Difference between revisions of "Multipath interference"
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) |
Onnowpurbo (talk | contribs) m (Multipath fading moved to Multipath interference) |
(No difference)
| |
Latest revision as of 10:30, 29 January 2010
Multipath interference is a phenomenon in the physics of waves whereby a wave from a source travels to a detector via two or more paths and, under the right condition, the two (or more) components of the wave interfere. Multipath interference is a common cause of "ghosting" in analog television broadcasts.
Conditions
The condition necessary is that the components of the wave remain coherent throughout the whole extent of their travel.
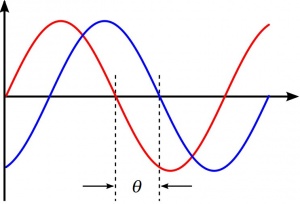
The interference will arise owing to the two (or more) components of the wave having, in general, travelled a different length (as measured by optical path length – geometric length and diffraction (differing optical speed)), and thus arriving at the detector out of phase with each other.
Models
There are various ways of mathematically modeling the effects of multipath interference; notable models include:
- Rayleigh fading, particularly used for modeling non-line-of-sight propagation (when there is no line-of-sight between transmitter and receiver);
- Rician fading, more general than Rayleigh fading, and particularly used for modeling line-of-sight propagation.