Difference between revisions of "VoIP Cookbook: How VoIP Works for Dummies"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
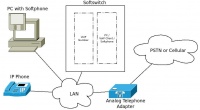
| − | A overly simplified figure on how VoIP network work is shown in Figure. The heart of VoIP network is the softswitch. It stores all information on the subscribers. In a simple view, a VoIP softswitch basically has a table mapping the phone number of the subscriber and the computer or IP address of the subscriber. | + | A overly simplified figure on how [[VoIP]] network work is shown in the Figure. The heart of [[VoIP]] network is the [[softswitch]]. It stores all information on the subscribers. In a simple view, a [[VoIP]] [[softswitch]] basically has a table mapping the phone number of the subscriber and the computer or [[IP address]] of the subscriber. |
| − | Everytime, a subscriber wants to make a call to another subscriber. The client equipment will ask the softswitch the destination address of the other subscriber. The destination address can be an IP address. Thus, the softswitch basically store in its table, the phone number of the subscriber and their IP address. | + | Everytime, a subscriber wants to make a call to another subscriber. The client equipment will ask the softswitch the destination address of the other subscriber. The destination address can be an [[IP address]]. Thus, the [[softswitch]] basically store in its table, the phone number of the subscriber and their [[IP address]]. |
| − | VoIP will be more fun, as we can use IP Phone instead of a computer as subscriber equipment. IP Phone looks similar to normal phone. However, it is much smaller than a computer. Thus, the client equipment may be run 24 hours without consuming too much electricity. | + | [[VoIP]] will be more fun, as we can use [[IP Phone]] instead of a [[computer]] as subscriber equipment. [[IP Phone]] looks similar to normal phone. However, it is much smaller than a [[computer]]. Thus, the client equipment may be run 24 hours without consuming too much electricity. |
[[Image:How-voip-works.jpg|center|200px|thumb|How VoIP Works]] | [[Image:How-voip-works.jpg|center|200px|thumb|How VoIP Works]] | ||
| − | For more advanced user, we may insert an an Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA) into the network. An ATA is another type of client equipment. It may act as gateway between VoIP network and legacy phone network. Thus, anyone on VoIP network may call to the old phone network. | + | For more advanced user, we may insert an an [[Analog Telephone Adapter]] ([[ATA]]) into the network. An [[ATA]] is another type of client equipment. It may act as gateway between [[VoIP]] network and legacy phone network. Thus, anyone on [[VoIP]] network may call to the old phone network. |
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
* [[VoIP Cookbook: Building your own Telecommunication Infrastructure]] | * [[VoIP Cookbook: Building your own Telecommunication Infrastructure]] | ||
* [[VoIP Cookbook: VoIP Overview]] | * [[VoIP Cookbook: VoIP Overview]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category: VoIP]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:50, 13 May 2010
A overly simplified figure on how VoIP network work is shown in the Figure. The heart of VoIP network is the softswitch. It stores all information on the subscribers. In a simple view, a VoIP softswitch basically has a table mapping the phone number of the subscriber and the computer or IP address of the subscriber.
Everytime, a subscriber wants to make a call to another subscriber. The client equipment will ask the softswitch the destination address of the other subscriber. The destination address can be an IP address. Thus, the softswitch basically store in its table, the phone number of the subscriber and their IP address.
VoIP will be more fun, as we can use IP Phone instead of a computer as subscriber equipment. IP Phone looks similar to normal phone. However, it is much smaller than a computer. Thus, the client equipment may be run 24 hours without consuming too much electricity.
For more advanced user, we may insert an an Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA) into the network. An ATA is another type of client equipment. It may act as gateway between VoIP network and legacy phone network. Thus, anyone on VoIP network may call to the old phone network.