Compatibility", klik tombol untuk "Change Settings for all users". Di jendela baru, cek "Run this program as an administrator".
Connecting
Setiap kali anda membuka GUI OpenVPN, Windows akan menanyakan apakah anda mengijinkan program untuk melakukan perubahan pada komputer anda. Klik "Yes". Meluncurkan aplikasi klien OpenVPN hanya menempatkan applet di system tray sehingga VPN dapat terhubung dan terputus sesuai kebutuhan; applet tersebut tidak benar-benar membuat koneksi VPN.
Setelah OpenVPN dimulai, jalankan koneksi dengan masuk ke system tray applet dan klik kanan pada ikon applet OpenVPN. Ini membuka menu context. Pilih client1 di bagian atas menu (itu profil client1.ovpn) dan pilih Connect.
Jendela status akan terbuka yang menunjukkan keluaran log saat koneksi dibuat, dan sebuah pesan akan muncul setelah klien terhubung.
Disconnect sambungan dari VPN dengan cara yang sama: Buka system tray applet, klik kanan ikon applet OpenVPN, pilih profil client dan klik Disconnect.
OS X
Installing
Tunnelblick adalah client OpenVPN yang free dan open source untuk Mac OS X. Anda dapat mendownload disk image versi terakhir dari Tunnelblick Downloads page. Double-click file .dmg dan ikuti prompt untuk menginstalasi.
Di akhir proses instalasi, Tunnelblick akan bertanya apakah anda memiliki file konfigurasi. Akan lebih mudah untuk menjawab "np" dan membiarkan Tunnelblick selesai. Buka Finder window dan double-click client1.ovpn. Tunnelblick akan menginstalasi client profile. Administrative privilege dibutuhkan untuk itu.
Connecting
Jalankan Tunnelblick dengan double-clicking Tunnelblick di Application folder. Setelah Tunnelblick di jalankan, akan ada icon Tunnelblick di menu bar di sebelah kanan atas layar untuk mengatur sambungan. Klik icon, dan kemudian Connect menu item untuk memulai sambungan VPN. Pilih client1.
Linux
Instalasi
Jika anda menggunakan Linux, ada banyak tools yang dapat di gunakan tergantung dari distribusi linux yang digunakan. Desktop atau windows manager mungkin menyediakan utilitas untuk connection.
Cara yang paling umum untuk connecting, adalah dengan menggunakan software OpenVPN.
Di Ubuntu atau Debian, proses instalasi tidak berbeda jauh dengan di server dengan menulis:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install openvpn
Di CentOS kita dapat mengenable EPEL repository dan menginstalasi-nya dengan menulis:
sudo yum install epel-release sudo yum install openvpn
Configuring
Cek apakah distribusi anda memasukan script /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf:
ls /etc/openvpn
Output
update-resolve-conf
Selanjutnya, edit file konfigurasi client OpenVPN:
nano client1.ovpn
Uncomment tiga kalimat yang kita letakan untuk mengatur setting DNS jika anda dapat memperoleh file update-resolv-conf: client1.ovpn
script-security 2 up /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf down /etc/openvpn/update-resolv-conf
Jika anda menggunakan CentOS, ubah group dari nogroup ke nobody agar cocok dengan group yang tersedia di distribusi: client1.ovpn
group nobody
Sava dan close file tersebut.
Connection
Sekarang, anda dapat connect ke VPN (untuk client1.ovpn) melalui perintah:
sudo openvpn --config client1.ovpn
Jika tersambung akan muncul interface baru tun0
ifconfig
Output, kira-kira
tun0 Link encap:UNSPEC HWaddr 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00
inet addr:10.8.0.6 P-t-P:10.8.0.5 Mask:255.255.255.255
UP POINTOPOINT RUNNING NOARP MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:32 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:42 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:100
RX bytes:5080 (5.0 KB) TX bytes:5457 (5.4 KB)
Jika ada routing ke arah openvpn 10.8.0.x
netstat -nr
Output
Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.223 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 enp3s0 10.8.0.1 10.8.0.5 255.255.255.255 UGH 0 0 0 tun0 10.8.0.5 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 UH 0 0 0 tun0 50.235.87.130 192.168.0.223 255.255.255.255 UGH 0 0 0 enp3s0 169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 enp3s0 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 enp3s0 192.168.10.0 10.8.0.5 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 tun0 222.124.18.79 192.168.0.223 255.255.255.255 UGH 0 0 0 enp3s0
Jika di perlukan untuk membuat routing tambahan ke LAN (misalnya 192.168.10.0/24) di balik server openvpn (gateway 10.8.0.5), dapat menggunakan perintah
sudo route add -net 192.168.10.0/24 gw 10.8.0.5