Difference between revisions of "JAVA: Loop di Java"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
* '''Initialization condition:''' Here, we initialize the variable in use. It marks the start of a for loop. An already declared variable can be used or a variable can be declared, local to loop only. | * '''Initialization condition:''' Here, we initialize the variable in use. It marks the start of a for loop. An already declared variable can be used or a variable can be declared, local to loop only. | ||
| − | * '''Testing Condition:''' It is used for testing the exit condition for a loop. It must return a boolean value. It is also an Entry Control Loop as the condition is * checked prior to the execution of the loop statements. | + | * '''Testing Condition:''' It is used for testing the exit condition for a loop. It must return a boolean value. It is also an '''Entry Control Loop''' as the condition is * checked prior to the execution of the loop statements. |
* '''Statement execution:''' Once the condition is evaluated to true, the statements in the loop body are executed. | * '''Statement execution:''' Once the condition is evaluated to true, the statements in the loop body are executed. | ||
* '''Increment/ Decrement:''' It is used for updating the variable for next iteration. | * '''Increment/ Decrement:''' It is used for updating the variable for next iteration. | ||
Revision as of 10:09, 4 May 2022
Looping dalam bahasa pemrograman adalah fitur yang memfasilitasi eksekusi serangkaian instruksi/fungsi berulang kali sementara beberapa kondisi bernilai benar.
Java menyediakan tiga cara untuk mengeksekusi loop. Sementara semua cara menyediakan fungsionalitas dasar yang serupa, mereka berbeda dalam sintaks dan waktu pemeriksaan kondisi.
while loop:
Loop while adalah pernyataan aliran kontrol yang memungkinkan code dieksekusi berulang kali berdasarkan kondisi Boolean yang diberikan. Perulangan while dapat dianggap sebagai pernyataan if yang berulang.
Syntax :
while (boolean condition)
{
loop statements...
}
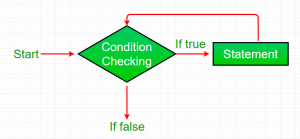
Flowchart:
While loop dimulai dengan pengecekan kondisi. Jika bernilai true, maka body perintah perulangan akan di jalankan jika tidak, pernyataan pertama setelah perulangan akan di jalankan. Untuk alasan ini juga disebut Entry control loop
Setelah kondisi dievaluasi ke true, pernyataan di badan loop di jalankan. Biasanya pernyataan berisi nilai yang di update untuk variabel yang sedang diproses untuk iterasi berikutnya.
Ketika kondisi menjadi false, loop berakhir yang menandai akhir dari siklus loop tersebut.
// Java program to illustrate while loop
class whileLoopDemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int x = 1;
// Exit when x becomes greater than 4
while (x <= 4)
{
System.out.println("Value of x:" + x);
// Increment the value of x for
// next iteration
x++;
}
}
}
Output:
Value of x:1 Value of x:2 Value of x:3 Value of x:4
for loop:
for loop menyediakan cara ringkas untuk menulis struktur loop. Tidak seperti perulangan while, pernyataan for menggunakan inisialisasi, kondisi, dan kenaikan/penurunan dalam satu baris sehingga memberikan struktur perulangan yang lebih pendek dan mudah di-debug.
Syntax:
for (initialization condition; testing condition;
increment/decrement)
{
statement(s)
}
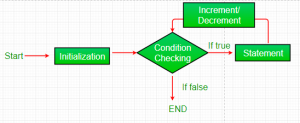
Flowchart:
- Initialization condition: Here, we initialize the variable in use. It marks the start of a for loop. An already declared variable can be used or a variable can be declared, local to loop only.
- Testing Condition: It is used for testing the exit condition for a loop. It must return a boolean value. It is also an Entry Control Loop as the condition is * checked prior to the execution of the loop statements.
- Statement execution: Once the condition is evaluated to true, the statements in the loop body are executed.
- Increment/ Decrement: It is used for updating the variable for next iteration.
Loop termination:When the condition becomes false, the loop terminates marking the end of its life cycle.
// Java program to illustrate for loop.
class forLoopDemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// for loop begins when x=2
// and runs till x <=4
for (int x = 2; x <= 4; x++)
System.out.println("Value of x:" + x);
}
}
Output:
Value of x:2 Value of x:3 Value of x:4 Enhanced For loop
Java also includes another version of for loop introduced in Java 5. Enhanced for loop provides a simpler way to iterate through the elements of a collection or array. It is inflexible and should be used only when there is a need to iterate through the elements in a sequential manner without knowing the index of the currently processed element. Also note that the object/variable is immutable when enhanced for loop is used i.e it ensures that the values in the array can not be modified, so it can be said as read-only loop where you can’t update the values as opposite to other loops where values can be modified. We recommend using this form of the for statement instead of the general form whenever possible.(as per JAVA doc.)
Syntax:
for (T element:Collection obj/array)
{
statement(s)
}
Lets take an example to demonstrate how enhanced for loop can be used to simplify the work. Suppose there is an array of names and we want to print all the names in that array. Let’s see the difference between these two examples Enhanced for loop simplifies the work as follows-
// Java program to illustrate enhanced for loop
public class enhancedforloop
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
String array[] = {"Ron", "Harry", "Hermoine"};
//enhanced for loop
for (String x:array)
{
System.out.println(x);
}
/* for loop for same function
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)
{
System.out.println(array[i]);
}
*/
}
}
Output:
Ron Harry Hermoine
do while:
do while loop is similar to while loop with only difference that it checks for condition after executing the statements, and therefore is an example of Exit Control Loop.
Syntax:
do
{
statements..
}
while (condition);
Flowchart: do-while
do while loop starts with the execution of the statement(s). There is no checking of any condition for the first time. After the execution of the statements, and update of the variable value, the condition is checked for true or false value. If it is evaluated to true, next iteration of loop starts.
When the condition becomes false, the loop terminates which marks the end of its life cycle. It is important to note that the do-while loop will execute its statements atleast once before any condition is checked, and therefore is an example of exit control loop.
// Java program to illustrate do-while loop
class dowhileloopDemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int x = 21;
do
{
// The line will be printed even
// if the condition is false
System.out.println("Value of x:" + x);
x++;
}
while (x < 20);
}
}
Output:
Value of x: 21 Pitfalls of Loops
Infinite loop:
One of the most common mistakes while implementing any sort of looping is that that it may not ever exit, that is the loop runs for infinite time. This happens when the condition fails for some reason.
Contoh:
//Java program to illustrate various pitfalls.
public class LooppitfallsDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// infinite loop because condition is not apt
// condition should have been i>0.
for (int i = 5; i != 0; i -= 2)
{
System.out.println(i);
}
int x = 5;
// infinite loop because update statement
// is not provided.
while (x == 5)
{
System.out.println("In the loop");
}
}
}
Another pitfall is that you might be adding something into you collection object through loop and you can run out of memory. If you try and execute the below program, after some time, out of memory exception will be thrown.
//Java program for out of memory exception.
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Integer1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<Integer> ar = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE; i++)
{
ar.add(i);
}
}
}
Output:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space at java.util.Arrays.copyOf(Unknown Source) at java.util.Arrays.copyOf(Unknown Source) at java.util.ArrayList.grow(Unknown Source) at java.util.ArrayList.ensureCapacityInternal(Unknown Source) at java.util.ArrayList.add(Unknown Source) at article.Integer1.main(Integer1.java:9)